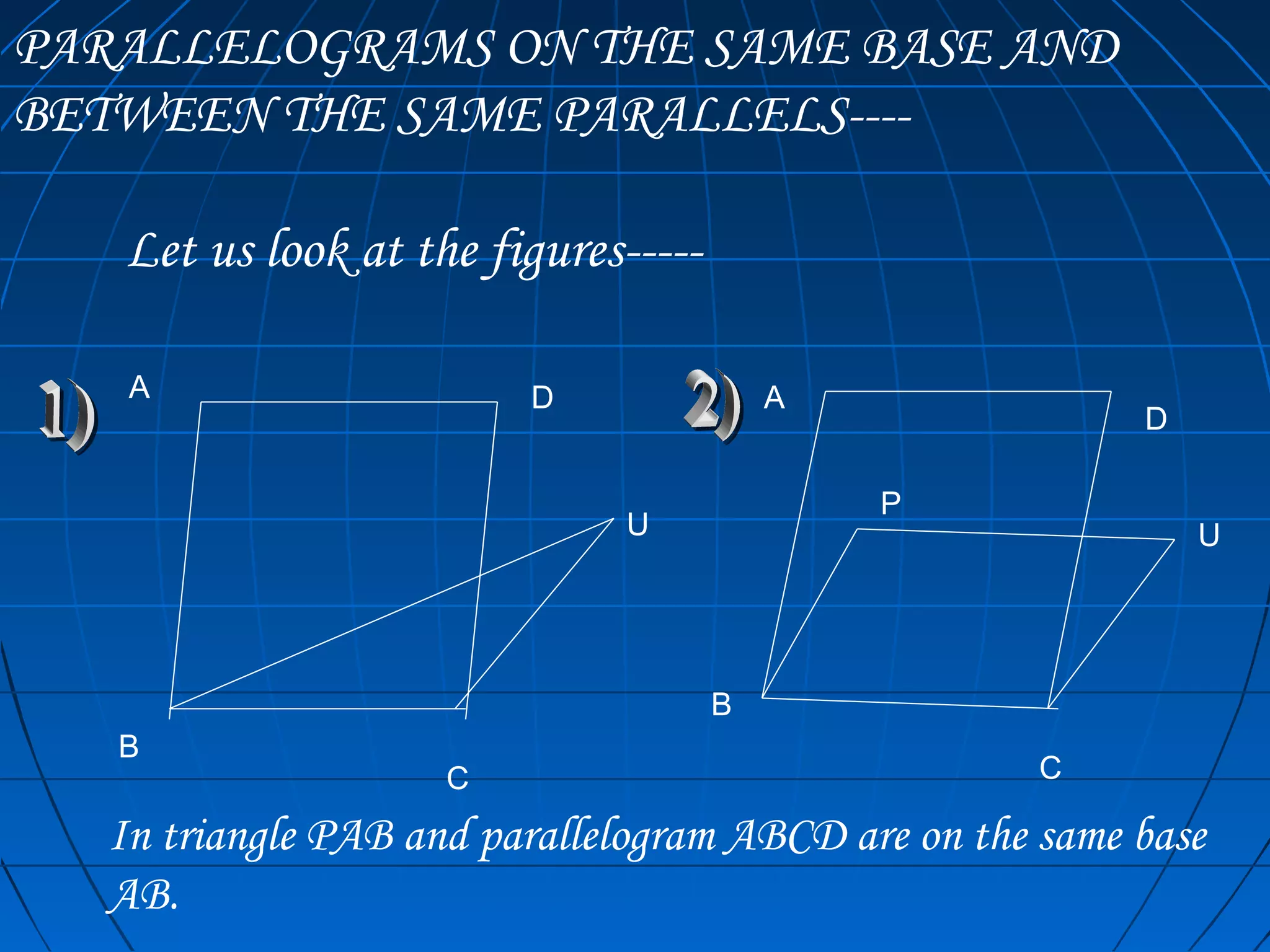
The document discusses relationships between the areas of plane figures such as parallelograms, triangles, and rectangles that share the same base or lie between the same parallels. It defines what it means for figures to be on the same base and between the same parallels. The key points are that parallelograms on the same base and between the same parallels have equal areas, and triangles on the same base and between the same parallels also have equal areas. Formulas for calculating the areas of parallelograms and triangles are reviewed.