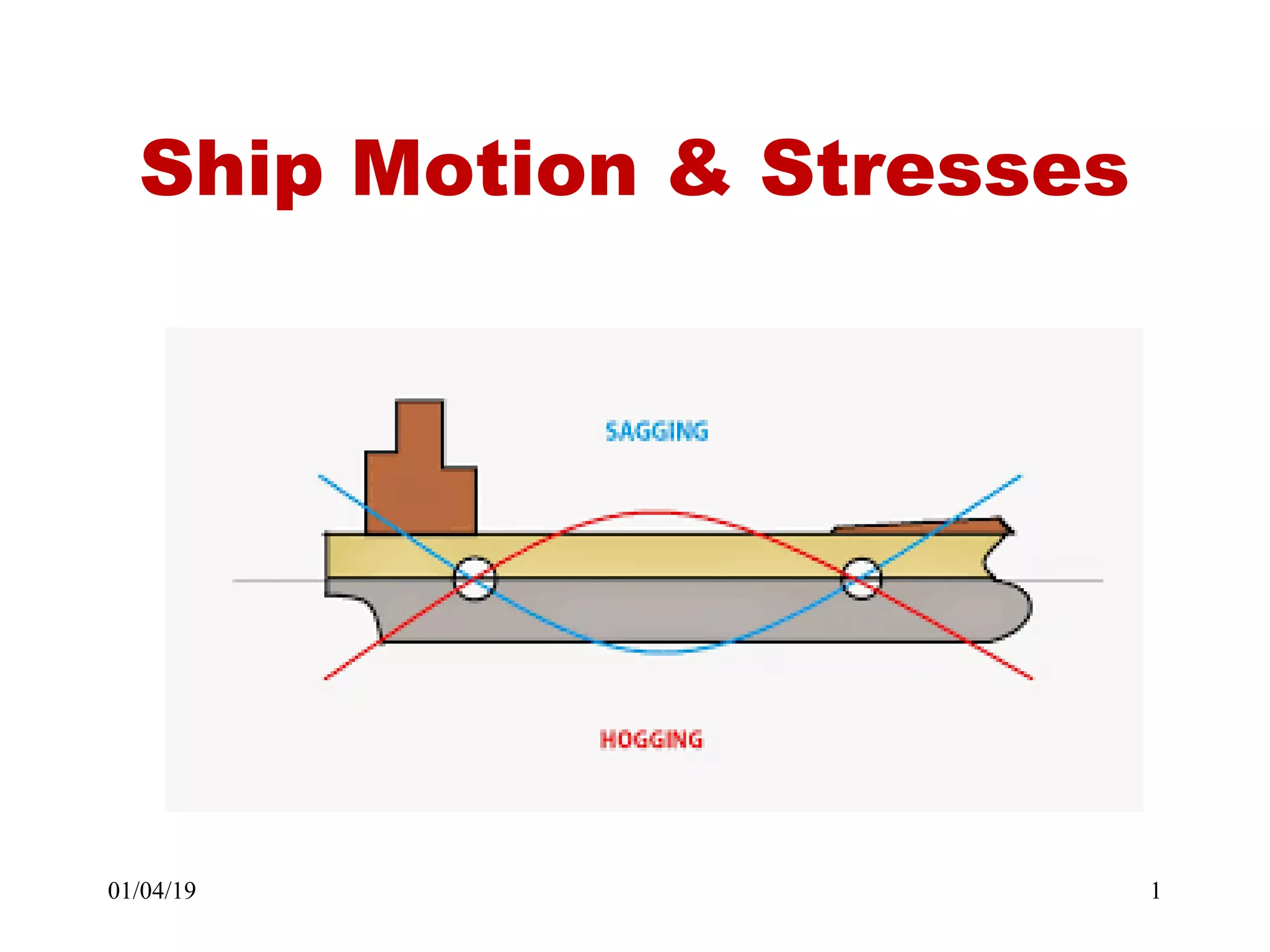
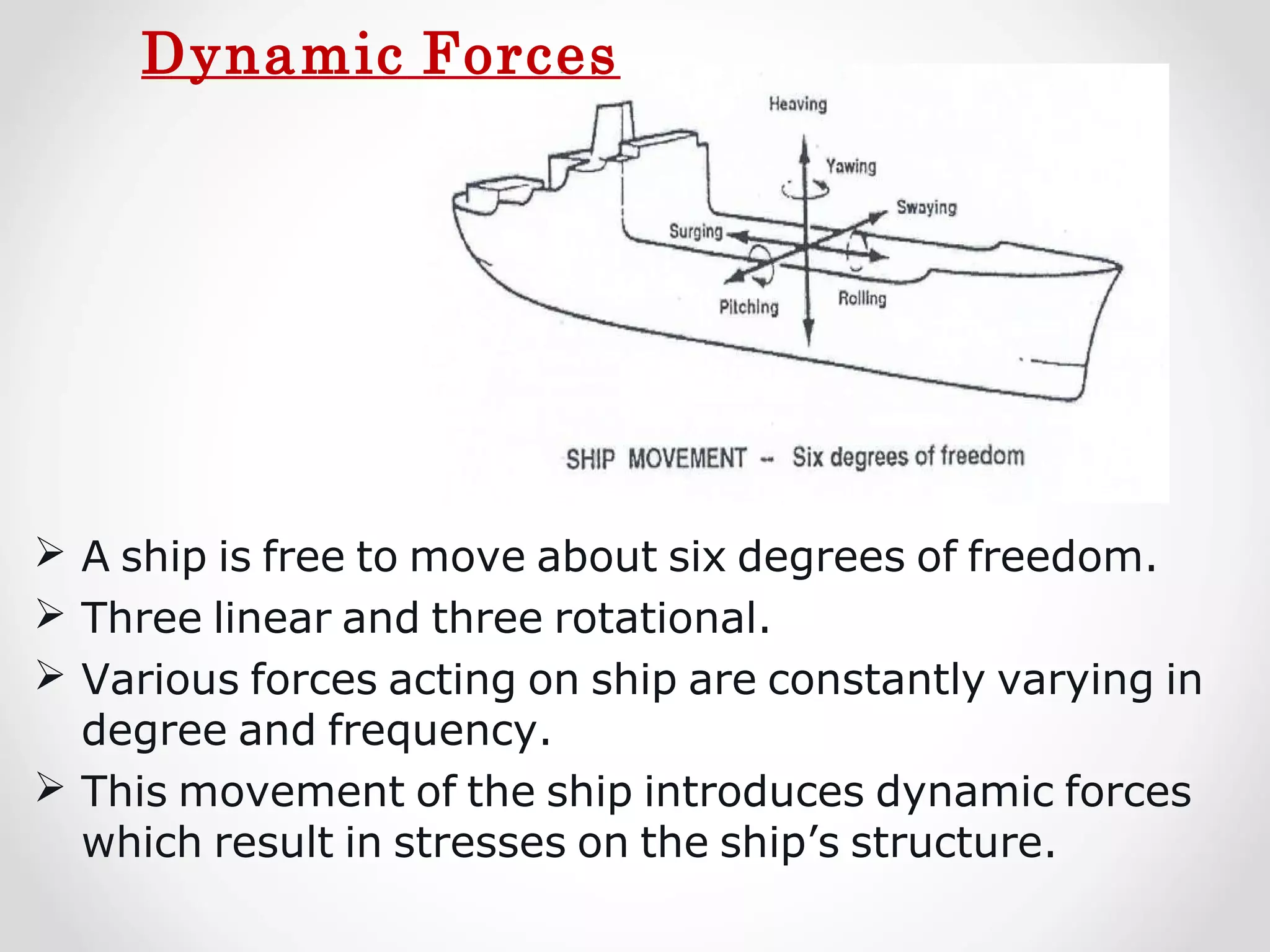
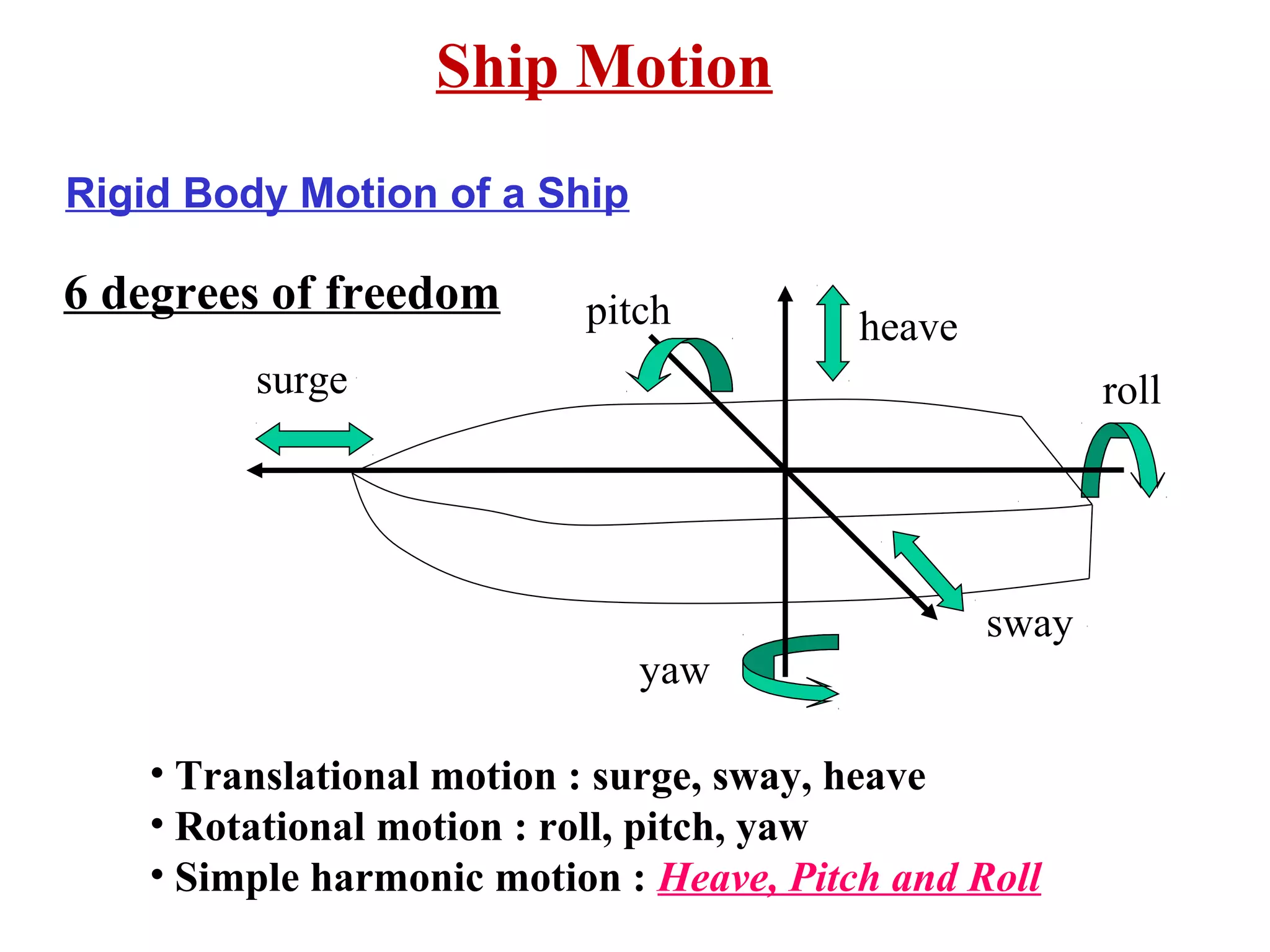
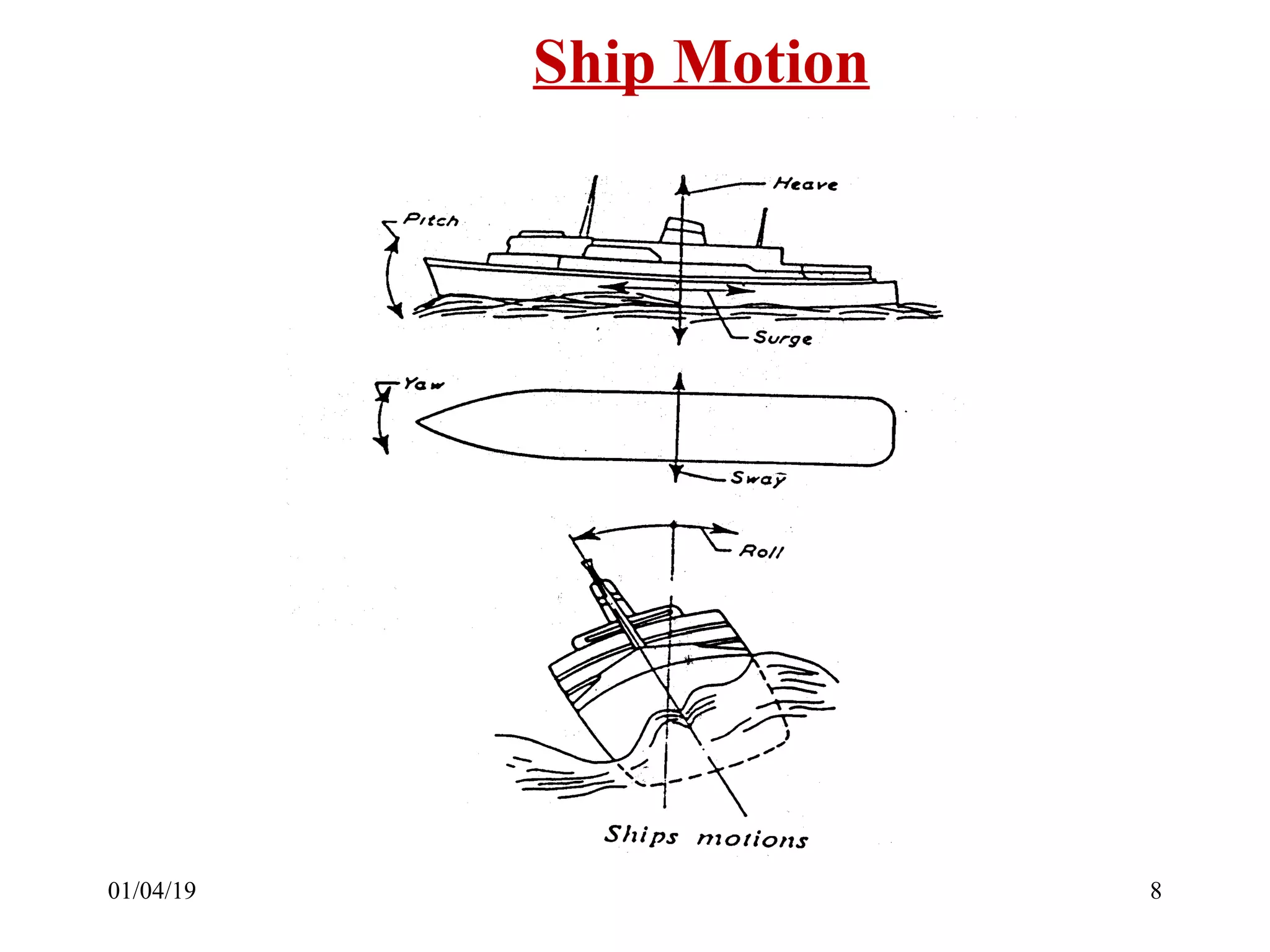
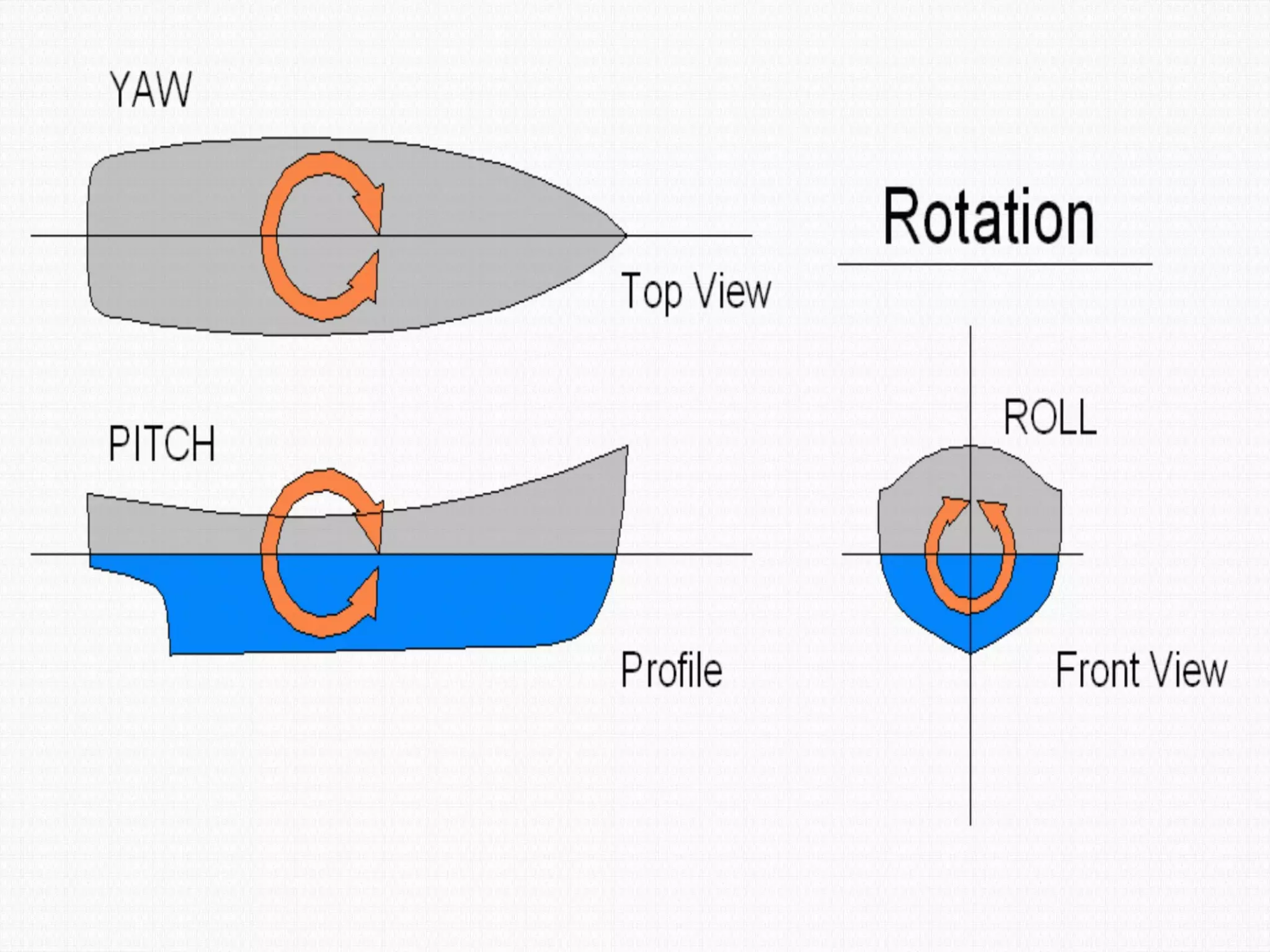
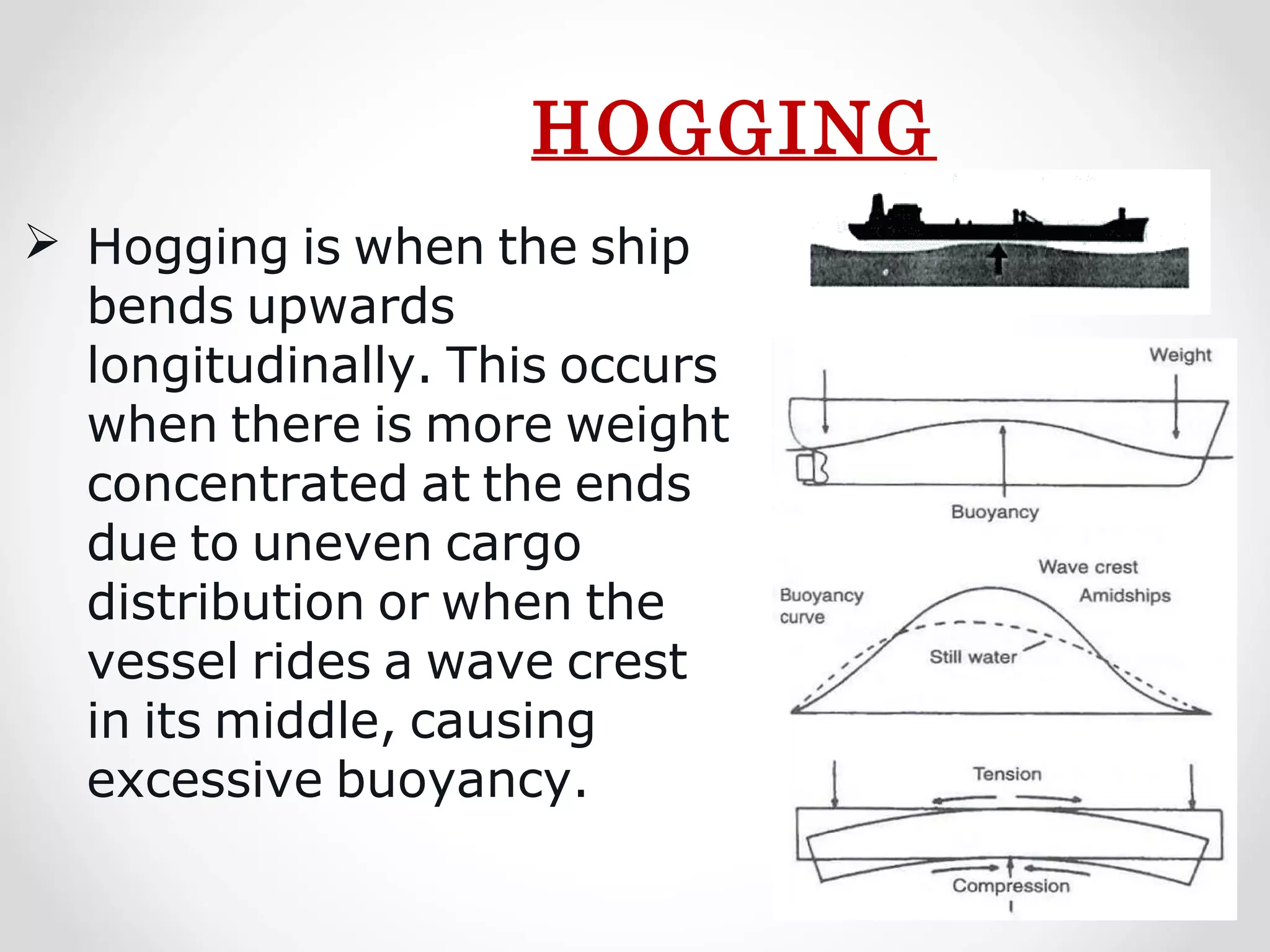
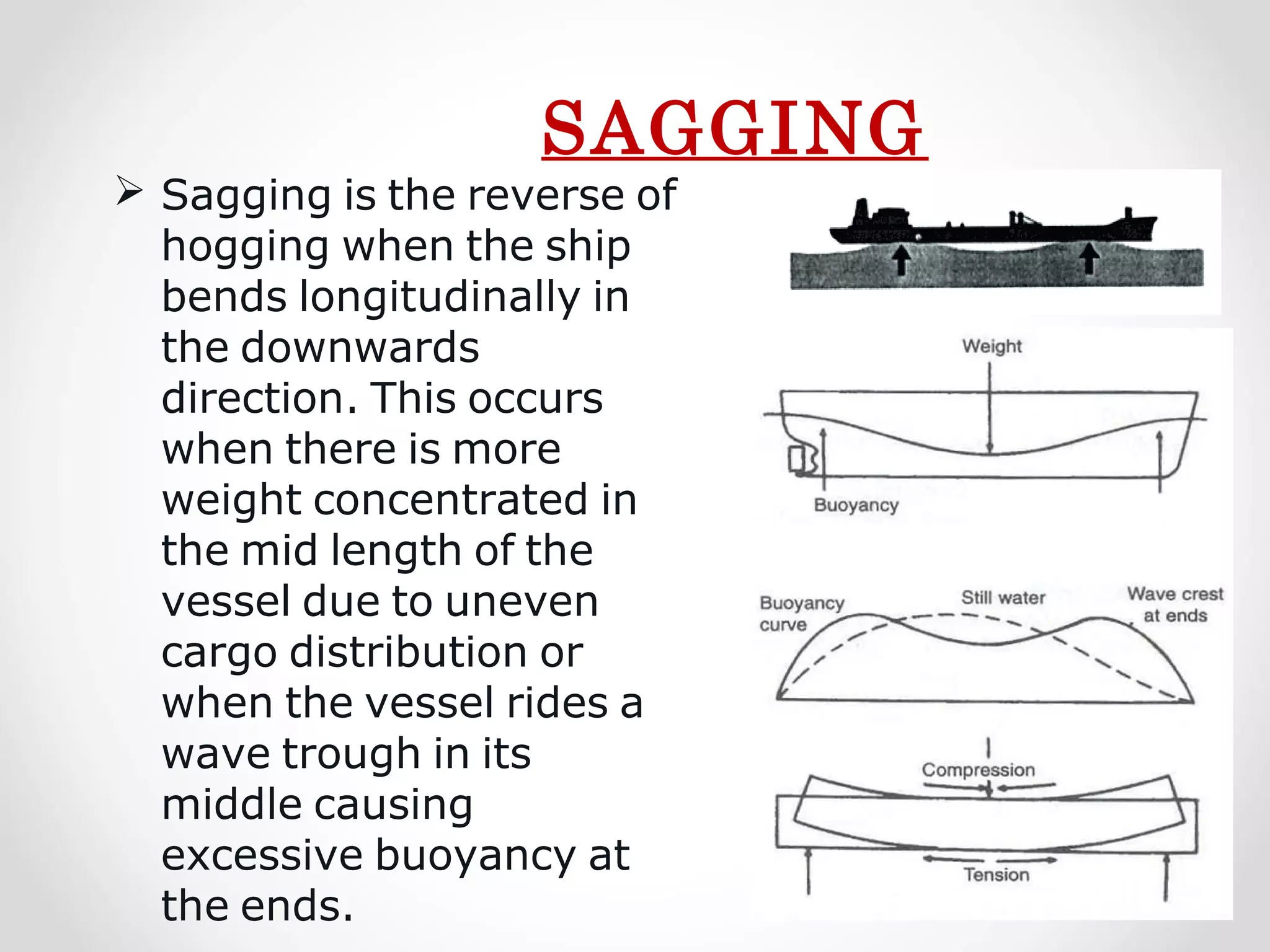
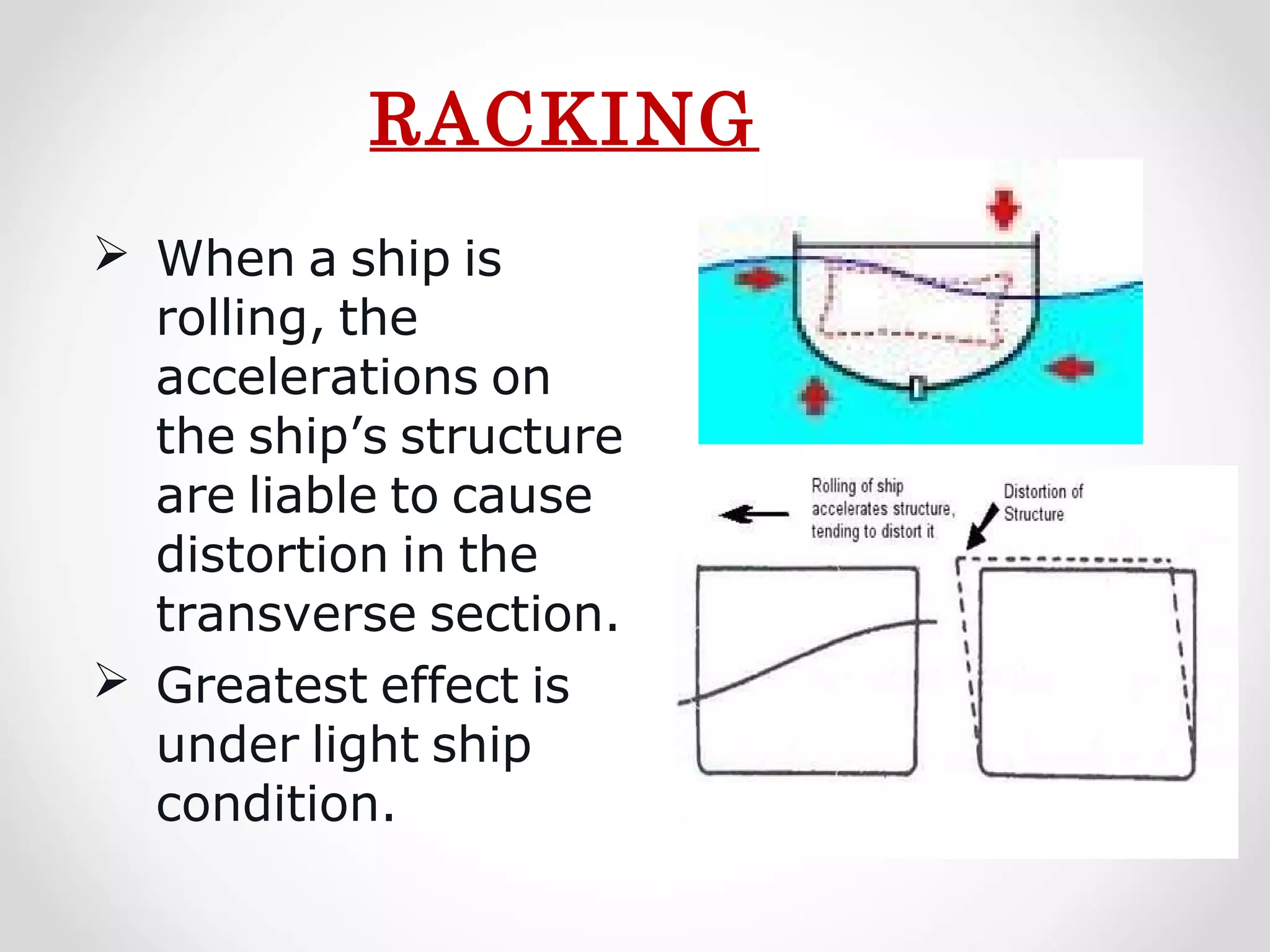
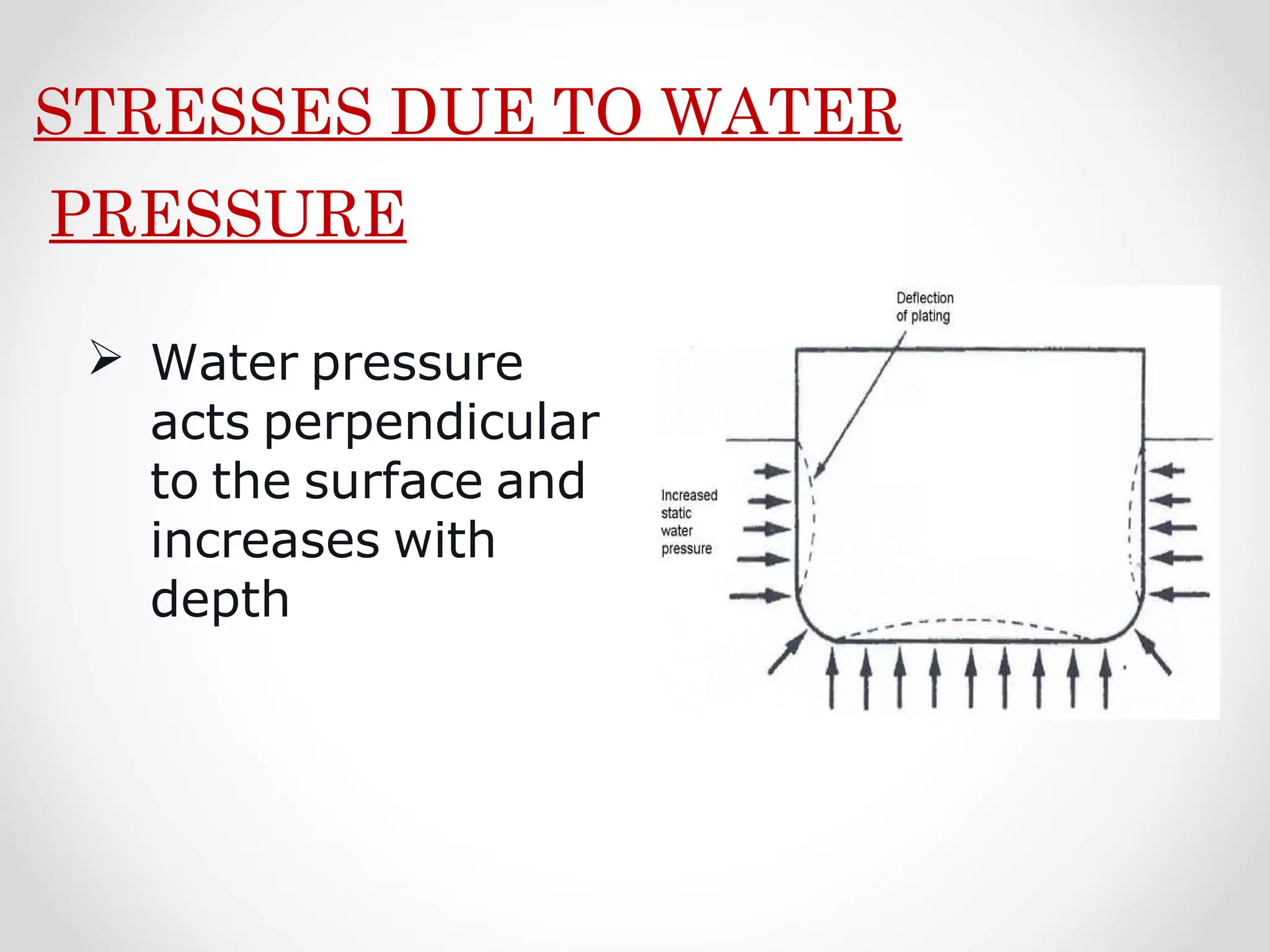
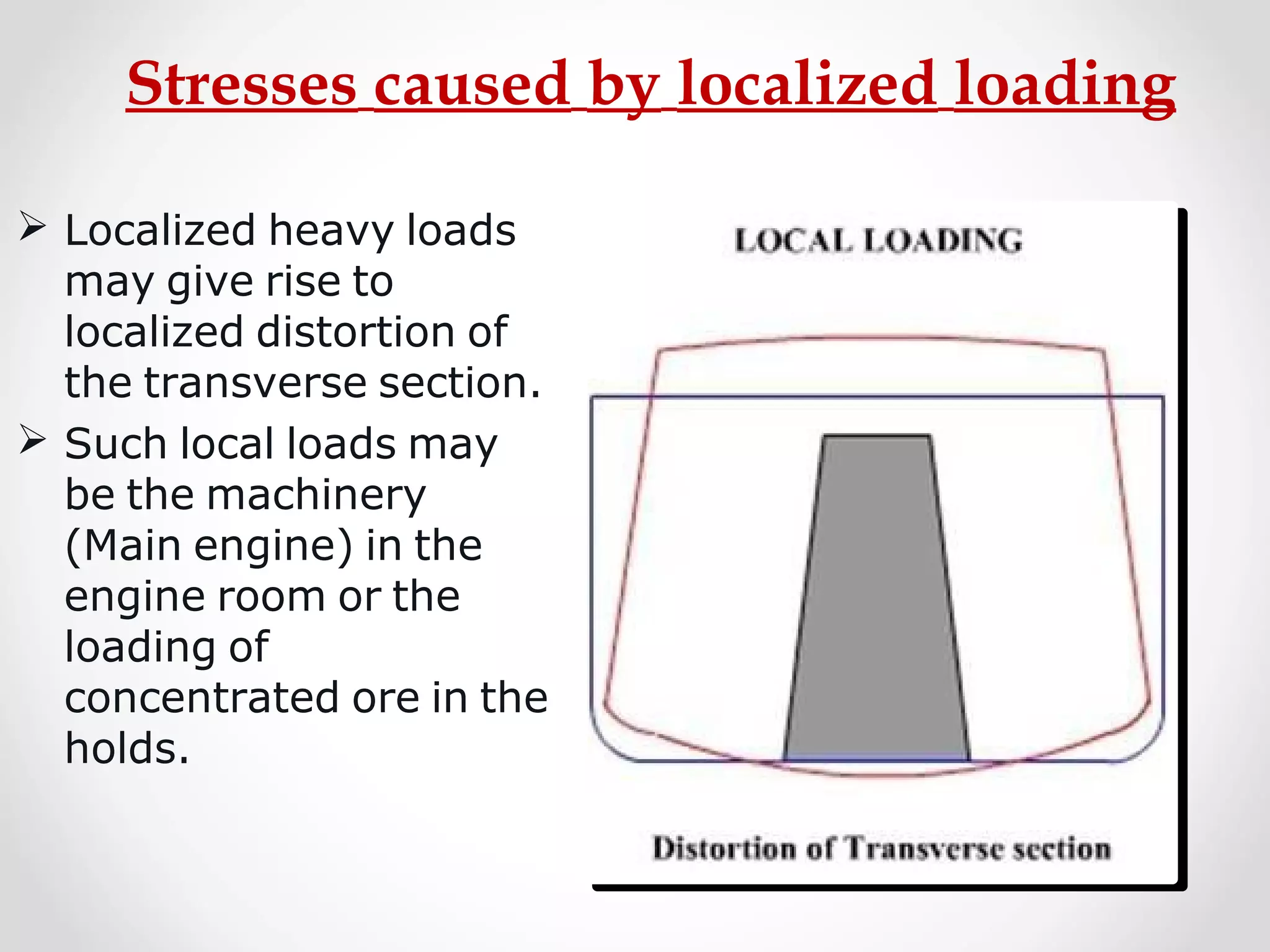
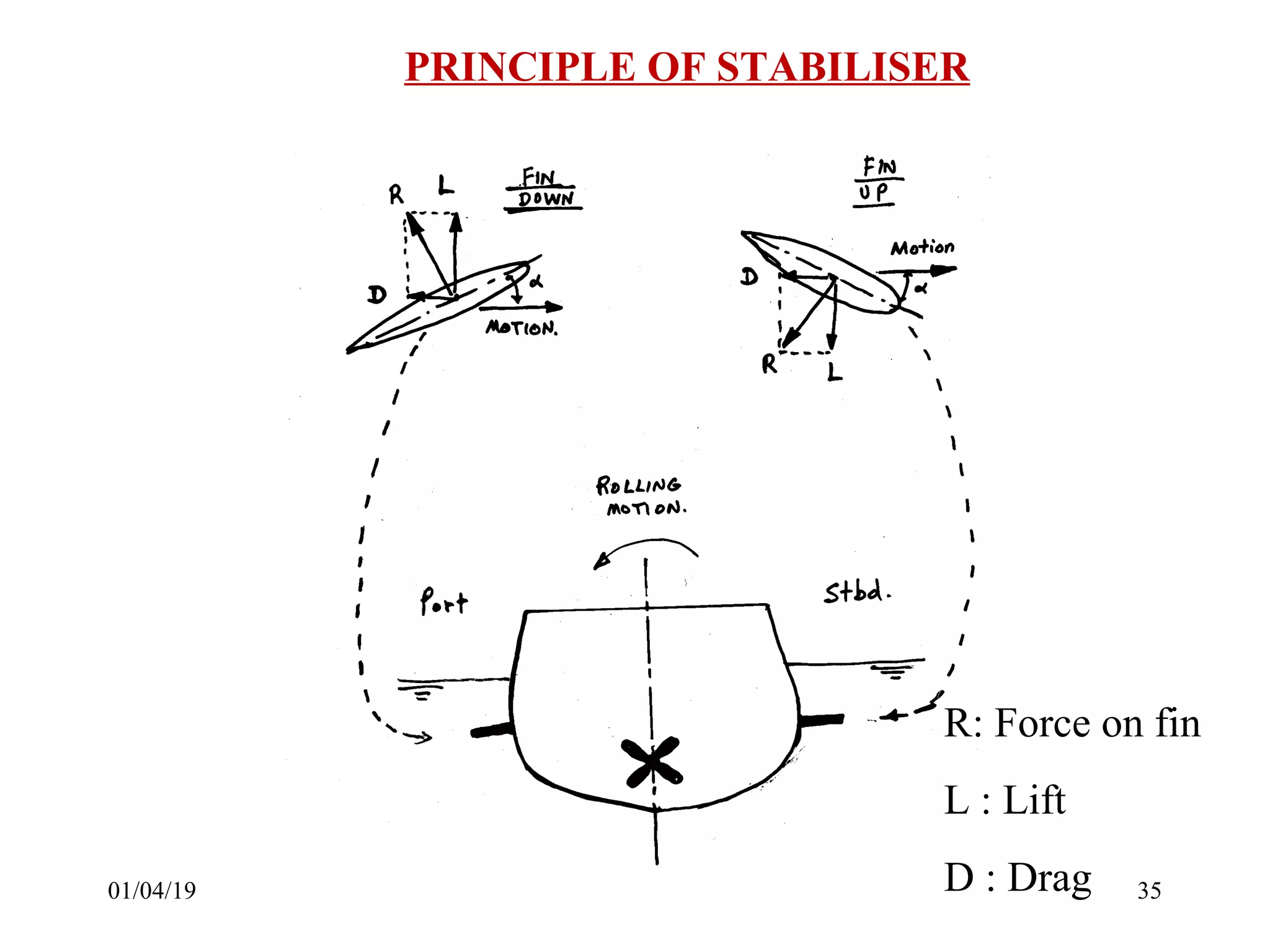
Static forces on a ship include internal forces from structural weight and cargo and external static forces from hydrostatic pressure. Dynamic forces result from ship motion at sea, wind and waves, and operating machinery. A ship has six degrees of freedom of motion: rolling, surging, pitching, swaying, heaving, and yawing. Ship motion introduces dynamic forces that cause stresses on the ship's structure. Methods to reduce rolling include bilge keels, passive tanks, controlled passive tanks, active tanks, and fin stabilizers.