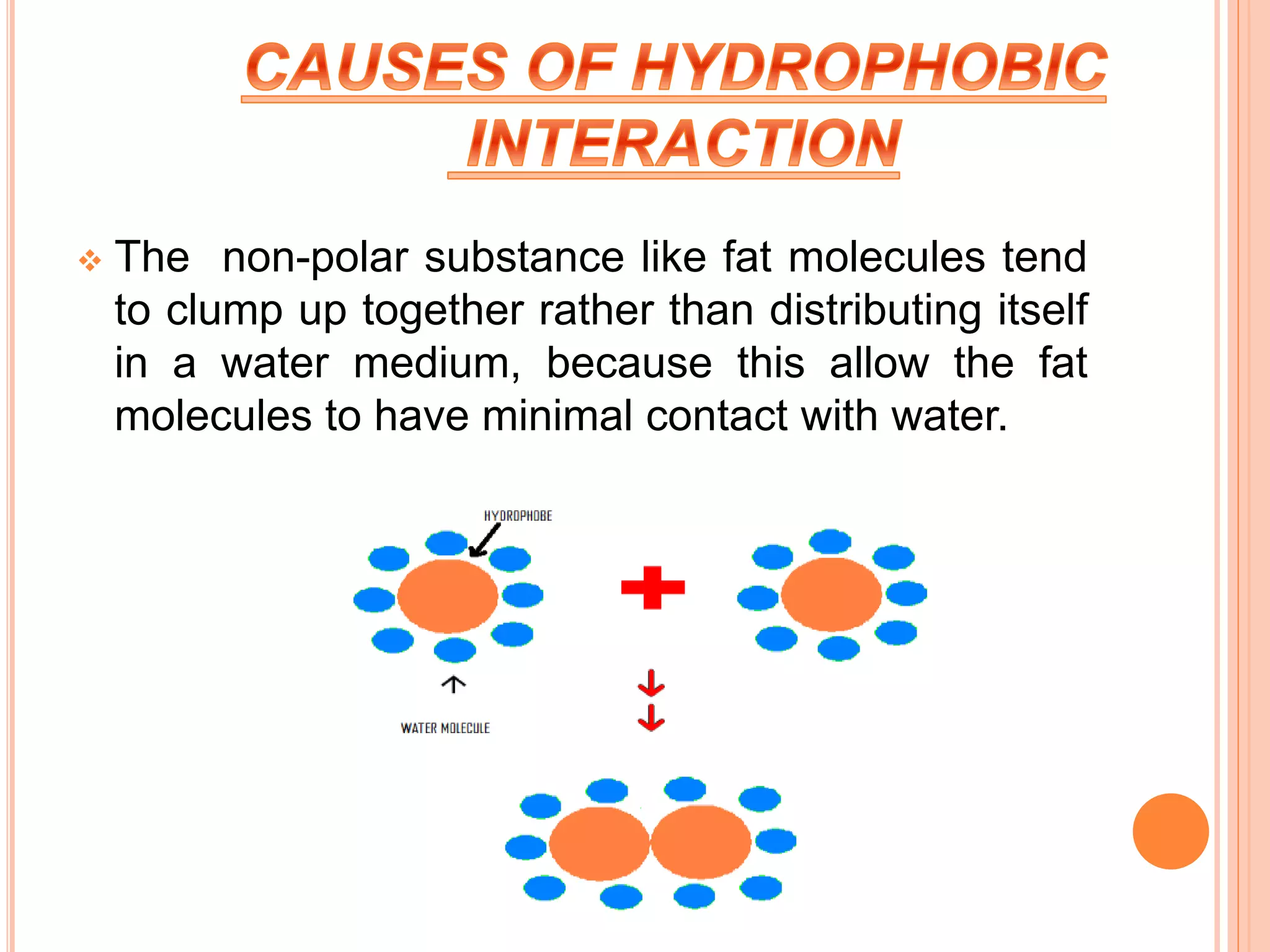
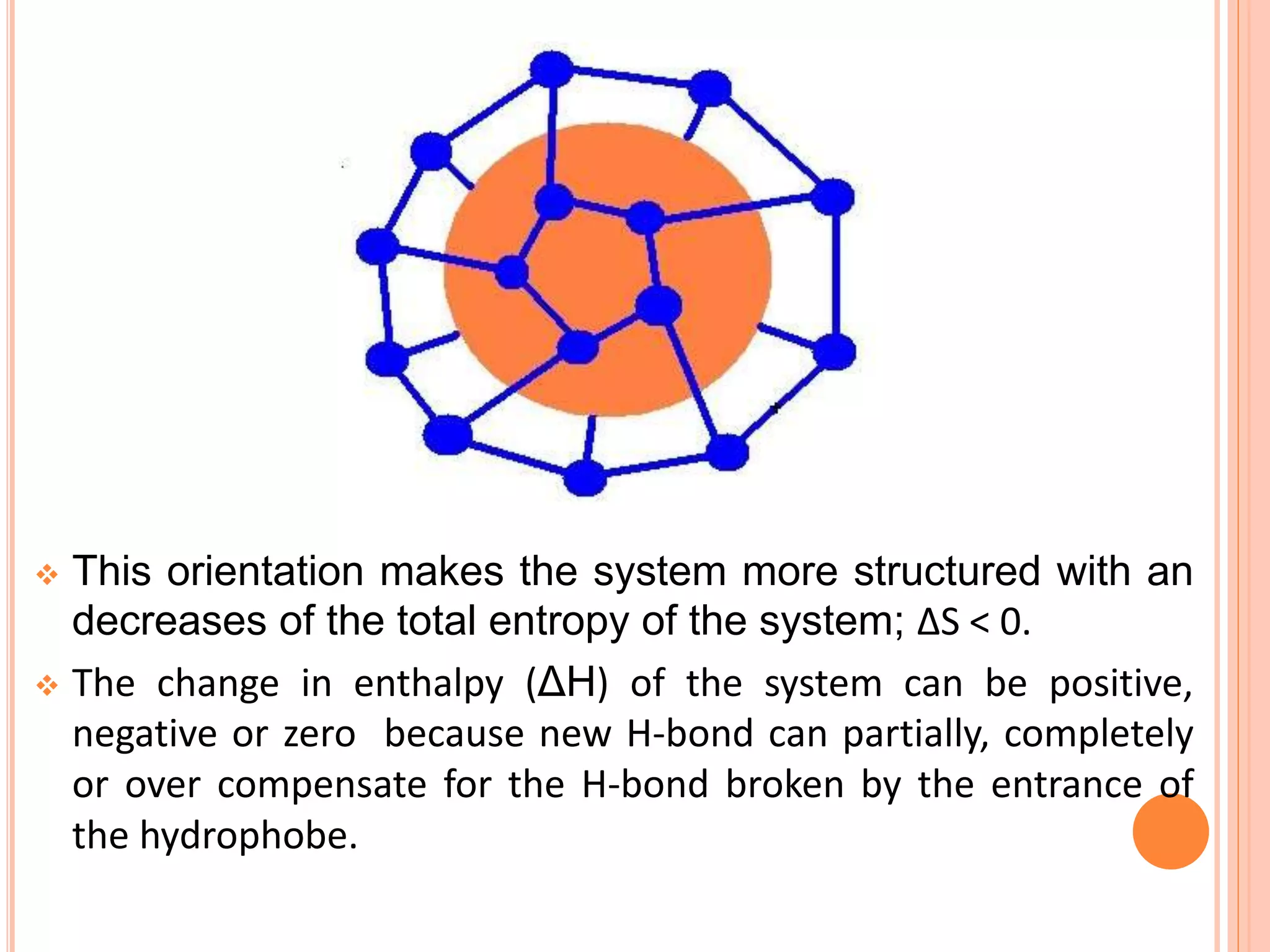
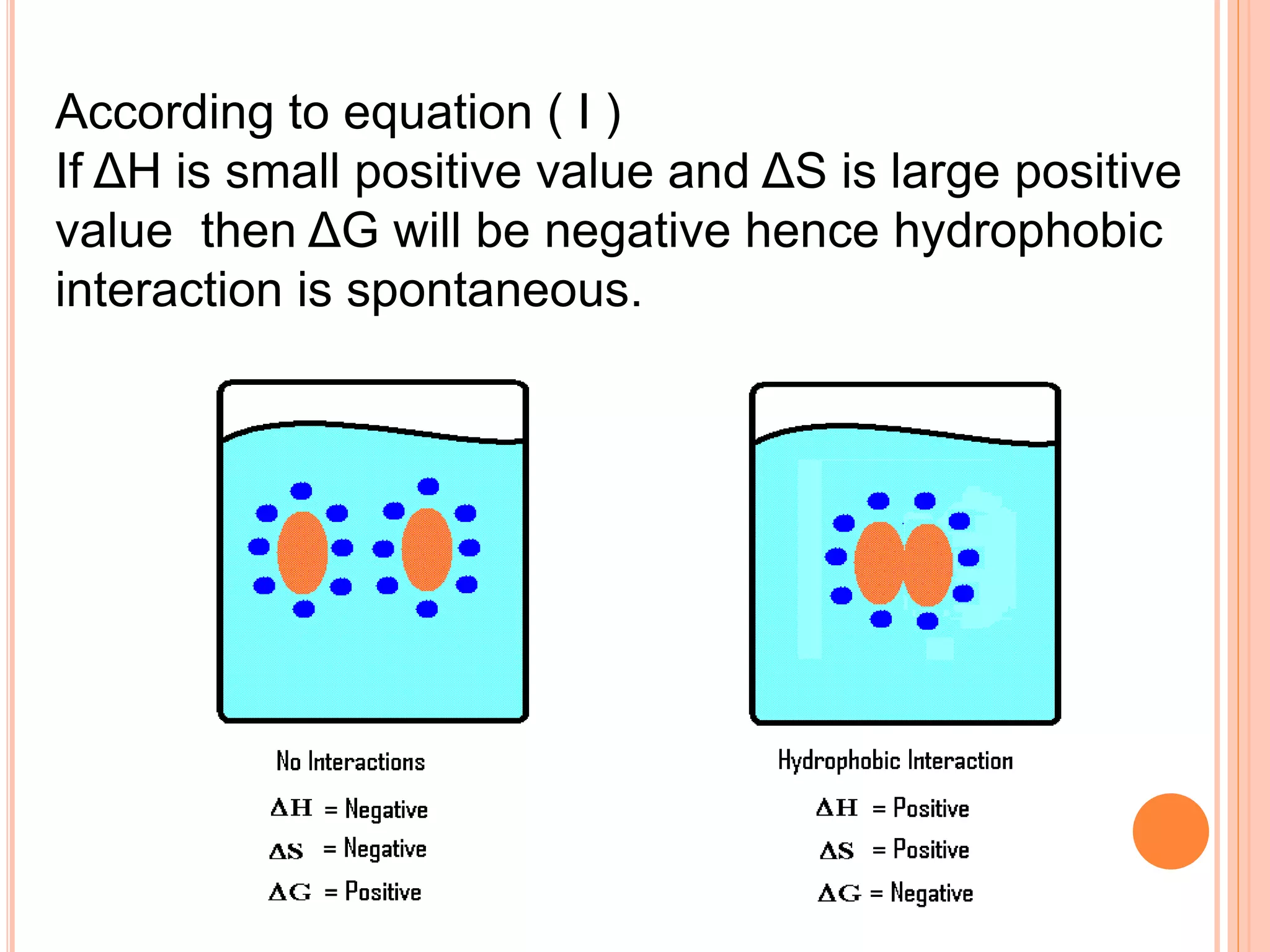
The document discusses hydrophobic interactions and effects. It defines hydrophobicity as molecules that do not interact well with water, such as nonpolar substances. When these molecules are introduced into water, they aggregate together to minimize contact with water molecules. This occurs because breaking hydrogen bonds between water and the hydrophobic molecules is entropically unfavorable. The hydrophobic effect is driven by this entropy change and causes nonpolar substances to cluster together in aqueous solutions.