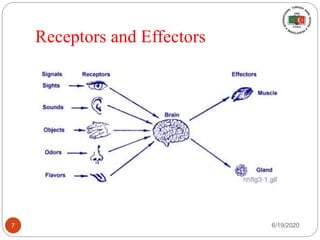
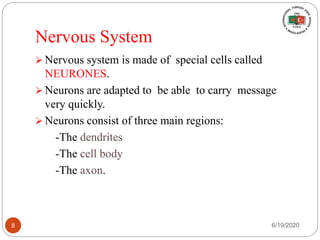
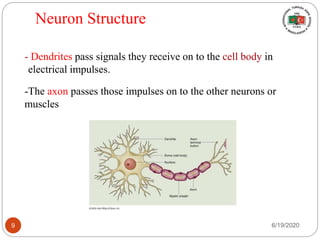
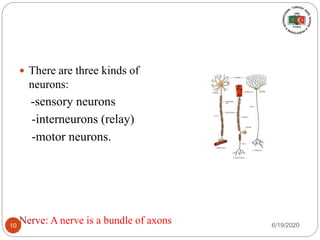
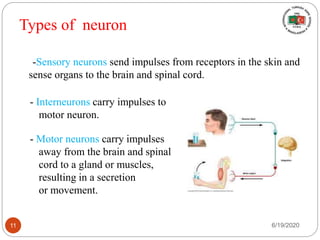
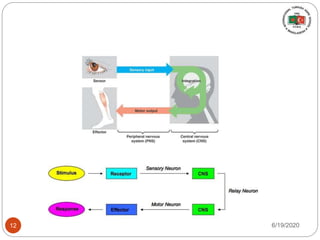
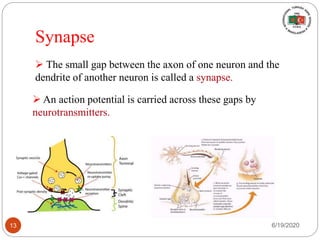
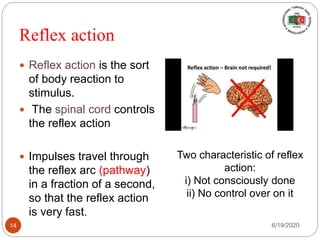
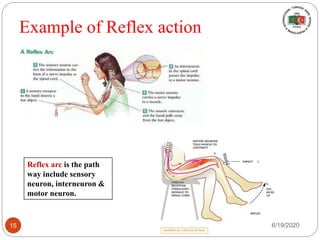
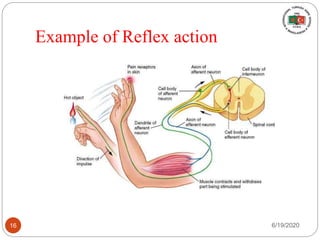
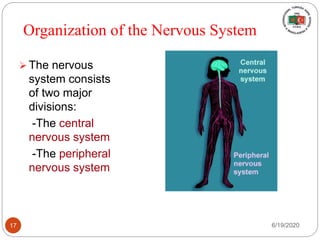
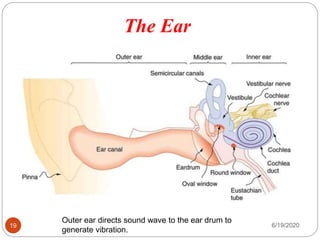
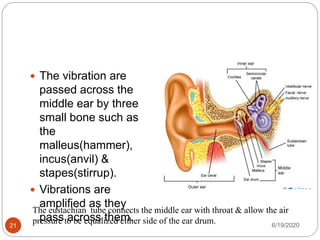
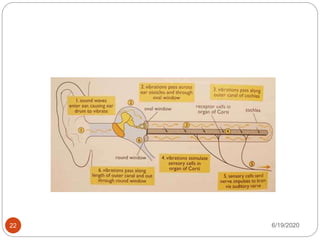
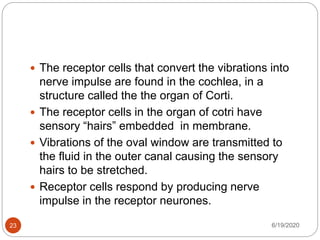
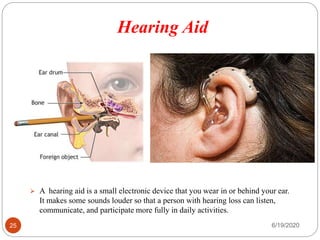
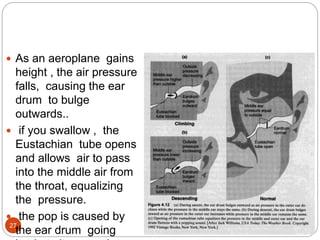
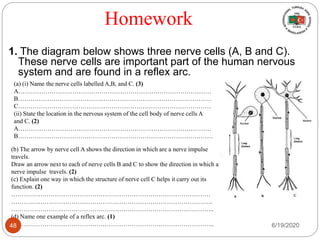
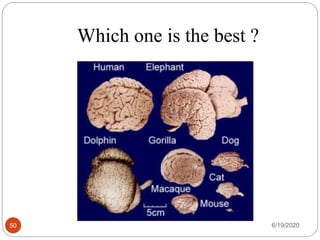
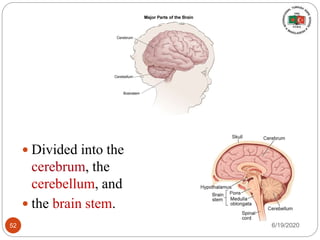
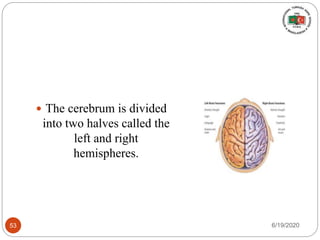
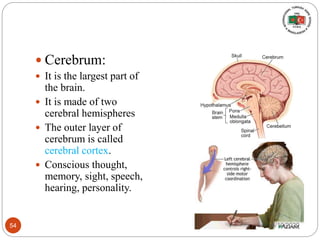
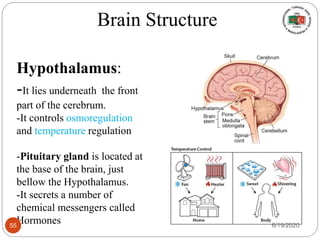
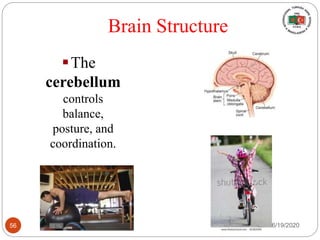
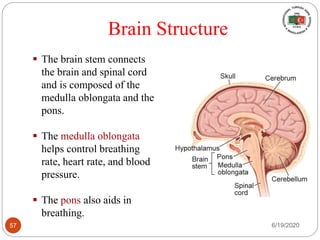
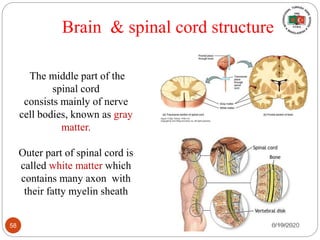
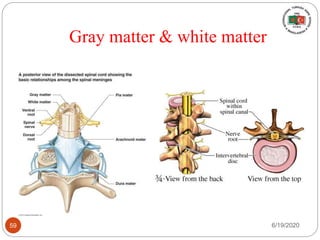
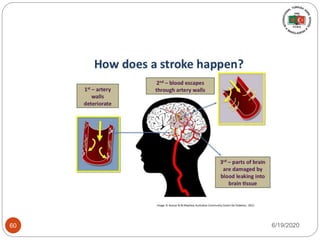
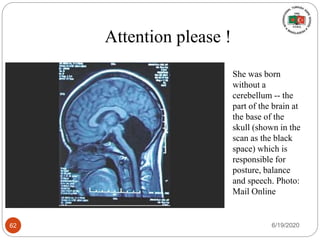
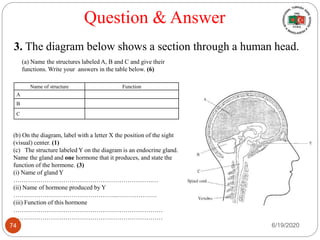
The document provides information about the structure and function of the human nervous system and brain. It discusses topics like stimuli and receptors, neurons, reflex action, and the organization of the central and peripheral nervous systems. It also describes the structure and function of key parts of the brain like the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem. Homework questions at the end ask students to label parts of neurons, explain reflex arcs, and identify structures of the brain.