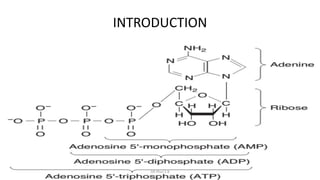
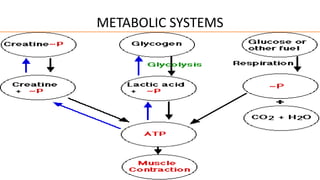
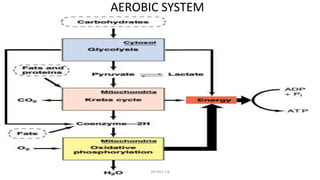
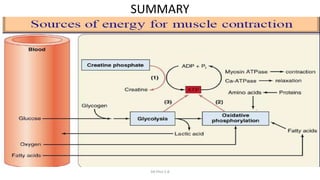
This document discusses three main metabolic systems that provide energy for muscle contraction:
1) The phosphocreatine-creatine system provides quick energy during high intensity activities like sprinting. It builds up a store of phosphorylcreatine that is hydrolyzed to form ATP.
2) The glycogen-lactic acid system breaks down glycogen stores in muscle into glucose and then lactate, producing ATP through glycolysis even without oxygen.
3) The aerobic system fully breaks down fuels like fats and carbohydrates with oxygen to produce substantially more ATP over longer periods.