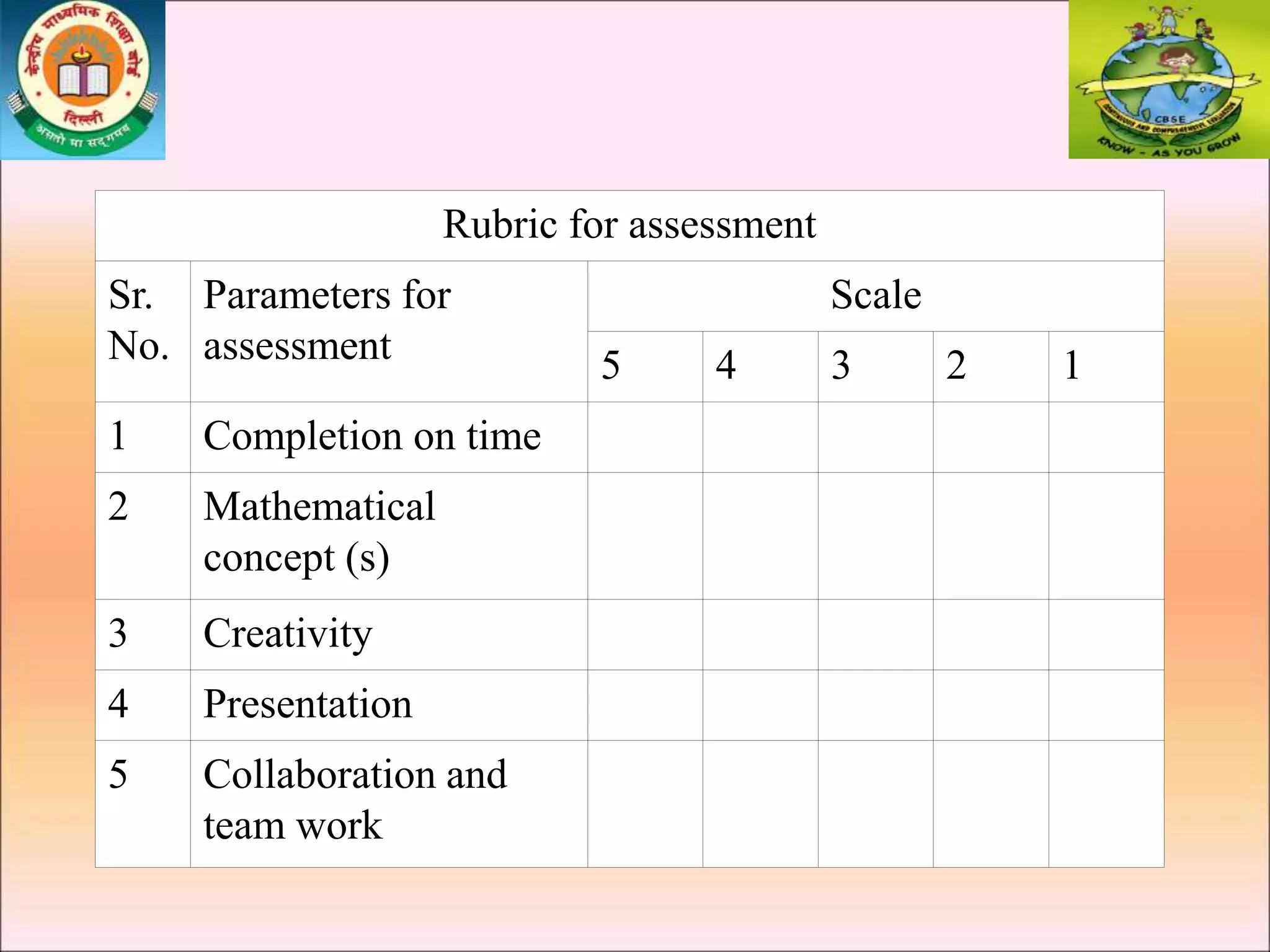
This document provides examples of interdisciplinary project-based learning activities that integrate multiple subjects. It describes a sample soil science project that involves geography, science, IT, and English language arts. Students study soil types and properties, write from the perspective of microorganisms, and create presentations. Another example integrates chemistry, physics, biology and math to study food adulteration. Students test for adulterants, learn about nutrition and balanced diets, and analyze dietary data. The document outlines steps, assessments, and tips for implementing interdisciplinary projects in the classroom.