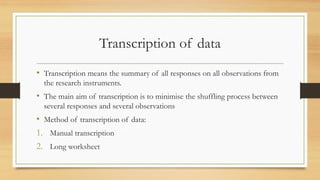
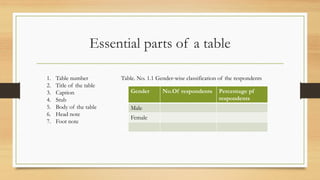
This document discusses the process of data processing. It defines data processing as the intermediary stage between data collection and data interpretation. The key steps in data processing include identifying the data structure, editing the data, coding and classifying the data, transcribing the data, and tabulating the data. These steps prepare the raw data for meaningful analysis and interpretation to test research hypotheses. Proper data processing requires advance planning and defines the variables and relationships between them.