Matrices Questions & Answers
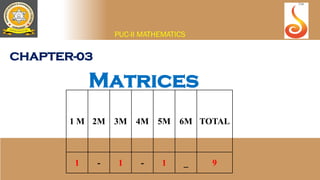
- 1. CHAPTER-03 Matrices PUC-II MATHEMATICS 1 M 2M 3M 4M 5M 6M TOTAL 1 - 1 - 1 _ 9
- 2. One Mark questions 1. Define a scalar matrix. (K) Scalar Matrix is a diagonal matrix whose principal diagonal elements are same 4 0 0 0 4 0 0 0 4 Examples 5 0 0 0 5 0 0 0 5
- 3. One Mark questions 2. Define an Identity matrix. (K) Identity Matrix is a scalar matrix whose principal diagonal elements are equal to 1 3 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 I IExamples 1 0 I 0 1
- 4. One Mark questions 3. Define a diagonal matrix. Diagonal matrix is a square matrix whose non- principal diagonal elements are zero irrespective of principal diagonal elements.
- 5. One Mark questions 4. In the matrix 2 5 19 7 5 35 2 12 2 3 1 5 17 Write: (i) the order of the matrix (ii) The number of elements (iii) Write the elements , , , , R1 R2 R3 C1 C2 C3 C4 =12 a13 a21 a33 a42a23 a13 a21 a33a42 a23 a24 3 4 a24
- 6. One Mark questions 5. If a matrix has 24 elements, what are the possible orders it can have? What, if it has 13 elements? Soln: 1 24 24 1 2 12 12 2 3 8 8 3 4 6 6 4 Soln: 1 13 13 1
- 7. One Mark questions 6. If a matrix has 18 elements, what are the possible orders it can have? What, if it has 5 elements? Soln: 1 18 18 1 2 9 9 2 3 6 6 3 Soln: 1 5 5 1
- 8. One Mark questions 8. If a matrix has 8 elements, what are the possible orders it can have?
- 9. One Mark questions 7. Find the number of all possible matrices of order 3 ×3 with each entry 0 or 1 ? Solution: since order is 3 ×3 ∴ matrices having 9 elements (entries) Given that: Each entry is either 0 or 1 i.e. TWO ways to be filled an entry . ∴According to Fundamental Principle of counting 9 entries can be filled in 2 × 2×2 ×…….. 9 times ∴ No. of possible matrices = 9 2
- 10. One Mark questions 9. Construct a 2 × 2 matrix, 11 12 21 22 a a a a A = whose elements are given by ija i j Solution : Let 2 × 2 matrix ija i j 11 1 1 2a 12 1 2 3a 21 2 1 3a 22 2 2 4a ∴Required matrix is 2 3 3 4 A = 11For , put 1& 1a i j Given
- 11. One Mark questions 9. Construct a 2 × 2 matrix, 11 12 21 22 a a a a A = whose elements are given by Solution : Let 2 × 2 matrix 11 1 3 1 1 2 2 a 12 1 5 3 1 2 2 2 a 21 1 7 3 2 1 2 2 a 22 1 3 2 2 4 2 a ∴Required matrix is 5 2 2 7 4 2 A = 11For , put 1& 1a i j Given 1 3 2 ija i j 1 3 2 ija i j
- 12. One Mark questions 9. Construct a 2 × 2 matrix, ijA = a whose elements are given by; ) ij i iii a j ) ijiv a i j
- 13. One Mark questions 9. Construct a 2 × 2 matrix, ijA = a whose elements are given by; ) 2ijv a i j 2 ) ijvi a i j 2 ) 2 ij i j viii a 2 2 ) 2 ij i j vii a
- 14. One Mark questions 9. Construct a 3 × 3 matrix, 11 12 13 21 22 23 31 32 33 A = a a a a a a a a a whose elements are given by Solution : Let 2 × 2 matrix 11 1 1 3 1 1 2 a 12 1 5 1 3 2 2 2 a 21 1 1 2 3 1 2 2 a 22 1 2 3 2 2 2 a ∴Required matrix is Given 1 3 2 ija i j 5 1 4 2 1 7 2 2 2 3 0 3 2 A = 13 1 1 3 3 4 2 a 23 1 7 2 3 3 2 2 a 31 1 3 3 1 0 2 a 32 1 3 3 3 2 2 2 a 32 1 3 3 3 3 2 a 1 3 2 ija i j
- 15. One Mark questions 11. Construct a 3 × 4 matrix, whose elements are given by: 1 ) 3 2 iji a i j ) 2ijii a i j
- 16. One Mark questions 12. Find the values of x, y and z if 4 3 y z x 5 1 5 Solution: By definition of Equality of Two matrices, we have corresponding elements are equal 4 y 3 z 1x ∴ 1x 4y 3z
- 17. One Mark questions 12. Find the values of x, y and z if Solution: By definition of Equality of Two matrices, we have corresponding elements are equal 9x y z 5x z 7y z 7 9x 4y 3z x y z 9 x z 5 y z 7 2x 2 5z 3 7y ∴ 2x 4y 3z 7 y z
- 18. One Mark questions 13. Find x and y, if 1 3 y 0 5 6 2 0 x 1 2 1 8 Solution: By definition of Scalar Multiplication of a Matrix, Addition & Equality of Two matrices, we have 2x 2 1 3x 2 8 5y 3y
- 19. One Mark questions 14. if 2 1 10 x y 3 1 5 Find the values of x & y 2 1 10 ........ 1x y 3 1 5.......... 2x y 5 15 3x x Adding (1) and (2),we get Substitute x=3 in eqn (2),we get 3 3 5 4 y y Solution:
- 20. One Mark questions 15. Find X, if & 3 2 Y 1 4 1 0 2X Y 3 2 1 0 2X Y 3 2 Solution: By properties of Matrix addition 1 0 2X Y 3 2 ∴ 1 0 3 2 2X 3 2 1 4 2 2 2X 4 2 By Scalar Multiplication of a Matrix 1 1 X 2 1 Given
- 21. One Mark questions 16. Find the values of x and y from the following equation x 5 3 4 7 6 2 7 y 3 1 2 15 16 Solution : 2 3 7 2 3 2 16x y By definition of Scalar Multiplication of a Matrix, Addition & Equality of Two matrices, we have 2 7 3 2 -6 2 16x y ∴ 2 10x y
- 22. One Mark questions 17. Find the value of a, b, c and d from the equation: a b 2a c 1 5 2a b 3c d 0 13 Solution : By definition of Equality of Two matrices, we have 1........ 1a b 2 0 .... 2a b 2 5....... 3a c 3 13....... 4c d From (2), 2 .... *b a Substitute in (1),we get 2 1 1 a a a From (*) b = 2 From (3) c = 3 Substitute c=1 in (4) 4d 1, 2 3& 4 a b c d
- 23. One Mark questions 18. Show that the matrix 1 1 5 A 1 2 1 5 1 3 is a symmetric matrix Solution: Since A' 1 1 5 1 2 1 A 5 1 3 A is a symmetric matrix ∴
- 24. One Mark questions 19. Show that the matrix 0 1 1 A 1 0 1 1 1 0 is a skew symmetric matrix Solution: ∴ ' 0 1 1 Since A 1 0 1 1 1 0 A is a skew symmetric matrixA
- 25. One Mark questions 22. Given Find 1 2 3 A and 2 3 1 3 1 3 B 1 0 2 2A B Solution: 1 2 3 3 1 3 2A B 2 2 3 1 1 0 2 2 4 6 3 1 3 4 6 2 1 0 2 2 3 4 1 6 3 4 1 6 0 2 2 1 5 3 5 6 0
- 26. One Mark questions 23. Given 3 1 1 A and 2 3 0 2 5 1 B 1 2 3 2 Find A B
- 27. One Mark questions 25.Find AB 6 9 A 2 3 and 2 6 0 B 7 9 8 If Solution : 6 9 2 6 0 AB 2 3 7 9 8 6 2 9 7 6 6 9 9 6 0 9 8 2 2 3 7 2 6 3 9 2 0 3 8 75 117 72 25 39 24
- 28. One Mark questions 26. if 1 0 A 0 1 and 0 1 B 1 0 then prove that 0 1 i AB 1 0 0 1 ii BA 1 0
- 29. One Mark questions 27. Simplify cos sin sin cos cos sin sin cos cos sin Solution: cos sin sin cos cos sin sin cos cos sin cos cos sin sin sin cos cos sin cos sin cos sin 2 2 2 2 cos sin cos sin sin cos cos sin sin cos cos sin 2 2 2 2 1 0 0 1 I Addition of Matrices Scalar Multiplication of a Matrix 2 2 cos sin 1
- 30. One Mark questions 28. Find 1 P if it exists , given 10 2 P 5 1 Solution: 10 2 Since P 0 5 1 does not exist Hence P is a Singular Matrix 1 P
- 31. One Mark questions Solution: 30.If 3 3 2 A 4 2 0 2 1 2 B 1 2 4 Verify that ' 'i A A ' ' 'ii A B A B ' 3 4 3 3 2 A A 3 2 4 2 0 2 0 ' 2 1 2 1 2 B B 1 2 1 2 4 2 4 ' 3 4 i A 3 2 2 0 ' ' 3 3 2 A A 4 2 0 Clearly ' 5 5 5 3 1 4 A B A B 3 1 4 5 4 4 4 4 Clearly ' ' 3 54 2 1 5 A B 3 2 1 2 3 1 4 2 0 2 4 4 4
- 32. Solution: 31. Compute the following 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 a b b c 2ab 2bc i 2ac 2aba c a b 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 a b b c 2ab 2bc 2ac 2aba c a b 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 a b 2ab b c 2bc a c 2ac a b 2ab 2 2 2 2 a b b c a c a b
- 33. 31. Compute the following a b a b ii b a b a 1 4 6 12 7 6 iii 8 5 16 8 0 5 2 8 5 3 2 4 cos sin sin cos sin cos cos sin 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 x x x x iv x x x x
- 34. a b a b i b a b a 32. Compute the indicated products: Solution: a b a b b a b a 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 a b ab ba ba ab b a a b 0 0 a b 1 0 a b 0 1 a b I
- 35. 1 ii 2 2 3 4 3 32. Compute the indicated products: Solution: 1 2 2 3 4 3 1 3Order 3 1 3 3 2 3 4 4 6 8 6 9 12
- 36. 32. Compute the indicated products: 1 2 1 2 3 iii 2 3 2 3 1 2 3 4 1 3 5 iv 3 4 5 0 2 4 4 5 6 3 0 5 2 1 1 0 1 v 3 2 1 2 1 1 1 2 3 3 1 3 vi 1 0 1 0 2 3 1
- 37. Three Mark questions 1. Find the values of x, y and z from the following equations x y 2 6 2 5 z xy 5 8 By definition of Equality of Two matrices, we have 6..... 1 8..... 2x y xy Solution:
- 38. x y 2 6 2 5 z xy 5 8 Solution: Given By definition of Equality of Two matrices, we have 6..... 1 8..... 2x y xy 1 6From y x 2 2 6 - 8 - 6 8 0 4 2 =0 4 or 2 From (1) 2 or 4 x x x x x x x x y y 2 6 8becomes x x
- 39. 2. Solve the equation for x, y, z and t, if x z 1 1 3 5 2 3 3 y t 0 2 4 6 Solution: Given x z 1 1 3 5 2 3 3 y t 0 2 4 6 By definition of Scalar Multiplication of a matrix & Addition ,we have 2 3 9x 2 3 15z 2 0 12y 2 6 18t 3x 9z 6y 6t By definition of Equality of Two matrices, we have 2x 2z 3 3 9 15 2y 2t 0 6 12 18 2 3 2 3 9 15 2 0 2 6 12 18 x z y t
- 40. 3. Given x y x 6 4 x y 3 z w 1 2w z w 3 find the values of x, y, z and w By definition of Scalar Multiplication of a matrix, Addition & Equality of Two matrices, we have Solution: Given x y x 6 4 x y 3 z w 1 2w z w 3 3 4 2x x x 3 6 using 2 we get 4y x y x y 3 2 3 3w w w 3 1 Using w=3 we get 1z z w z
- 41. 4. Find the values of a, b, c and d from the following equation 2a b a 2b 4 3 5c d 4c 3d 11 24 Solution: By definition of Equality of Two matrices, we have ...... .... 2a b 4 1 a 2b 3 2 ..... ..... 5c d 11 3 4c 3d 24 4 Consider 2(1)+(2), we get 4a 2b 8 a 2b 3 + 5 5 1a a From (1) we get 2b Consider 3(1)+(2), we get 15c 3d 33 4c 3d 24 + 19 57 3c c From (3) we get 4d
- 42. 5. If x 3 z 4 2y 7 0 6 3y 2 6 a 1 0 6 3 2c 2 b 3 21 0 2b 4 21 0 Find the values of a, b, c, x, y and z. Solution: By definition of Equality of Two matrices, we have 3, 2, 5 2, 1, 7x z y a c b
- 43. 6. Using elementary transformations, find the inverse of 1 1 2 3 Solution: Let given matrix be 1 1 A 2 3 Find , sing Elementary Row Operation(ERO)1 A U Consider A IA Apply '2 2 1 R R 2R 1 1 1 0 A 2 3 0 1 1 0 1 1 A2 1 0 1 5 5 1 1 1 0 A 0 5 2 1 Apply '2 2 1 R R 5 Apply '1 1 2 R R R 0 3 1 1 5 5 A 0 1 2 1 5 5 . .i e I BA By definition of Invertible Matrix, 1 B A 1 3 1 5 5 2 1 5 5 A
- 44. Using elementary transformations, find the inverse of Solution: Let given matrix be Find , sing Elementary Row Operation(ERO)1 A U Consider A IA Apply 1 2 R R 2 6 1 0 A 1 2 0 1 0 1 1 2 A1 0 1 1 2 1 2 0 1 A 2 6 1 0 Apply '2 2 1 R R 2 Apply '1 1 2 R R 2R . .i e I BA By definition of Invertible Matrix, 1 B A 2 6 1 22 6 A 1 2 Apply '2 2 1 R R 2R 1 2 0 1 A 0 2 1 2 1 3 1 0 A1 0 1 1 2 1 1 3 A 1 1 2
- 45. Using elementary transformations, find the inverse of Solution: Let given matrix be Find , sing Elementary Row Operation(ERO)1 A U Consider A IA Apply '1 1 2 R R R 4 5 1 0 A 3 4 0 1 Apply '1 1 2 R R R . .i e I BA By definition of Invertible Matrix, 1 B A Apply '2 2 1 R R 3R 1 4 5 A 3 4 4 5 3 44 5 A 3 4 1 1 1 1 A 3 4 0 1 1 1 1 1 A 0 1 3 4 1 0 4 5 A 0 1 3 4
- 46. Using elementary transformations, find the inverse of Solution: Let given matrix be Find , sing Elementary Row Operation(ERO)1 A U Consider A IA Apply '1 1 2 R R R 2 3 1 0 A 1 2 0 1 Apply '1 1 2 R R R . .i e I BA By definition of Invertible Matrix, 1 B A Apply '2 2 1 R R R 1 2 3 A 1 2 2 3 1 22 3 A 1 2 1 1 1 1 A 1 2 0 1 1 1 1 1 A 0 1 1 2 1 0 2 3 A 0 1 1 2
- 47. Using elementary transformations, find the inverse of Solution: Let given matrix be Find , sing Elementary Row Operation(ERO)1 A U Consider A IA Apply '2 2 1 R R 2R 3 1 1 0 A 5 2 0 1 Apply '2 2 1 R R 3R . .i e I BA By definition of Invertible Matrix, 1 B A Apply '2 2 R 1 R 1 2 1 A 5 3 3 1 A 5 2 3 1 5 2 3 1 1 0 A 1 0 2 1 3 1 1 0 A 1 0 2 1 Apply 1 2 R R 1 0 2 1 A 3 1 1 0 1 0 2 1 A 0 1 5 3
- 48. 8. Find X and Y, if 7 0 X Y 2 5 and 3 0 X Y 0 3 Solution: Given ..... 7 0 X Y 1 2 5 3 0 X Y 0 3 Adding (1) & (2),We get 7 0 3 0 X Y X Y 2 5 0 3 10 0 2X 2 8 5 0 X 1 4 From (1) 7 0 Y X 2 5 7 0 5 0 Y 2 5 1 4 2 0 Y 1 1
- 49. 9. Find X and Y, if 2 3 2X 3Y 4 0 2 2 3X 2Y 1 5 Solution: Given that ...... 2 3 2X 3Y 1 4 0 ...... 2 2 3X 2Y 2 1 5 Consider 3(1) – 2(2), We get 2 3 6X 9Y 3 4 0 2 2 6X 4Y 2 1 5 __ __ (--)(--) - 6 9 4 4 5Y 12 0 2 10 2 13 5Y 14 10 2 13 5 5 Y 14 2 5 Consider 2(1) – 3(2), We get 4 6 6 6 5X 8 0 3 15 2 12 2 12 5 5 5X X 11 15 11 3 5
- 50. 10. If 8 0 A 4 2 3 6 and 2 2 B 4 2 5 1 then find the matrix X, such that 2A 3X 5B Solution : For Given 8 0 A 4 2 3 6 2 2 B 4 2 5 1 By properties of Matrix Addition & Scalar Multification of a matrix 2A 3X 5B 3X 5B 2A 2 2 8 0 3X 5 4 2 2 4 2 5 1 3 6 10 10 16 0 3X 20 10 8 4 25 5 6 12 6 10 3X 12 14 31 7 10 6 3 3 14 X 4 3 31 7 3 3
- 51. Three Mark questions 11. Find X and Y, if 5 2 X Y 0 9 and 3 6 X Y 0 1 12. If 2 5 1 3 3 1 2 4 A 3 3 3 7 2 2 3 3 and 2 3 1 5 5 1 2 4 B 5 5 5 7 6 2 5 5 5 Then compute 3A 5B
- 52. 13. if cos sin ( ) sin cos x x 0 F x x x 0 0 0 1 Show that F x F y F x y Solution: LHS= F x F y cos sin cos sin sin cos sin cos x x 0 y y 0 x x 0 y y 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 cos cos sin sin cos siny sinxcosy sin cos cos sin sin sin cos cos cos sin sin cos x y x y x 0 x y x y x y x y 0 0 0 1 x y x y 0 x y x y 0 0 0 1 F x y RHS
- 53. 15.(i) if cos sin sin cos A then verify that 'A A I Solution: Given that cos sin sin cos A cos sin ' sin cos A cos sin cos sin ' sin cos sin cos LHS A A cos sin sin coscos sin sin cossin cos cos sin 2 2 2 2 1 0 0 1 I RHS
- 54. 14. Show that 5 1 2 1 2 1 5 1 6 7 3 4 3 4 6 7 (ii) if sin cos cos sin A then verify that 'A A I
- 55. 16.Show that 1 2 3 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 2 3 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 2 3 4 2 3 4 1 1 0 Solution: 1 2 3 1 1 0 LHS 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 2 3 4 1 0 6 1 2 9 0 2 12 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 5 6 14 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 2 3 RHS 0 1 1 0 1 0 2 3 4 1 1 0 1 0 0 2 1 0 3 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 2 0 4 4 3 4 6 0 0 1 1 3 1 0 0 6 11 6 By Definition of equality of Two Matrices LHS RHS
- 56. 17. if 1 2 3 A 5 7 9 2 1 1 and 4 1 5 B 1 2 0 1 3 1 then verify that ' ' 'i A B A B ' ' 'ii A B A B
- 57. 18. if ' 3 4 A 1 2 0 1 and 1 2 1 B 1 2 3 then verify that ' ' 'i A B A B ' ' 'ii A B A B
- 58. 19. if ' 2 3 A 1 2 and 1 0 B 1 2 then find 'A 2B Solution: Given that Consider 2 1 1 0 A 2B 2 1 2 1 2 2 1 2 0 1 2 2 4 2 2 1 0 1 2 2 4 A+2B 4 1 3 6 4 3 2 ' 1 6 A B
- 59. 20. if 1 2 3 A 4 2 5 and 2 3 B 4 5 2 1 AB BA then find AB, BA Show that Solution: Given that 1 2 3 A 4 2 5 = 2 3 1 2 3 AB 4 5 4 2 5 2 1 2 8 6 3 10 3 8 8 10 12 10 5 0 4 10 3 2 3 B 4 5 2 1 = 2 3 1 2 3 BA 4 5 4 2 5 2 1 2 12 4 6 6 15 4 20 8 10 12 25 2 4 4 2 6 5 10 2 21 16 2 37 2 2 11By definition of Equality of Two matrices AB ≠ BA
- 60. 21. If A and B are symmetric matrices of the same order, then show that AB is symmetric if and only if A and B are commutative, that is AB = BA. Solution: A and B are symmetric matrices of the same order First, We consider AB is symmetric To Prove : AB = BA 'AB AB Now Consider ' and 'A A B B ' ' ' But ' & ' = Hence proved LHS AB AB B A A A B B BA Secondly,We consider AB BA To Prove : AB is symmetric Now Consider ' ' ' But ' & ' = '= Hence AB is symmetric matrix LHS AB B A A A B B BA AB AB
- 61. 22. If 3 2 A 4 2 and 1 0 I 0 1 Find k so that 2 A kA 2I Solution: Given that 3 2 A 4 2 1 0 I 0 1 & We have 2 = A = 2 A AA 3 2 3 2 4 2 4 2 9 8 6 4 12 8 8 4 1 2 4 4 Given that 2 A kA 2I 1 2 3 2 1 0 k 2 4 4 4 2 0 1 1 2 3k 2 2k 0 4 4 4k 0 2k 2 3k 2 1 k 1
- 62. 23. For the matrix 1 5 A 6 7 verify that 'i A A is a symmetric matrix 'ii A A is a skew symmetric matrix Solution:Given that ' 1 5 1 6 A A 6 7 5 7 ' ' 1 5 1 6 i A A 6 7 5 7 2 11 A A X say 11 14 2 11 Since ' 11 14 ' is symmetric X X X A A ' ' 1 5 1 6 ii A A 6 7 5 7 0 1 A A X say 1 0 0 1 ' - -1 0 ' is skew-symmetric Since X X X A A
- 63. Solution:Given that 24. Find ' 1 A A 2 ' 1 and A A 2 When 0 a b A a 0 c b c 0
- 64. Solution: Let A be the given matrix 25. Express the matrix as the sum of a symmetric and skew symmetric matrix: 6 2 2 2 3 1 2 1 3 ' 6 2 2 6 2 2 A 2 3 1 A 2 3 1 2 1 3 2 1 3 We have 1 1 ' ' 2 2 = * 6 2 2 1 ' = 2 3 1 2 2 1 3 0 0 0 1 & ' 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 A A A A A P Q say where P A A Q A A 6 2 2 Clearly ' 2 3 1 =P 2 1 3 P is a symmetric matrix P 0 0 0 ' 0 0 0 0 0 0 is a skew-symmetric matrix Clearly Q Q Q From * , matrix A sum of symmetric & skew-symmetric matrices is
- 65. Solution: Let A be the given matrix 25. Express the matrix as the sum of a symmetric and skew symmetric matrix: ' 2 2 2 2 1 1 B 1 3 4 B 2 3 2 1 2 3 2 4 3 We have 1 1 B = B + B' + B - B' 2 2 = P + Q say * -3 32 2 22 -2 2 2 -1 1 1 1 -3where P = B + B' = -1 3 4 + -2 3 - 2 P = 3 1 22 2 1 -2 -3 2 4 - 3 3 1 - 3 2 2 -2 2 2 -1 1 1 & Q = B - B' = -1 3 4 - 2 2 1 -2 -3 1 1 10 2 21 -2 3 - 2 Q = 0 3 2 2 4 - 3 -1 -3 0 2 2 2 2 B 1 3 4 1 2 3 Clearly ' and ' is symmetric and is skew-symmetricP P Q Q P Q Therefore from * B= symmetric matrix +skew-symmetric matrix
- 66. 25. Express the following matrix as the sum of a symmetric and skew symmetric matrix: 3 5 1 1Solution:
- 67. 30.If A and B are invertible matrices of the same order, then prove that 1 1 1 AB B A Proof: Given that A and B are invertible matrices 1 1 AA A A I 1 1 BB B B I And 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 Consider = = is invertible. = = AB B A A B B A A BB A A IA B A A I 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 Consider matrix multiplication is associative = = B is invertible. = B A AB B A A B B A A B B I A B = B I Therefore AB is invertible & 1 1 1 AB B A
- 68. 31.Prove that for any square matrix A with real number entries, A+ A’ is a symmetric matrix and A- A’ is a skew symmetric matrix. Solution : Let A be a square matrix To show : A+A’ is a symmetric matrix Let 'X A A Consider ' ' ' = ' ' ' = ' ' ' = ' '= ' is symmetric matrix X A A A A A A A A A A X X X A A 'Y A A Consider ' ' ' = ' ' ' = ' ' ' = - ' '= ' is skew-symmetric matrix Y A A A A A A A A A A Y Y Y A A To show : A-A’ is skew symmetric matrix
- 69. 32. Prove that any square matrix can be expressed as the sum of symmetric and skew symmetric matrix Solution: 1 2 2 1 2 1 ' ' 2 1 1 ' ' 2 2 = A A A A A A A A A A A A A A A A A P Q Let A be the square matrix 1 1 ' and ' 2 2 1 1 ' ' ' ' ' ' 2 2 1 1 = ' ' ' ' ' ' ' 2 2 1 1 = ' ' ' 2 2 1 ' = ' ' 2 where P A A Q A A P A A Q A A A A Q A A A A Q A A P P Q A A 'Q Q Any Square matrix can be expressed as the sum of symmetric and skew -symmetric matrix
- 70. 33.Prove inverse of a square matrix, if it exist, is unique Solution: Let A be a square matrix To prove : Uniqueness of the Inverse of a Matrix This can be proved by Contradiction Method Let us suppose that If possible matrix A has two inverses B & C Since B is a inverse of A ..... *AB BA I Since C is a inverse of A .... * *AC CA I matrix multiplication is associative Identity law B BI B AC AC I IC BA I C BA C Now , We have This is the contrdiction to our suppose therefore Matrix A has only one inverse
- 72. 1. If 2 4 1 3 6 5 A and B Verify that ( )AB B A Solution: Consider 2 2 6 12 4 1 3 6 4 12 24 5 5 15 30 AB 2 4 5 ' 6 12 15 12 24 30 LHS AB 2 1 4 ' 2 4 5 and 1 3 6 ' 3 5 6 A A B B 1 ' ' 3 2 4 5 6 2 4 5 = 6 12 15 12 24 30 RHS B A LHS = RHS ( )AB B A
- 73. 2. If 1 2 3 3 1 2 4 1 2 5 0 2 , 4 2 5 0 3 2 1 1 1 2 0 3 1 2 3 A B and C then compute that (A+B) & (B-C)Also verify that A+(B-C)=(A+B)-C Solution: 1 2 3 3 1 2 4 1 1 5 0 2 4 2 5 9 2 7 1 1 1 2 0 3 3 1 4 A B 3 1 2 4 1 2 1 2 0 , 4 2 5 0 3 2 4 1 3 2 0 3 1 2 3 1 2 0 B C 1 2 3 1 2 0 0 0 3 5 0 2 4 1 3 9 1 5 1 1 1 1 2 0 2 1 1 LHS A B C 4 1 1 4 1 2 0 0 3 9 2 7 0 3 2 9 1 5 3 1 4 1 2 3 2 1 1 A BRHS C LHS RHS
- 74. 3. Find 2 A 5A 6I 2 0 1 if A 2 1 3 1 1 0 Solution: 2 0 1 A 2 1 3 1 1 0 2 3 3 2 2 0 1 1 0 0 A 5A 6I 9 2 5 5 2 1 3 6 0 1 0 0 1 2 1 1 0 0 0 1 =2 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 4 0 1 2 0 0 3 3 2 A AA 2 1 3 2 1 3 4 2 3 0 1 3 2 3 0 9 2 5 1 1 0 1 1 0 2 2 0 0 1 0 1 3 0 0 1 2 3 3 2 10 0 5 6 0 0 3 10 6 3 0 0 2 5 0 9 2 5 10 5 15 0 6 0 9 10 0 2 5 6 5 15 0 0 1 2 5 5 0 0 0 6 0 5 0 1 5 0 2 0 6 1 3 3 1 1 10 5 4 4
- 75. Five Mark questions 5.If 0 6 7 A 6 0 8 7 8 0 0 1 1 B 1 0 2 1 2 0 2 C 2 3 Calculate AC, BC and (A + B) C. Also, verify that (A + B)C = AC + BC.
- 76. Five Mark questions 6. if 1 1 1 A 1 2 3 2 1 3 then show that 3 A 23A 40I O
- 77. Five Mark questions 7. If 1 0 2 A 0 2 1 2 0 3 then show that 3 2 A 6A 7A 2I O
- 78. 8. Let 2 1 A 3 4 5 2 B 7 4 2 5 C 3 8 Find a matrix D such that CD AB 0 Solution: Since matrices A & B are of order 2×2 therefore AB is also a matrix of order 2×2 Since C is the matrix of order 2×2 therefore D must be the matrix of 2×2. Let a b D c d 0CD AB 2 5 2 1 5 2 0 3 8 3 4 7 4 a b c d 2 5 2 5 10 7 4 4 0 3 8 3 8 15 28 6 16 a c b d a c b d 2 5 3 2 5 0 0 0 3 8 43 3 8 22 0 0 a c b d a c b d 2 5 3 0 2 5 0 0 3 8 43 0 3 8 22 0 a c b d a c b d Solving these equations by Cross Multiplication Method
- 79. 9. If tan tan 0 2A 02 and I is identity matrix of order 2, Show that cos sin sin cos tan cos sin tan sin cos tan cos sin sin costan cos tan sin sin tan cos tan cos RHS I A 01 0 2 0 1 02 1 2 1 2 2 2 2 sin tan sin os sin sin cos sin cos sin cos cos cos sin sin cos sin sin cos cos cos cos sin sin 2 2 2 2 c 2 2 22 2 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 22 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 sin sin sin cos cos sin sin cos sin sin sin cos tan tan 2 2 22 2 2 2 2 22 2 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 12 Solution: 0 tan1 0 2 tan0 1 02 1 tan 2 = tan 1 2 LHS I A
- 80. cos sin sin cos RHS I A 2 2 Useful sults 2 2 2 2 1 1 2 Re sin tan cos sin sin cos cos cos sin tan cos sin tan sin cos 01 0 2 0 1 02 tan cos sin sin costan 1 2 1 2 cos tan sin sin tan cos tan cos sin tan sin os 2 2 c 2 2 sin sin cos sin cos sin cos cos cos sin sin cos sin sin cos cos cos cos 2 2 2 22 2 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 22 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 sin sin sin sin sin cos cos sin sin cos sin sin sin cos 2 2 2 2 21 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 22 2 1 2 2 2 2 2 tan tan 1 2 LHS 12
- 86. One Mark questions 10. Construct a 3 × 3 matrix whose elements are given by 1 3 2 ija i j 11. Construct a 3 × 4 matrix, whose elements are given by: 1 ) 3 2 iji a i j ) 2ijii a i j
- 87. One Mark questions 12. Find the values of x, y and z from the following equations: 4 3 y z i x 5 1 5 x y z 9 ii x z 5 y z 7
- 88. One Mark questions 13. Find x and y, if 1 3 y 0 5 6 2 0 x 1 2 1 8 14. if 2 1 10 x y 3 1 5 Find the values of x & y
- 89. One Mark questions 15. Find X, if & 3 2 Y 1 4 1 0 2X Y 3 2 16. Find the values of x and y from the following equation x 5 3 4 7 6 2 7 y 3 1 2 15 16
- 90. One Mark questions 17. Find the value of a, b, c and d from the equation: a b 2a c 1 5 2a b 3c d 0 13 18. Show that the matrix 1 1 5 A 1 2 1 5 1 3 is a symmetric matrix
- 91. One Mark questions 19. Show that the matrix 0 1 1 A 1 0 1 1 1 0 is a skew symmetric matrix 20. let , , 2 4 1 3 2 5 A B C 3 2 2 5 3 4 Find each of the following
- 92. One Mark questions 22. Given 3 1 1 A and 2 3 0 2 5 1 B 1 2 3 2 Find A B 23. Given Find 1 2 3 A and 2 3 1 3 1 3 B 1 0 2 2A B
- 93. One Mark questions 25.Find AB If 6 9 A 2 3 and 2 6 0 B 7 9 8 26. if 1 0 A 0 1 and 0 1 B 1 0 then prove that 0 1 i AB 1 0 0 1 ii BA 1 0
- 94. One Mark questions 27. Simplify cos sin sin cos cos sin sin cos cos sin 28. Find 1 P if it exists , given 10 2 P 5 1
- 95. One Mark questions 29. Find the transpose of each of the following matrices 3 3 2 A 4 2 0 and 2 1 2 B 1 2 4 30.If 3 3 2 A 4 2 0 2 1 2 B 1 2 4 Verify that ' 'i A A ' ' 'ii A B A B
- 96. One Mark questions 31. Compute the following a b a b i b a b a 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 a b b c 2ab 2bc ii 2ac 2aba c a b 1 4 6 12 7 6 iii 8 5 16 8 0 5 2 8 5 3 2 4 cos sin sin cos sin cos cos sin 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 x x x x iv x x x x
- 97. One Mark questions 32. Compute the indicated products: a b a b i b a b a 1 ii 2 2 3 4 3 1 2 1 2 3 iii 2 3 2 3 1 2 3 4 1 3 5 iv 3 4 5 0 2 4 4 5 6 3 0 5
- 98. One Mark questions 2 1 1 0 1 v 3 2 1 2 1 1 1 2 3 3 1 3 vi 1 0 1 0 2 3 1 32. Compute the indicated products:
- 99. Three Mark questions 1. Find the values of x, y and z from the following equations x y 2 6 2 5 z xy 5 8
- 100. Three Mark questions 2. Solve the equation for x, y, z and t, if x z 1 1 3 5 2 3 3 y t 0 2 4 6
- 101. Three Mark questions 3. Given x y x 6 4 x y 3 z w 1 2w z w 3 find the values of x, y, z and w
- 102. Three Mark questions 4. Find the values of a, b, c and d from the following equation 2a b a 2b 4 3 5c d 4c 3d 11 24
- 103. Three Mark questions 5. If x 3 z 4 2y 7 0 6 3y 2 6 a 1 0 6 3 2c 2 b 3 21 0 2b 4 21 0 Find the values of a, b, c, x, y and z.
- 104. Three Mark questions 6. Using elementary transformations, find the inverse of each of the matrices 1 1 i 2 3 2 1 ii 1 1 1 3 iii 2 7 2 3 iv 5 7 2 1 v 7 4 2 5 vi 1 3
- 105. Three Mark questions 3 1 vii 5 2 4 5 viii 3 4 3 10 ix 2 7 2 6 x 1 2 6 3 xi 2 1 2 3 xii 1 2 Using elementary transformations, find the inverse of each of the matrices
- 106. Three Mark questions 7. By using elementary operations, find the inverse of the matrix 1 2 A 2 1 8. Find X and Y, if 7 0 X Y 2 5 and 3 0 X Y 0 3
- 107. Three Mark questions 9. Find X and Y, if 2 3 2X 3Y 4 0 and 2 2 3X 2Y 1 5 10. If 8 0 A 4 2 3 6 and 2 2 B 4 2 5 1 then find the matrix X, such that 2A 3X 5B
- 108. Three Mark questions 11. Find X and Y, if 5 2 X Y 0 9 and 3 6 X Y 0 1 12. If 2 5 1 3 3 1 2 4 A 3 3 3 7 2 2 3 3 and 2 3 1 5 5 1 2 4 B 5 5 5 7 6 2 5 5 5 Then compute 3A 5B
- 109. Three Mark questions 13. if cos sin ( ) sin cos x x 0 F x x x 0 0 0 1 Show that F x F y F x y 14. Show that 5 1 2 1 2 1 5 1 6 7 3 4 3 4 6 7
- 111. Three Mark questions 16.Show that 1 2 3 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 2 3 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 2 3 4 2 3 4 1 1 0 17. if 1 2 3 A 5 7 9 2 1 1 and 4 1 5 B 1 2 0 1 3 1 then verify that ' ' 'i A B A B ' ' 'ii A B A B
- 112. Three Mark questions 18. if ' 3 4 A 1 2 0 1 and 1 2 1 B 1 2 3 then verify that ' ' 'i A B A B ' ' 'ii A B A B
- 113. Three Mark questions 19. if ' 2 3 A 1 2 and 1 0 B 1 2 then find 'A 2B 20. if 1 2 3 A 4 2 5 and 2 3 B 4 5 2 1 AB BAthen find AB, BA Show that
- 114. Three Mark questions 21. If A and B are symmetric matrices of the same order, then show that AB is symmetric if and only if A and B are commutative, that is AB = BA.
- 115. Three Mark questions 22. If 3 2 A 4 2 and 1 0 I 0 1 Find k so that 2 A kA 2I
- 116. Three Mark questions 23. For the matrix 1 5 A 6 7 verify that 'i A A is a symmetric matrix 'ii A A is a skew symmetric matrix
- 117. Three Mark questions 24. Find ' 1 A A 2 ' 1 and A A 2 When 0 a b A a 0 c b c 0
- 118. Three Mark questions 25. Express the following matrices as the sum of a symmetric and skew symmetric matrix: 3 5 1 1 6 2 2 2 3 1 2 1 3
- 119. Three Mark questions 26. Express the matrix 2 2 2 B 1 3 4 1 2 3 as the sum of a symmetric and a skew symmetric matrix.
- 120. Three Mark questions 27. If A and B are symmetric matrices of the same order, then show that AB is symmetric if and only if AB = BA. 28.If A and B are invertible matrices of the same order, then prove that 1 1 1 AB B A
- 121. Three Mark questions 30.Prove that for any square matrix A with real number entries, A+ A’ is a symmetric matrix and A- A’ is a skew symmetric matrix.
- 122. Three Mark questions 32. Prove that any square matrix can be expressed as the sum of symmetric and skew symmetric matrix 33.Prove inverse of a square matrix, if it exist, is unique
- 123. Five Marks questions 1. If 2 4 1 3 6 5 A and B Verify that ( )AB B A
- 124. Five Marks questions 2. If 1 2 3 3 1 2 4 1 2 5 0 2 , 4 2 5 0 3 2 1 1 1 2 0 3 1 2 3 A B and C then compute that (A+B) & (B-C) Also verify that A+(B-C)=(A+B)-C
- 125. Five Mark questions 3. Find 2 A 5A 6I 2 0 1 if A 2 1 3 1 1 0
- 126. Five Mark questions 5.If 0 6 7 A 6 0 8 7 8 0 0 1 1 B 1 0 2 1 2 0 2 C 2 3 Calculate AC, BC and (A + B) C. Also, verify that (A + B)C = AC + BC.
- 127. Five Mark questions 6. if 1 1 1 A 1 2 3 2 1 3 then show that 3 A 23A 40I O
- 128. Five Mark questions 7. If 1 0 2 A 0 2 1 2 0 3 then show that 3 2 A 6A 7A 2I O
- 129. Five Mark questions 8. Let 2 1 A 3 4 5 2 B 7 4 2 5 C 3 8 Find a matrix D such that CD AB 0
- 130. Five Mark questions 9. If tan tan 0 2A 02 and I is identity matrix of order 2, Show that cos sin sin cos I A I A
- 131. Five Marks questions
- 133. CET questions (A) (B) (C) 3 (D) 2
- 134. Mr. Santosh T. M.Sc BasavaJyoti Science & Commerce P.U. College, Jamkhandi E-mail: santa1.6180@gmail.com Contact : 9591319967