The document discusses chronic kidney disease (CKD). It defines CKD as kidney damage or decreased glomerular filtration rate (GFR) lasting at least 3 months. CKD is staged based on GFR levels and can progress to kidney failure requiring dialysis or transplant. The causes, risk factors, complications, diagnostic evaluation and management of CKD are described with a focus on pediatric patients.














![SYSTEMIC FEATURES (contd.)
BONE AND MINERAL DISORDER [RENAL OSTEODYSTROPHY]
• Systemic disorder of bone & mineral metabolism manifested by either
one or a combination of the following:
– abnormlities of Ca++, phosphorous, PTH or vitamin D
– abnormalities in bone histology, linear growth or strength
– vascular or other soft tissue calcification
• As early as in CKD stage 2 vit D ↓ & serum PTH ↑
• Seen in 30% of patients with ESRD
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ckd-seminar-13-170412184542/85/Chronic-Kidney-Disease-21-320.jpg)


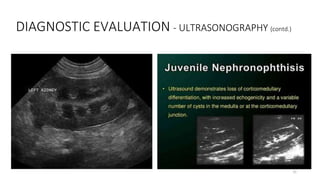
![DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION
DETAILED HISTORY
• Age at onset/ duration
• Polyuria/ polydipsia/ enuresis/hematuria
• Fever/ rash / arthralgia/ arthritis/odema
• Recurrent UTI
• Antenatal detection of any renal anomalies
• Spinal abnormalities
• Uraemic symptoms (fatigue/anorexia/vomiting)
• History of renal disease in the family [Alport syndrome/ Nephronophthisis/
congenital nephrotic syndrome]
24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ckd-seminar-13-170412184542/85/Chronic-Kidney-Disease-24-320.jpg)
![CLINICAL EXAMINATION
• vitals [blood pressure]
• assessment for the presence & severity of peripheral odema
• evaluation of growth, pubertal development & nutritional status
• features of anaemia & bone disease
• pericardial rub/ diminished heart sounds
• psychological & intellectual functions
DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION (contd.)
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ckd-seminar-13-170412184542/85/Chronic-Kidney-Disease-25-320.jpg)

![Urine Analysis
• Look for red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs)
• Most children with chronic kidney disease have broad hyaline casts
• Proteinuria
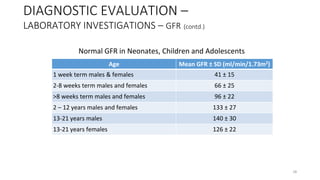
Glomerular Filteration Rate (GFR)
Estimation of GFR - Schwartz formula
GFR = k X height[cm] / serum creatinine [mg/dl]
k = 0.4 for preterm infants),
k = 0.45 for full-term infants
k = 0.55 for those aged 2-12 yrs and adolescent girls
k = 0.7 years in adolescent boys
DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION –
LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS (contd.)
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ckd-seminar-13-170412184542/85/Chronic-Kidney-Disease-27-320.jpg)
![Cystatin C
• Low molecular weight protein [13.36 kD]
• Freely filtered by the glomerulus & metabolized after tubular reabsorption
DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION –
LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS (contd.)
Reference Intervals
Preterm Infants 1.34 – 2.57
Fullterm Infants 1.36 – 2.23
>8 days – 1year 0.75 – 1.87
1 – 3 years 0.68 – 1.90
3 – 16 years 0.51 – 1.31
Reference Intervals for Cystatin C
29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ckd-seminar-13-170412184542/85/Chronic-Kidney-Disease-29-320.jpg)



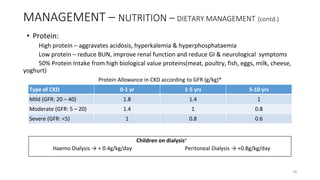






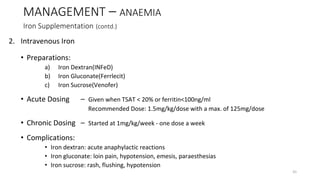
![MANAGEMENT (contd.)
CKD - MBD
• Control of levels of blood phosphate – most important factor in prevention & treatment of
secondary hyperparathyroidism
• Daily intake of phosphorous: 800 -1000mg
• Dairy products, chocolate, chicken, nuts, dried beans, aerated drinks to be avoided
Treatment Modalities
1. Phosphate binders:
• Calcium salts [calcium carbonate & calcium acetate]
• Sevelamer hydrochloride
2. Vitamin D & its analogues
3. Calcimimetic agents
4. Surgical intervention
42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ckd-seminar-13-170412184542/85/Chronic-Kidney-Disease-42-320.jpg)
![HYPERTENSION
• Target level < 90th percentile of bp for age , gender & height
• Salt restriction & diuretics
• Antihypertensive drugs:
1. Thiazides [hydrochlorothiazide 2mg/kg/24r] : GFR upto 30ml/min/1.73m2
2. Loop diuretics [furosemide 1-2mg/kg/dose] : GFR < 30
3. Calcium channel blockers [amlodipine]
4. Beta blockers [atenolol/metoprolol]
5. Centrally acting agents [clonidine]
MANAGEMENT (contd.)
43](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ckd-seminar-13-170412184542/85/Chronic-Kidney-Disease-43-320.jpg)