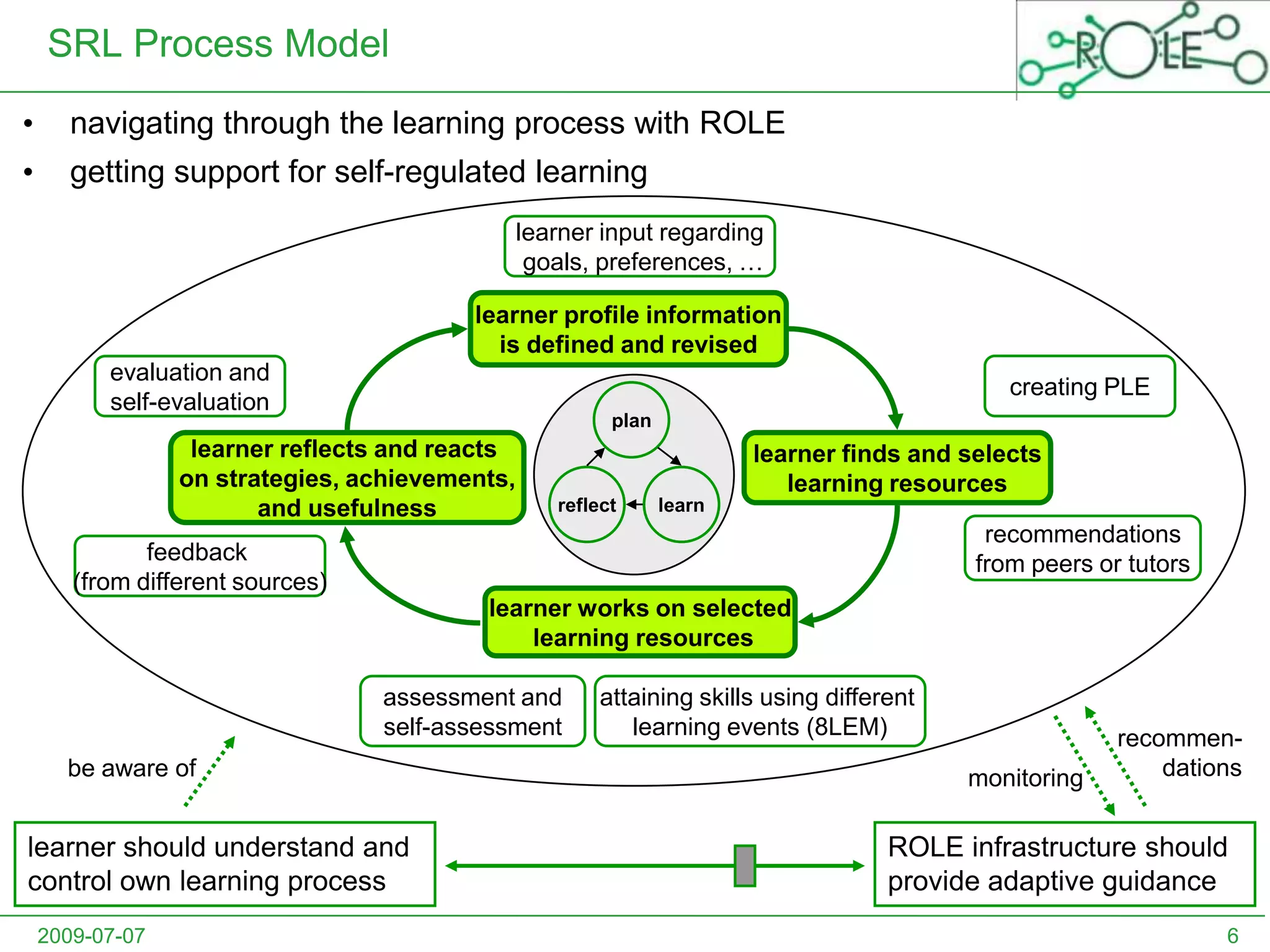
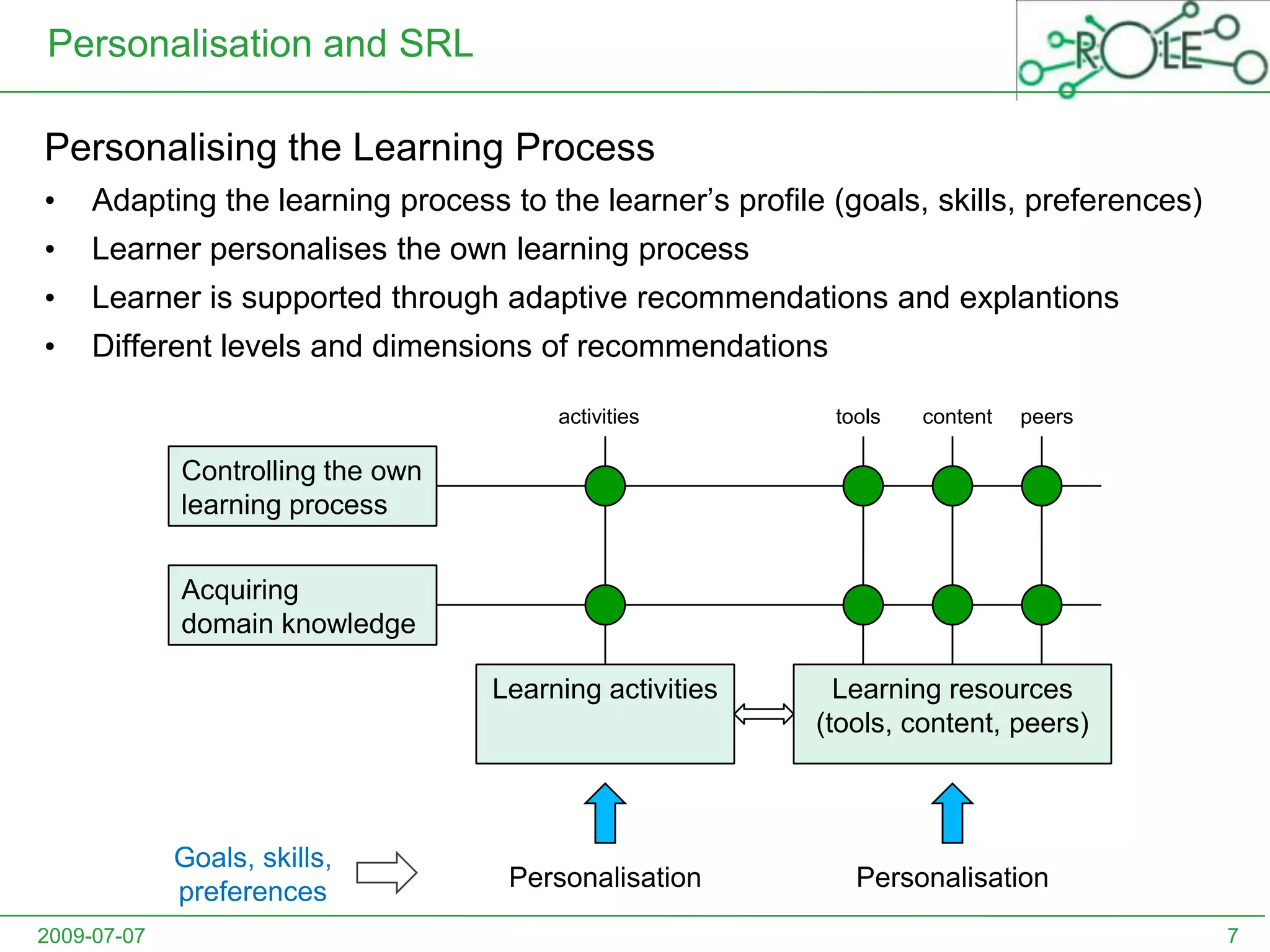
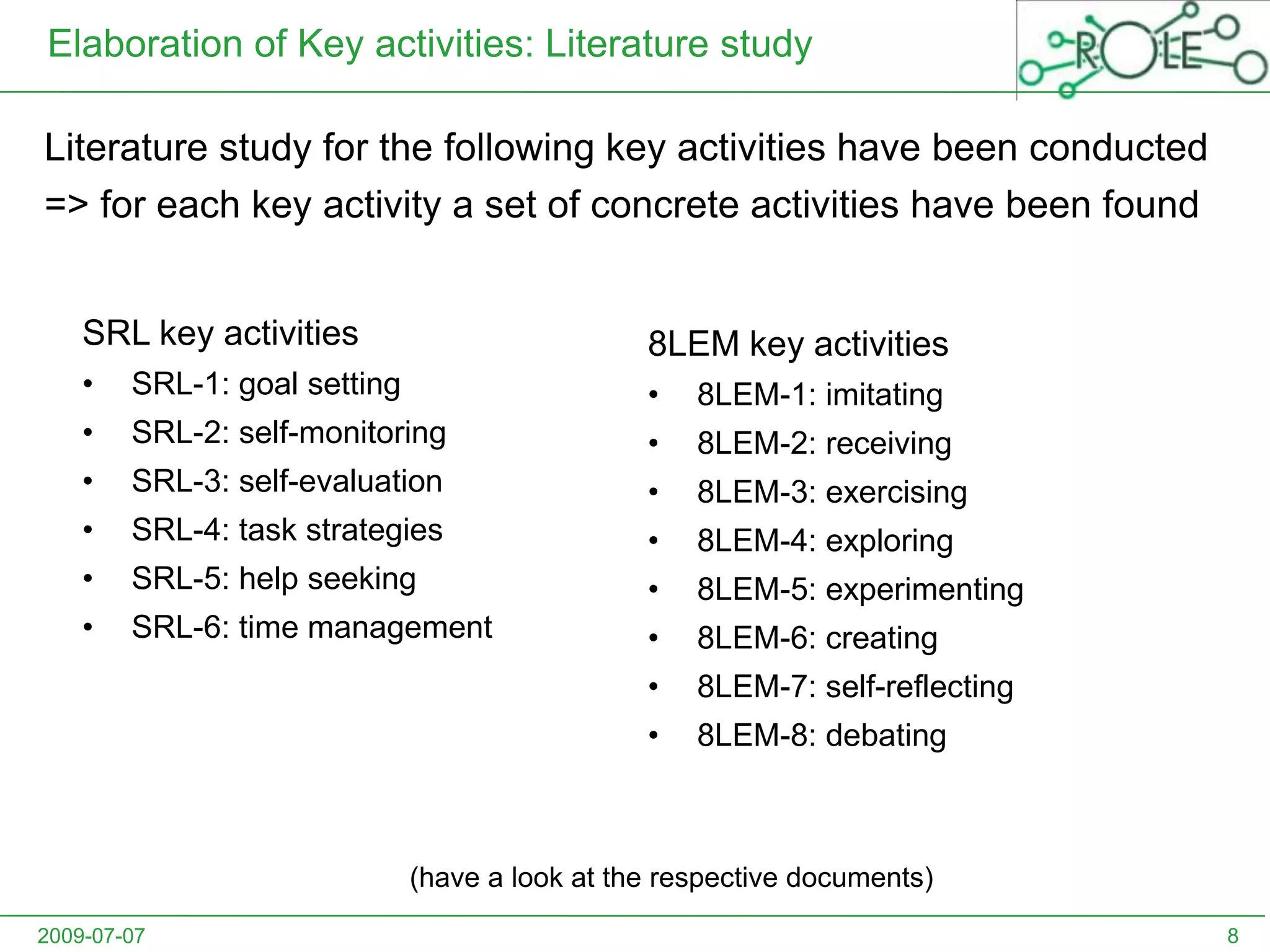
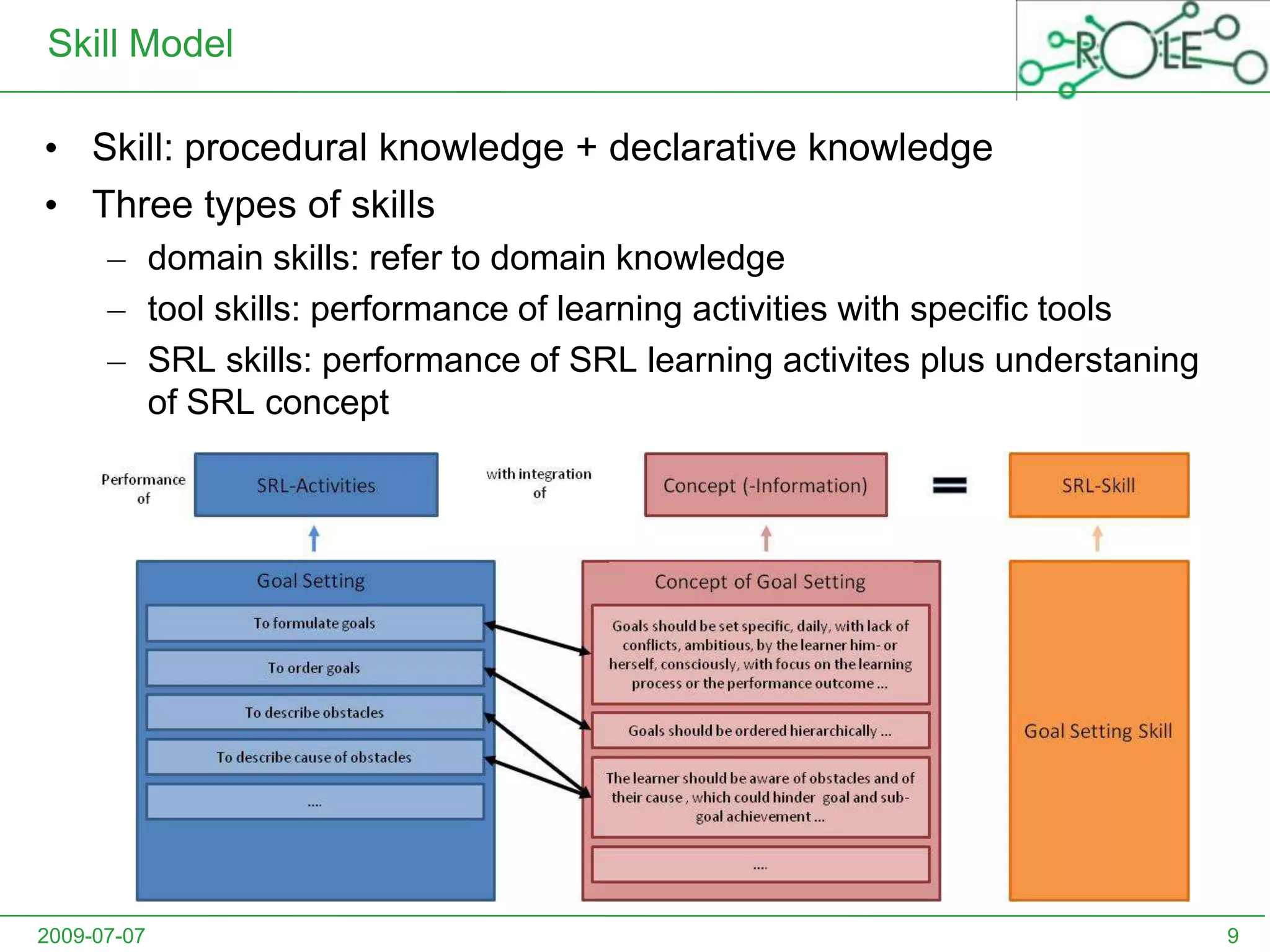
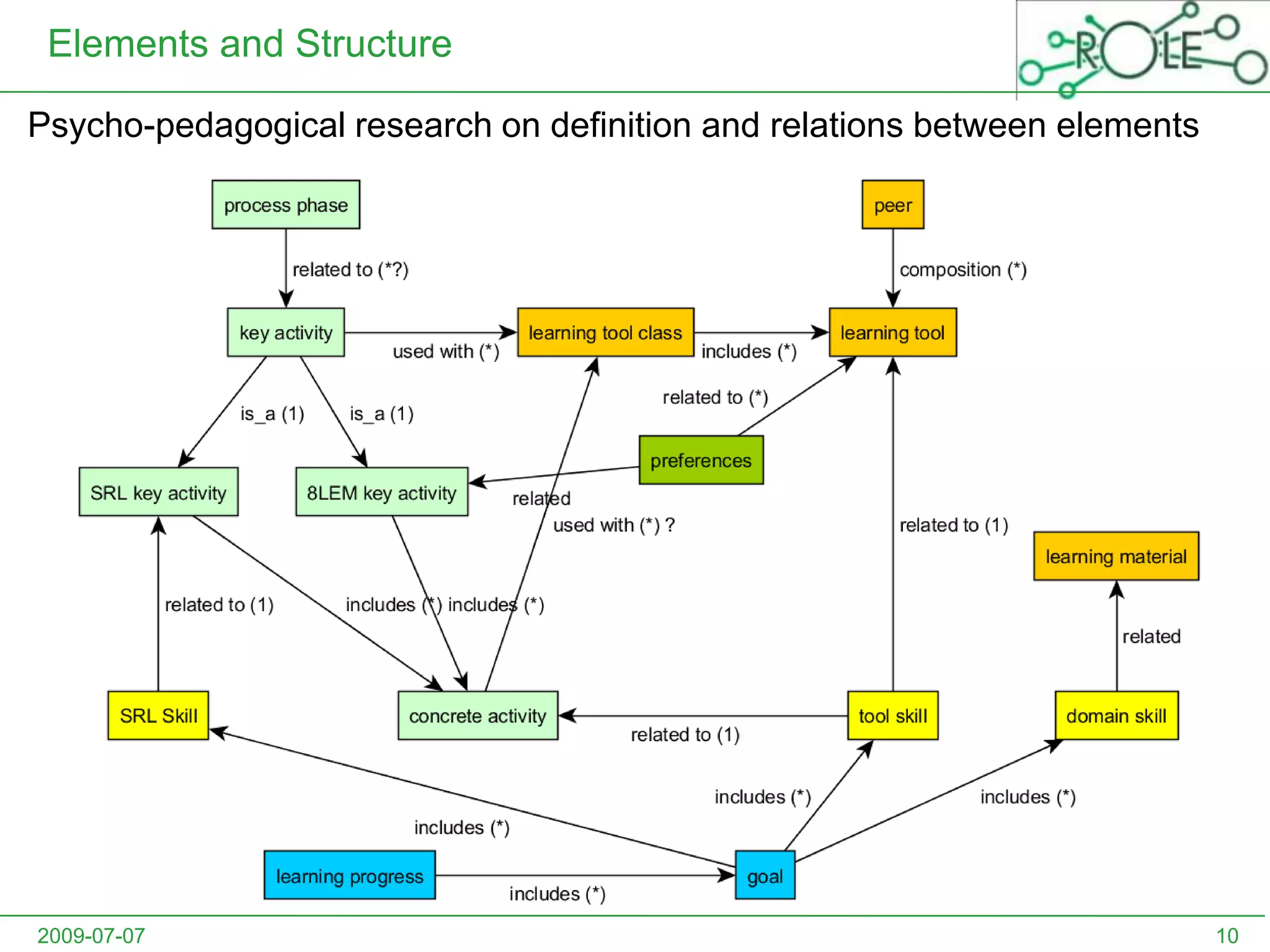
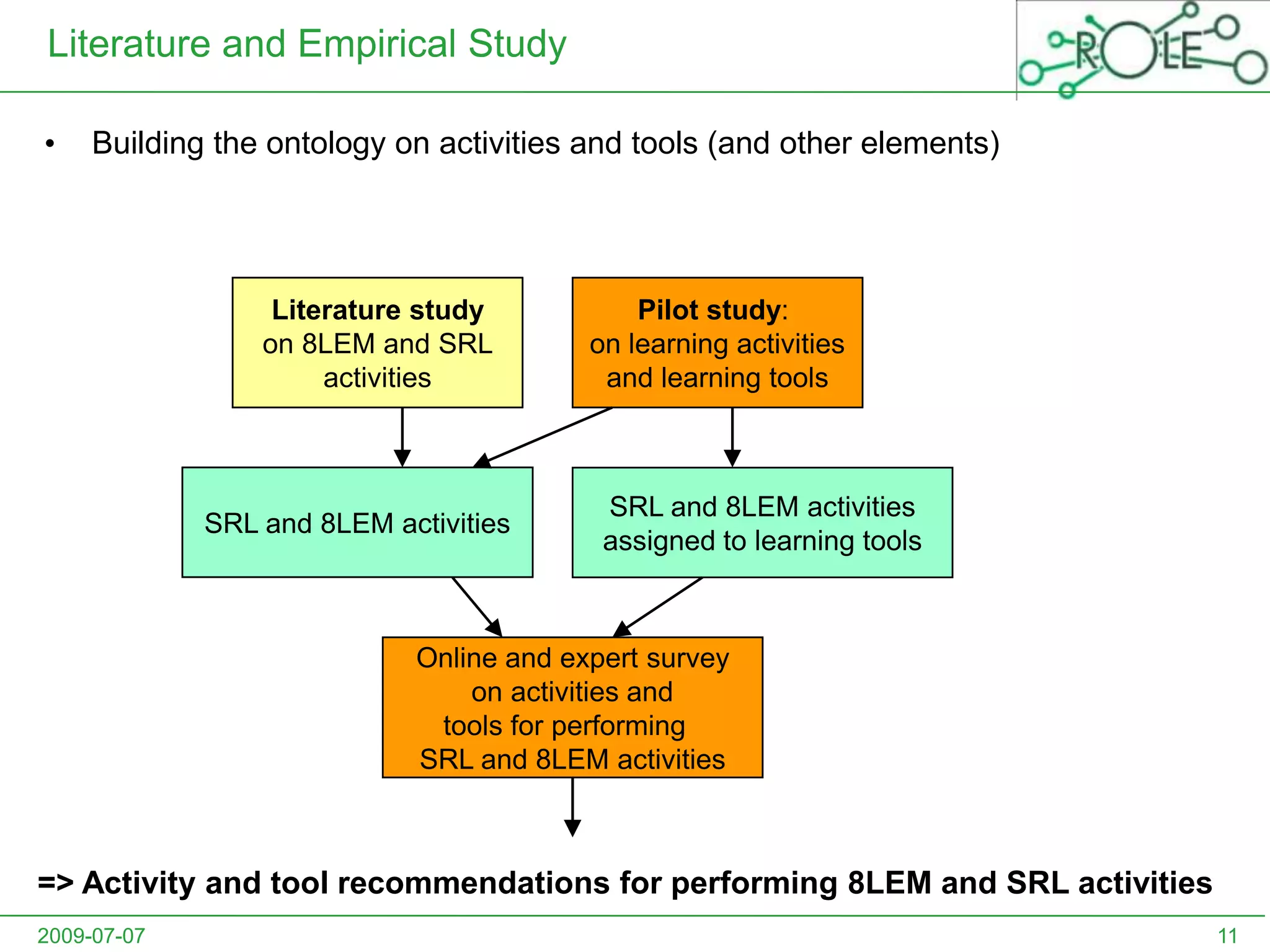
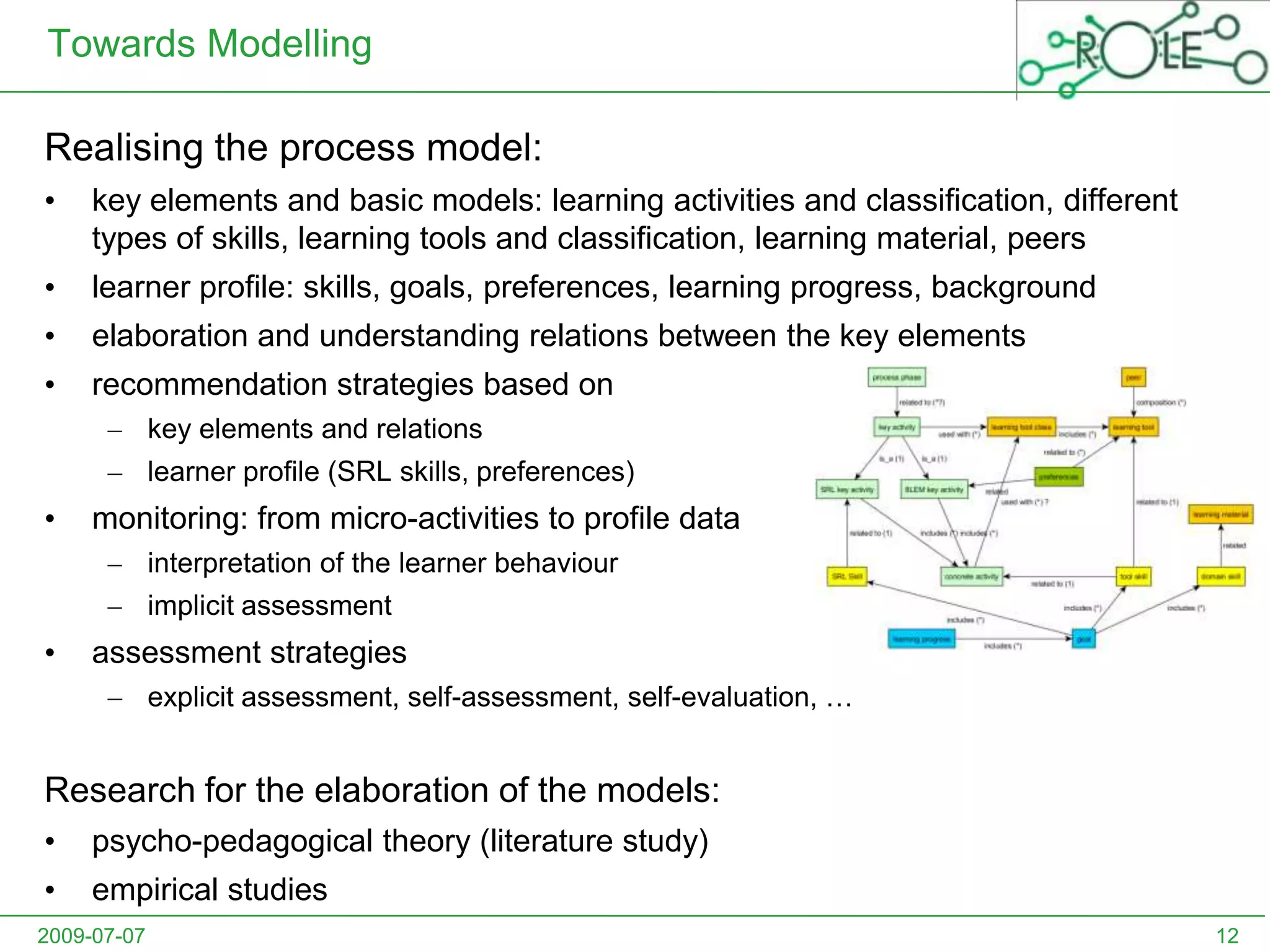
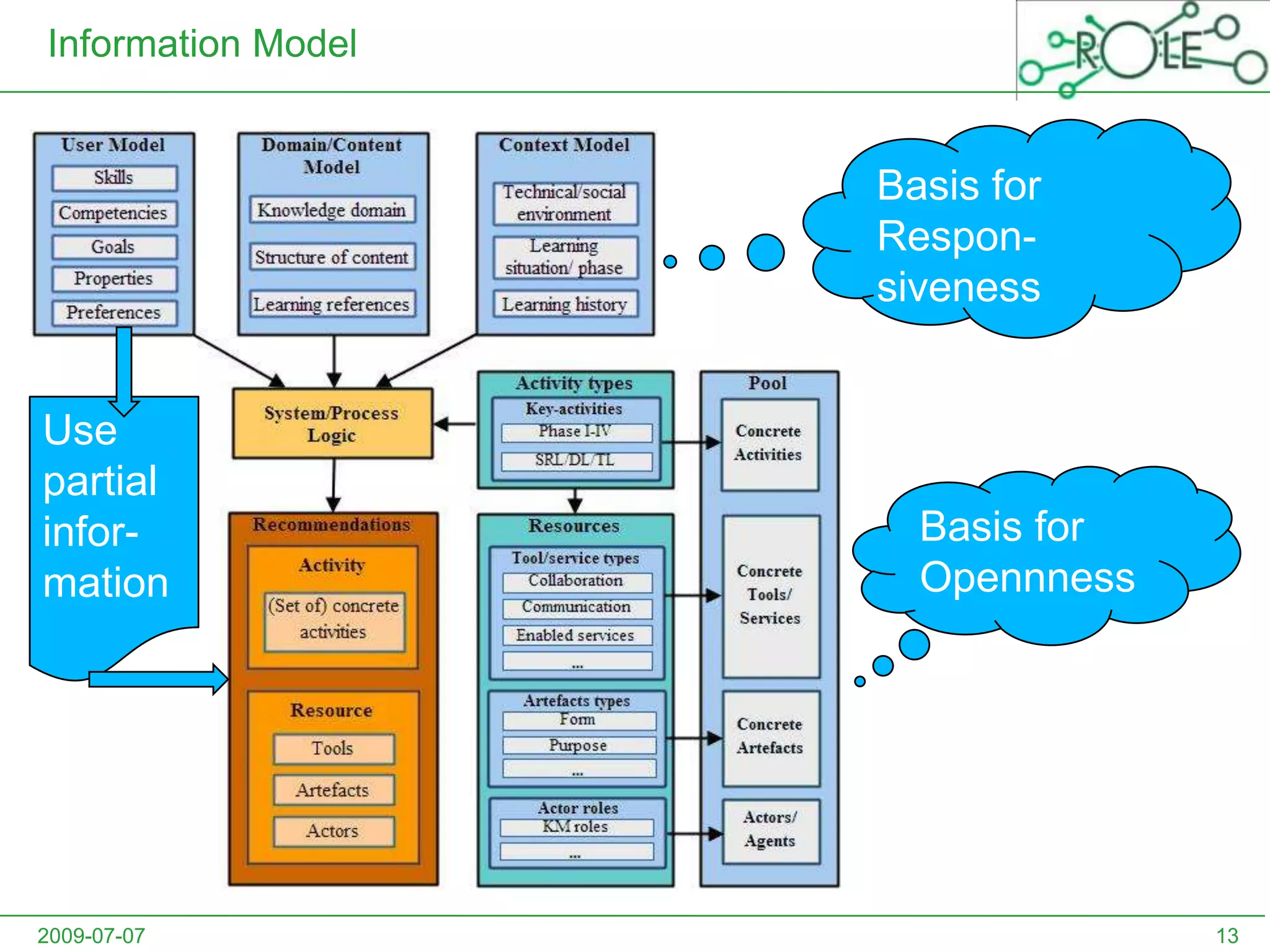
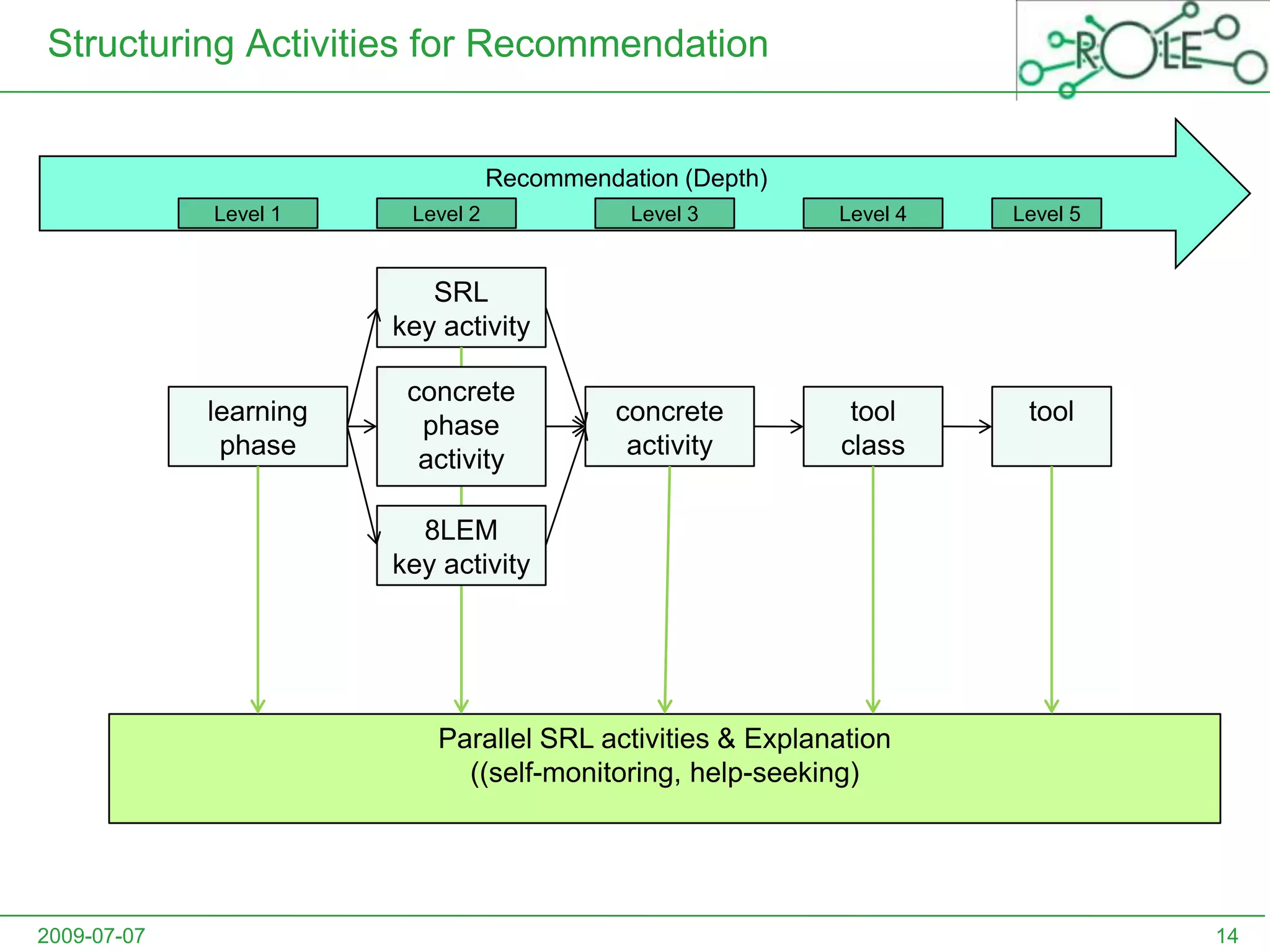
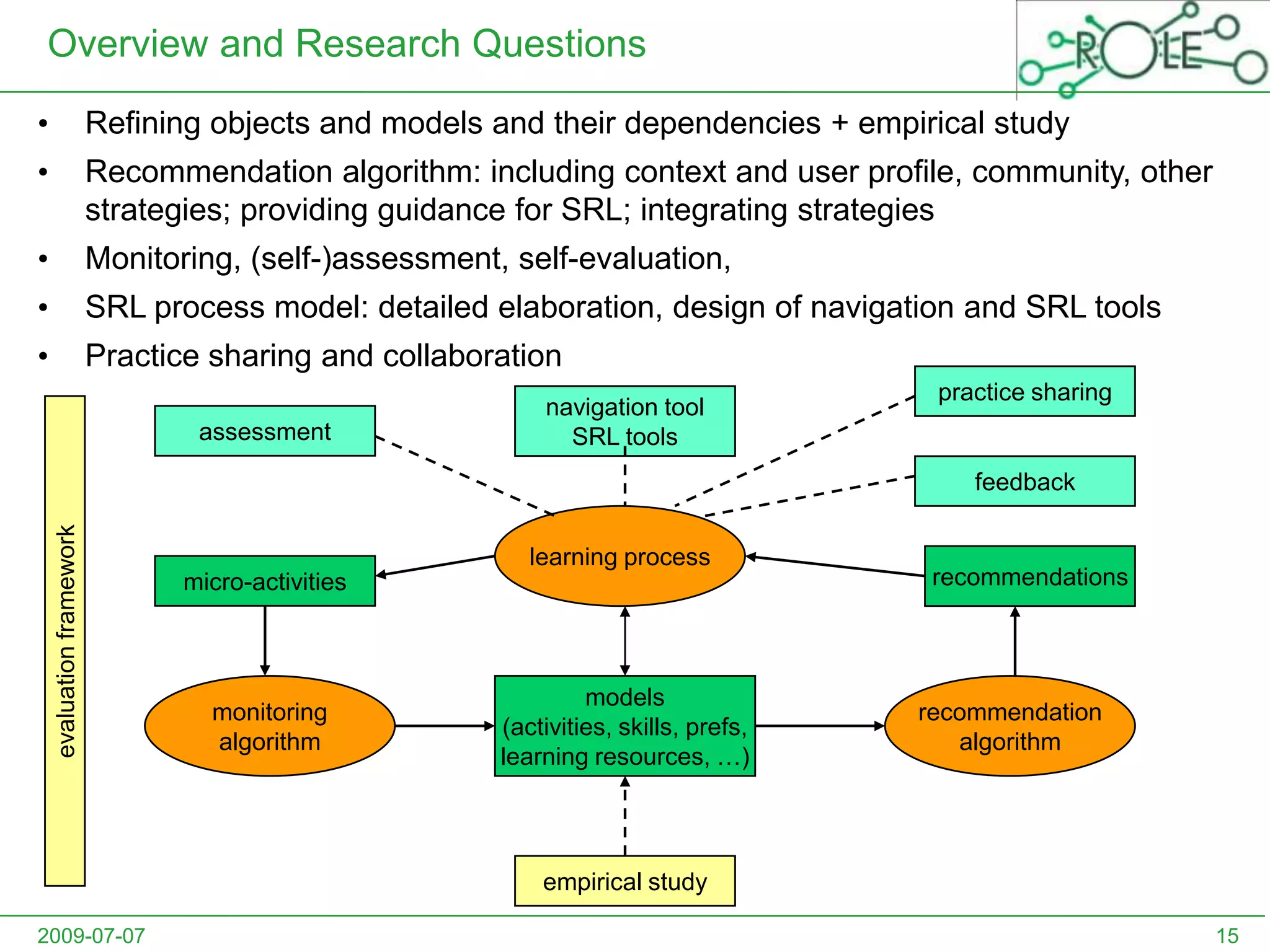
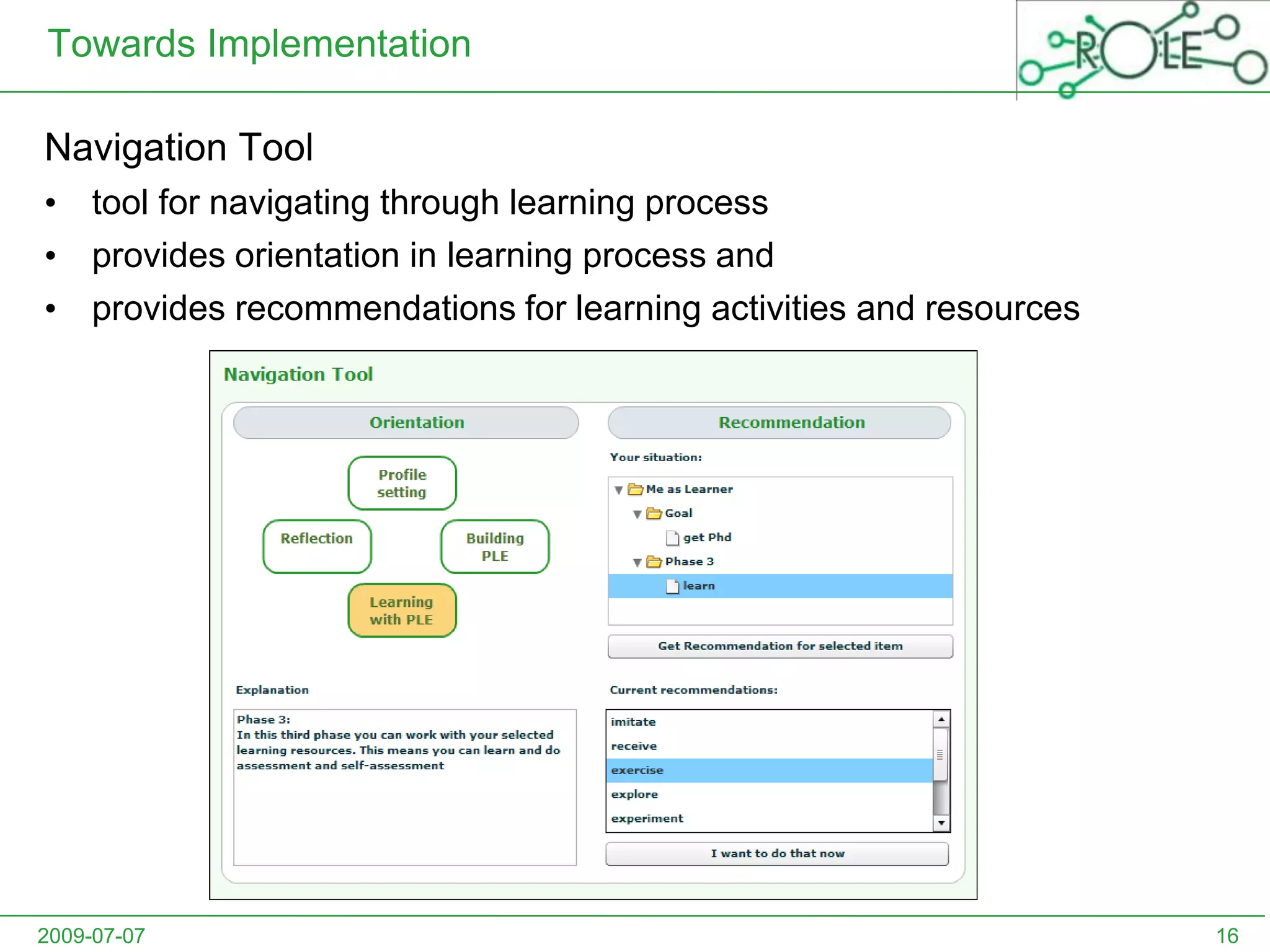
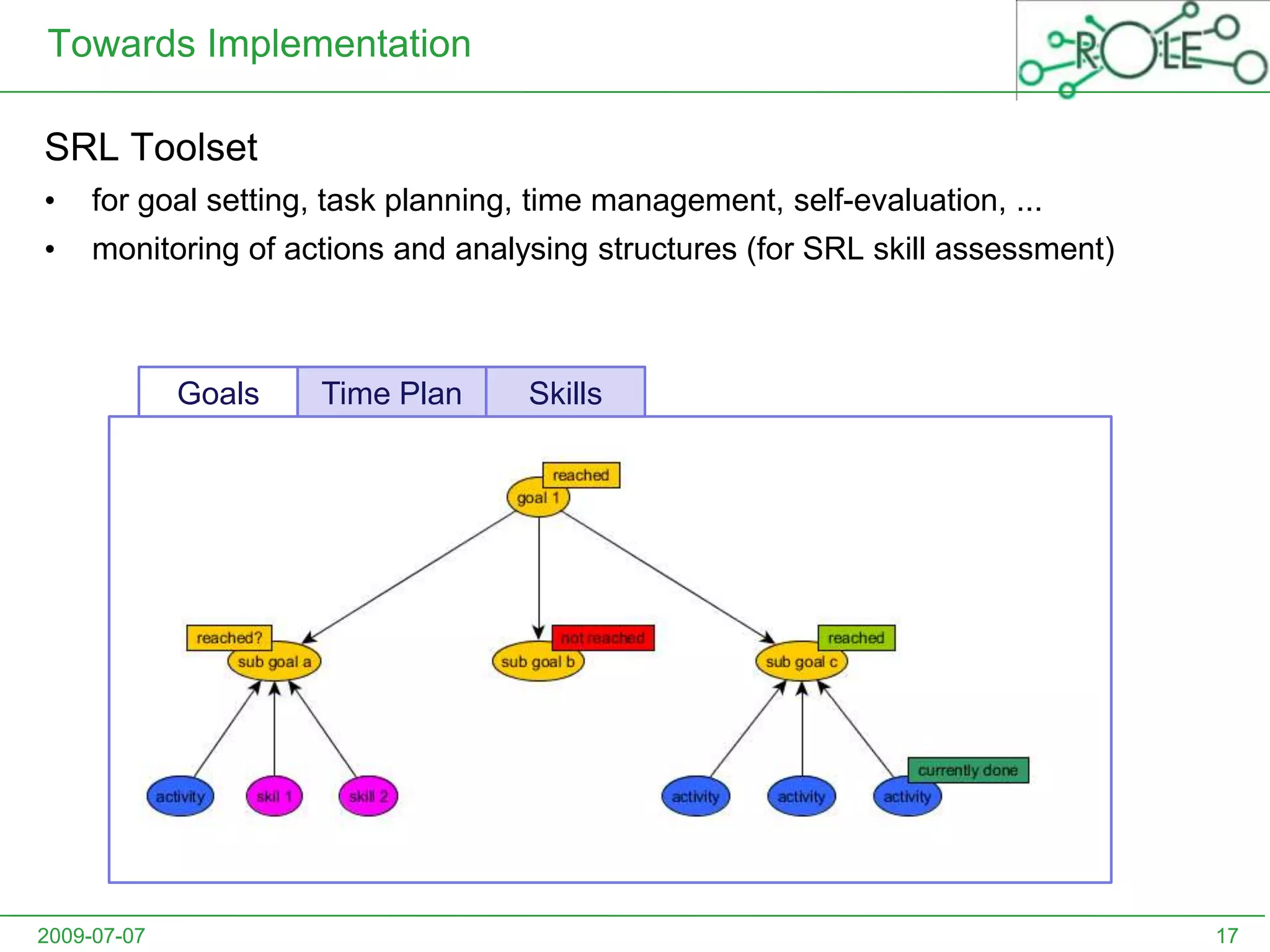
This document outlines a psycho-pedagogical approach to personalized learning environments. It discusses using self-regulated learning models and intrinsic motivation to help learners design their own learning process. Key elements include learner profiles, skill models, and recommendation strategies to guide learners. The approach is implemented through a navigation tool to guide the learning process and self-regulated learning tools to help with goal setting, planning, and evaluation. The overall goal is to empower learners to control their own learning through personalized recommendations and guidance.