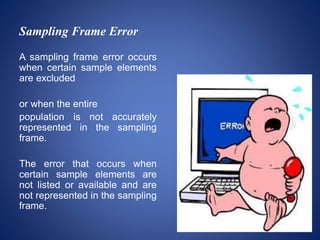
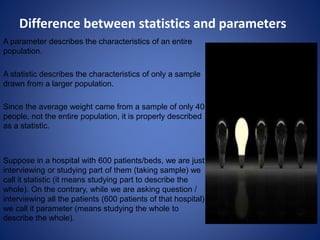
This document defines key sampling terminology used in research and statistics. It explains that an element is the basic unit of analysis, such as an individual person. A population is the entire group of elements, while a target population is the specific subset of elements that are relevant to the study. Sampling is selecting a small number of elements from the larger population. A sampling frame is the list of all elements in the target population. Sampling units refer to the individual items or groups selected from the sampling frame at each stage of sampling. Observation units are the elements from which the actual data is collected, which may be the same as or differ from the sampling and analysis units. The document also distinguishes between statistics, which describe characteristics of a