This document provides a summary of key concepts in electricity including:
1. Electric current is the flow of electrons through a conductor measured in amperes. Current flows from the positive terminal to the negative terminal of a battery.
2. Potential difference is the difference in electric potential provided by a battery that causes electric current. It is measured in volts.
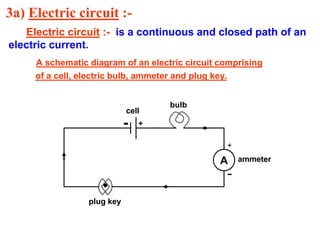
3. An electric circuit is a continuous loop through which electric current can flow, including components like batteries, wires, switches, and resistors.