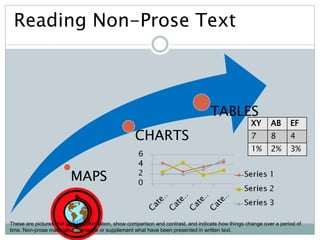
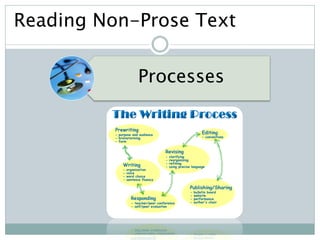
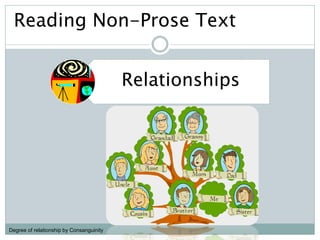
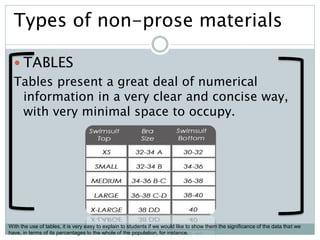
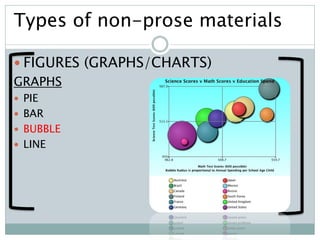
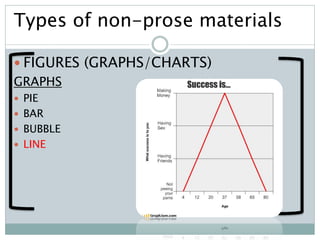
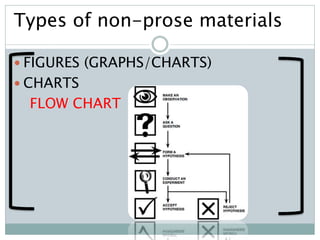
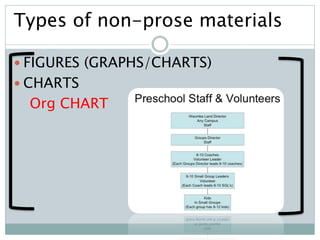
The document discusses the importance and utility of non-prose text, which includes visual aids such as charts, graphs, and tables that present information concisely. Non-prose materials help clarify complex concepts and relationships, making them easier for students to understand compared to traditional prose. Additionally, various types of non-prose materials are highlighted, including tables, figures, poetry, and cartoons, emphasizing their role in enhancing student engagement and learning.