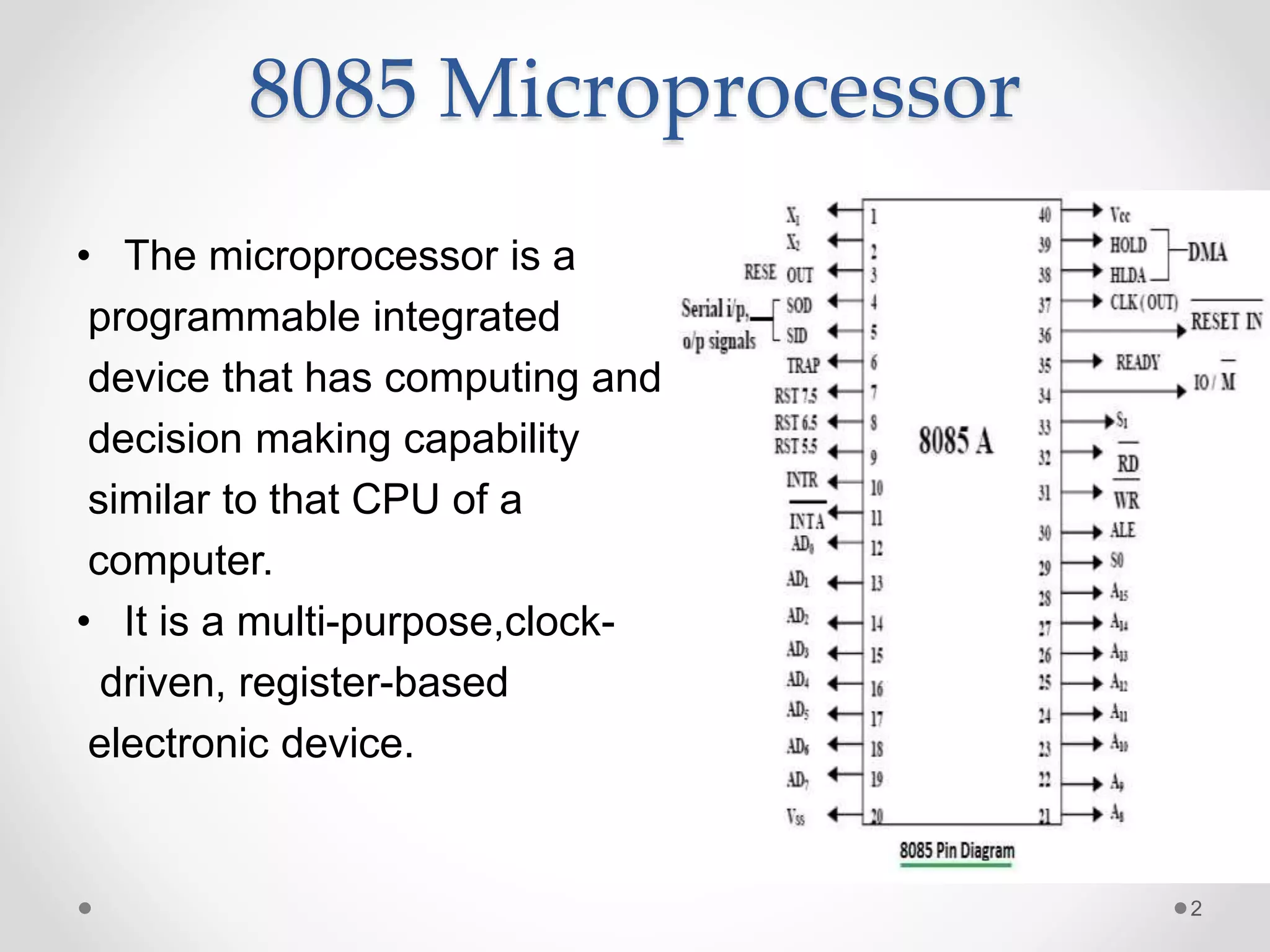
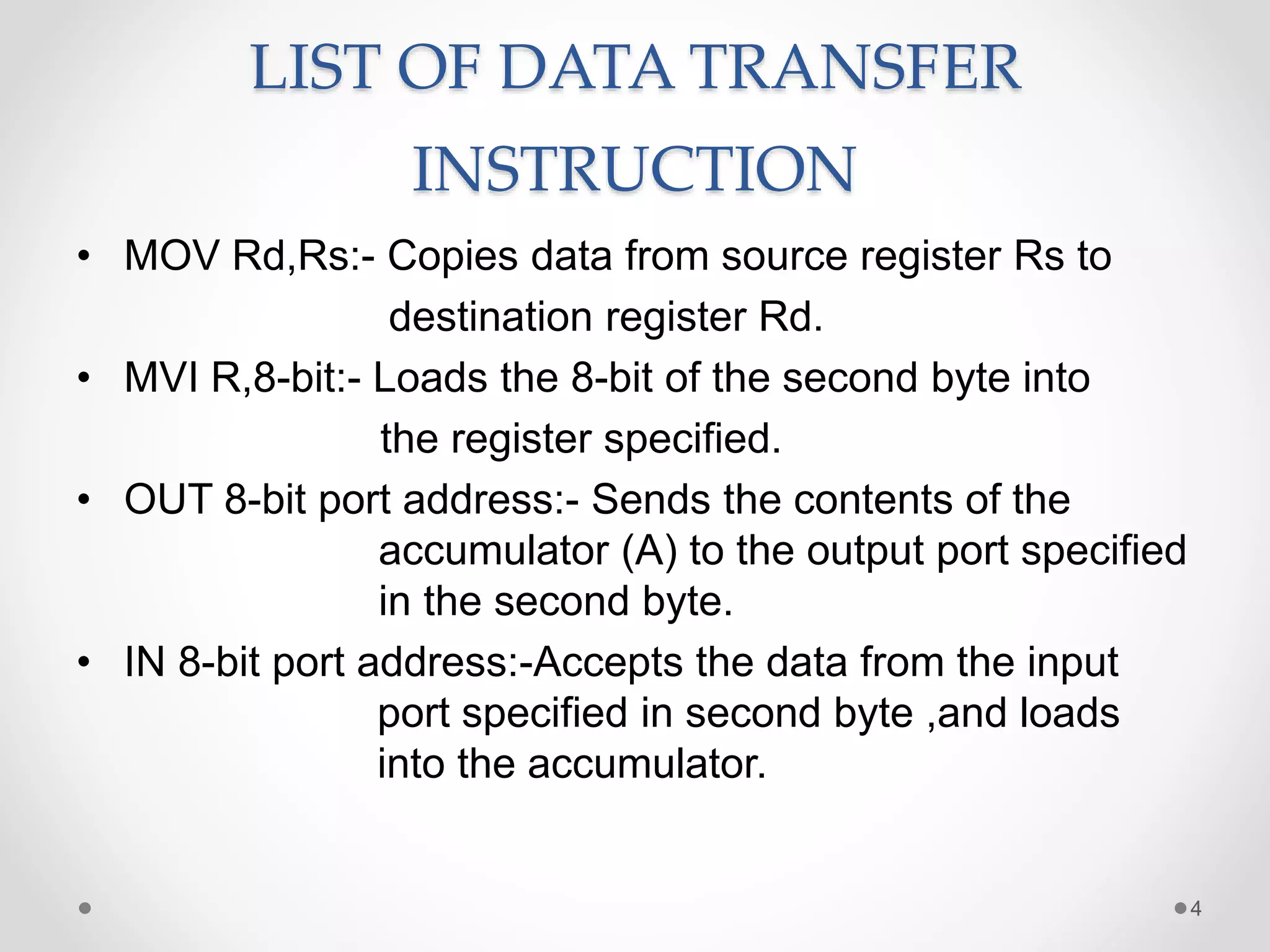
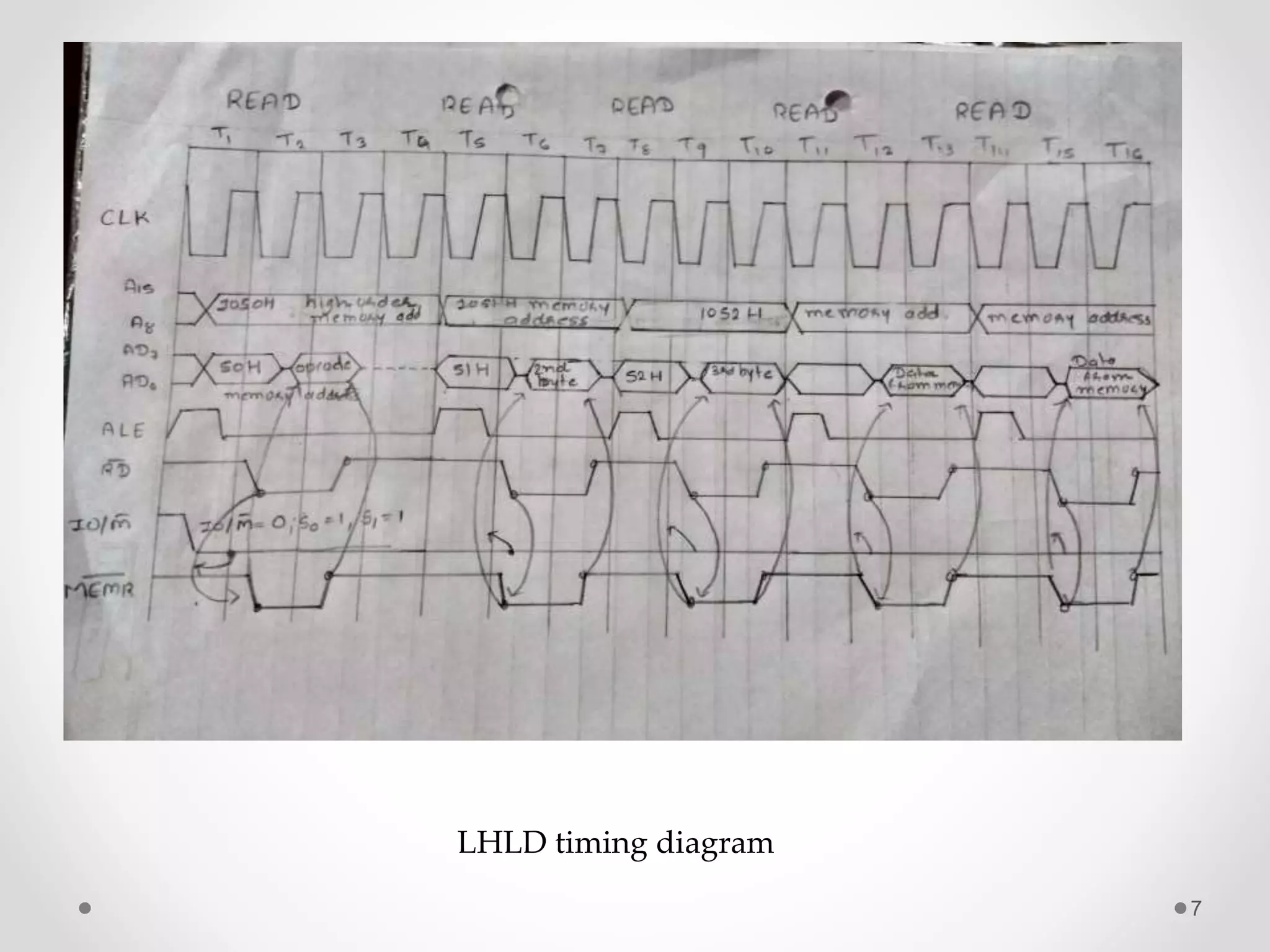
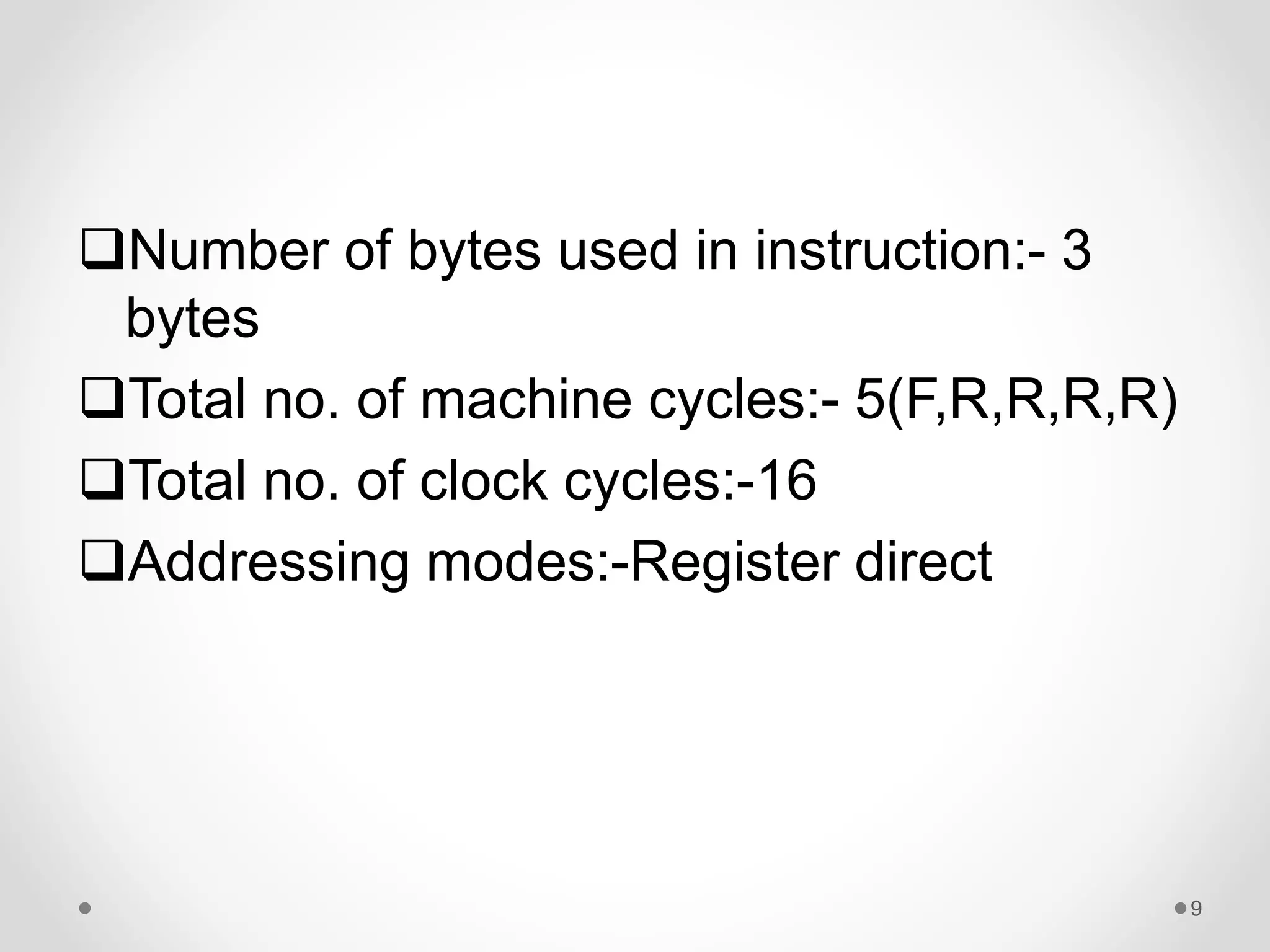
The document discusses data transfer instructions in 8085 microprocessor. It describes the LHLD and SHLD instructions. LHLD loads the contents of two consecutive memory locations pointed by a 16-bit address into the HL register pair. SHLD stores the contents of HL register pair into two consecutive memory locations pointed by a 16-bit address. Both instructions use 3 bytes and take 5 machine cycles (16 clock cycles) to execute, with LHLD performing read cycles and SHLD performing write cycles in the last two machine cycles.