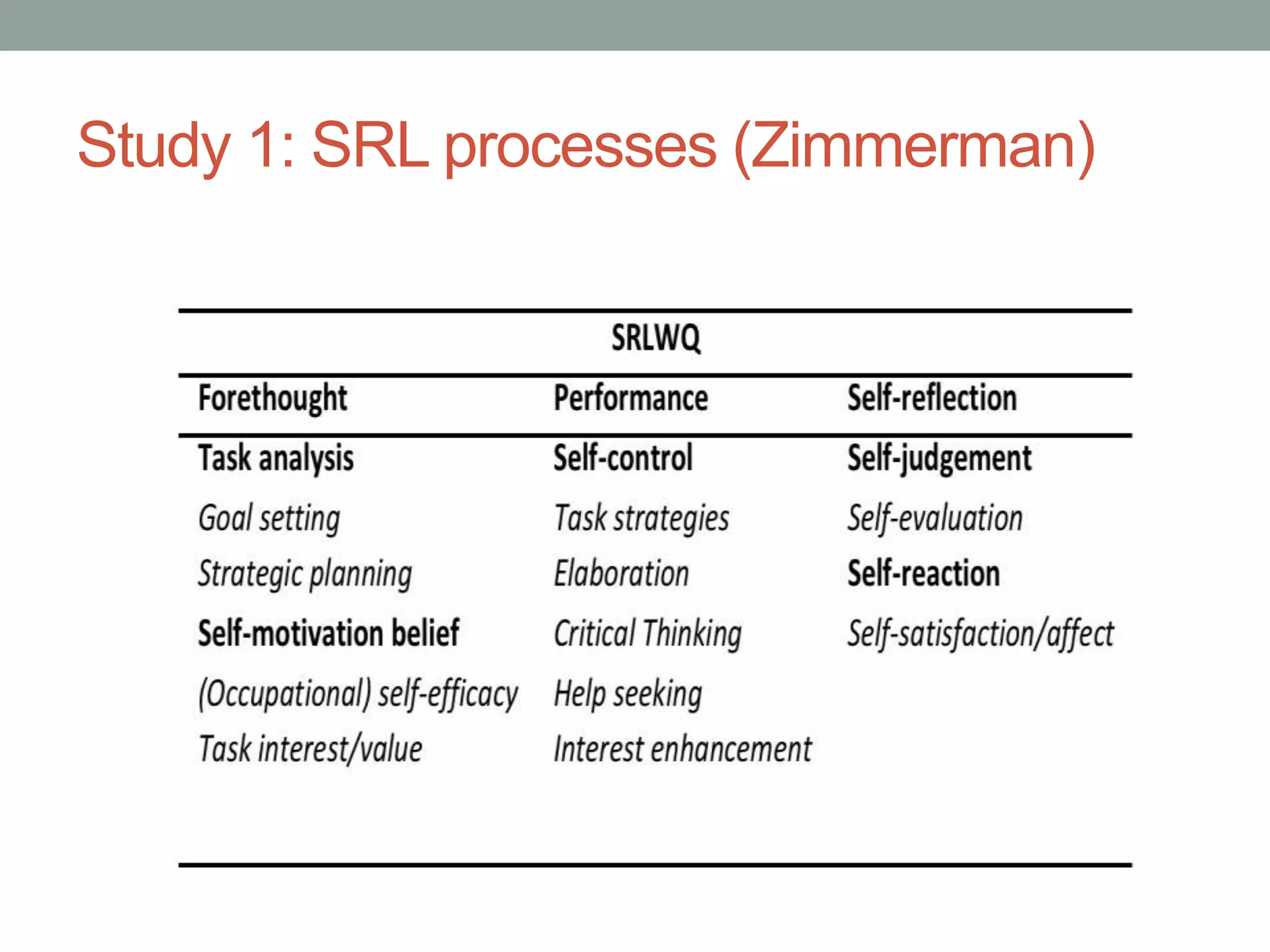
The document investigates self-regulated learning (SRL) in the workplace, focusing on strategies, practices, and influencing factors. Through three studies, it analyzes workplace learning contexts, methods, and key findings, revealing the significance of work-related characteristics on learning activities. The conclusions highlight the inadequacy of current SRL models and the need for further research and development in measuring and understanding workplace learning and self-regulation.