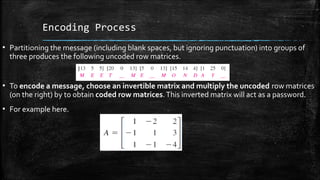
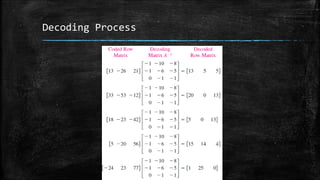
The document discusses the concept of matrices as rectangular arrangements of elements, highlighting their applications in various fields such as engineering, genetics, and cryptography. It explains how matrices can be used to encode and decode messages through a systematic process involving matrix multiplication. The encoding and decoding procedures require the use of an invertible matrix, where authorized receivers can easily decrypt messages by applying the inverse of the encoding matrix.