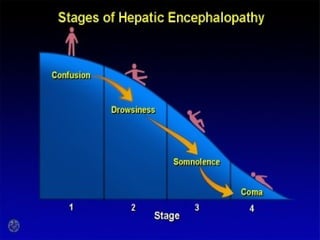
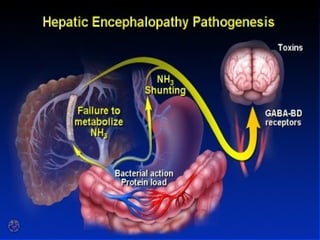
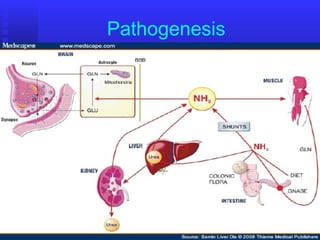
This document provides an overview of hepatic encephalopathy. It describes hepatic encephalopathy as a complex neuropsychiatric syndrome characterized by disturbances in consciousness and personality changes. Acute episodes can be reversible while chronic cases may progress to coma or death. Precipitating factors include constipation, surgery, and progressive liver disease. Ammonia plays a central role in pathogenesis, as the liver is unable to metabolize and excrete nitrogenous waste products, leading to accumulation of ammonia in the blood and brain. Treatment aims to remove precipitating factors, reduce nitrogenous load from the gut, and manage symptoms. Options include nutritional management, laxatives, antibiotics like rifaximin, and lactulose to produce