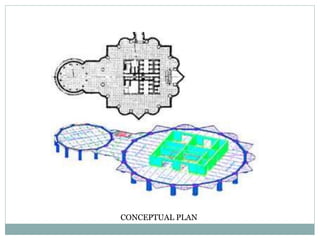
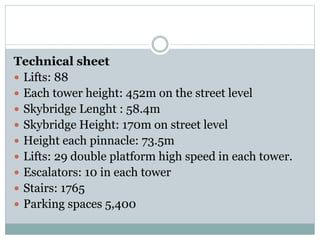
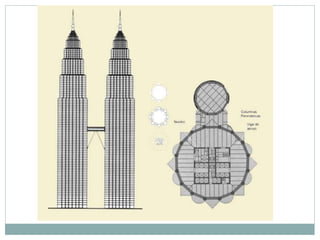
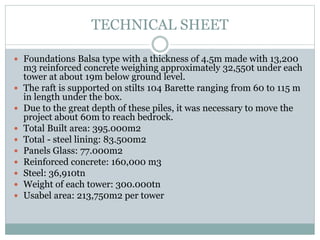
The Petronas Towers in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia were designed by architect Cesar Pelli and built between 1993-1999. The twin towers reach heights of 427 meters and have 88 floors. They are connected by a skybridge on the 41st and 42nd floors. The towers feature a steel and concrete structure with an innovative facade design incorporating geometric Islamic patterns and over 33,000 glass panels. They became both an iconic symbol of Malaysia's economic strength and modern architectural achievements.