This document discusses cluster computing and provides details on key topics such as:
- What a cluster is and how it links multiple computers together for parallel processing.
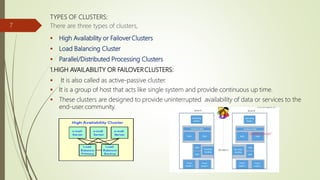
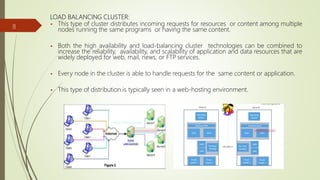
- The different types of clusters including high availability, load balancing, and parallel/distributed processing clusters.
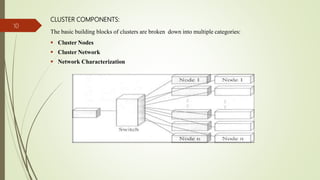
- The components that make up a cluster including cluster nodes and network.
- Classifications of clusters as open or closed.
- Applications of clusters such as compute intensive tasks, data intensive tasks, and transaction intensive tasks.
- Benefits of using cluster computing such as great processing power, availability, expandability, reliability and cost efficiency.





![CLASSIFICATIONS OF CLUSTER:
Open cluster
Close cluster
OPEN CLUSTURE:
All node can be seen from outside, hence it required more IP’s and security concern. But
they are more flexible and used for internet or web server task[1].
CLOSE CLUSTER:
Hide most of the cluster behind the gateway node. Consequently they need less IP’s and
provides better security. These are good for computing task[2].
1.Open clusture 2.close clusture
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clustercomputings-190514072020/85/Cluster-computings-11-320.jpg)



