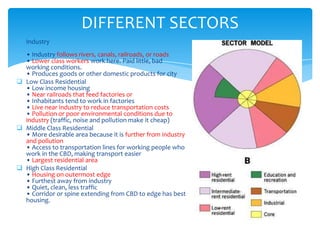
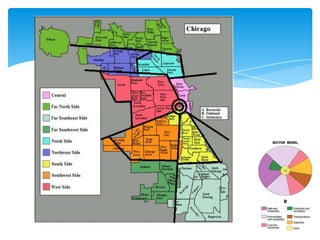
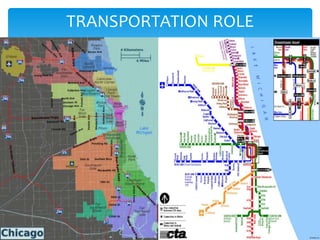
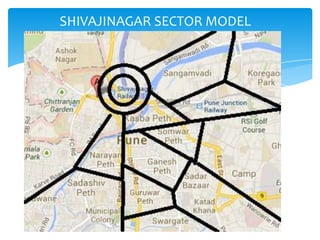
Homer Hoyt developed the sector theory or sector model of urban land use in 1939 as an alternative to the concentric zone model. The sector model posits that a city develops in wedge-shaped sectors centered around major transportation routes rather than concentric circles. Land uses cluster around transportation routes, with industry locating near ports, railroads, or roads. Residential areas then develop, with lower income housing nearer the industrial areas and transportation. Middle and high-income housing is located further out. The model was applied to Chicago and found to accurately describe the city's development around railroad lines.








![inference
Decentralization (or decentralisation) is the process of
redistributing or dispersing functions, powers, people or
things away from a central location or authority.[1][2] While
decentralization, especially in the governmental sphere, is
widely studied and practiced, there is no common
definition or understanding of decentralization. The
meaning of decentralization may vary in part because of
the different ways it is
Benefits—less tax,have to leave some space for residential
use](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sectortheory-131013014240-phpapp01/85/Sector-theory-13-320.jpg)
![Mixed land use
Mixed-use development is — in a broad sense — any
urban, suburban or village development, or even a single
building, that blends a combination of
residential, commercial, cultural, institutional, or industrial
uses, where those functions are physically and functionally
integrated, and that provides pedestrian
connections.[1][2] The term ("a mixed-use development")
may also be used more specifically to refer to a mixed-use
real estate development project — a building, complex of
buildings, or district of a town or city that is developed for
mixed-use by a private developer, (quasi-)governmental
agency, or a combination thereof](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sectortheory-131013014240-phpapp01/85/Sector-theory-14-320.jpg)
![benefits include:[3]
greater housing variety and density
reduced distances between
housing, workplaces, retail businesses, and other
destinations
more compact development
stronger neighborhood character
pedestrian and bicycle-friendly environments](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sectortheory-131013014240-phpapp01/85/Sector-theory-15-320.jpg)
