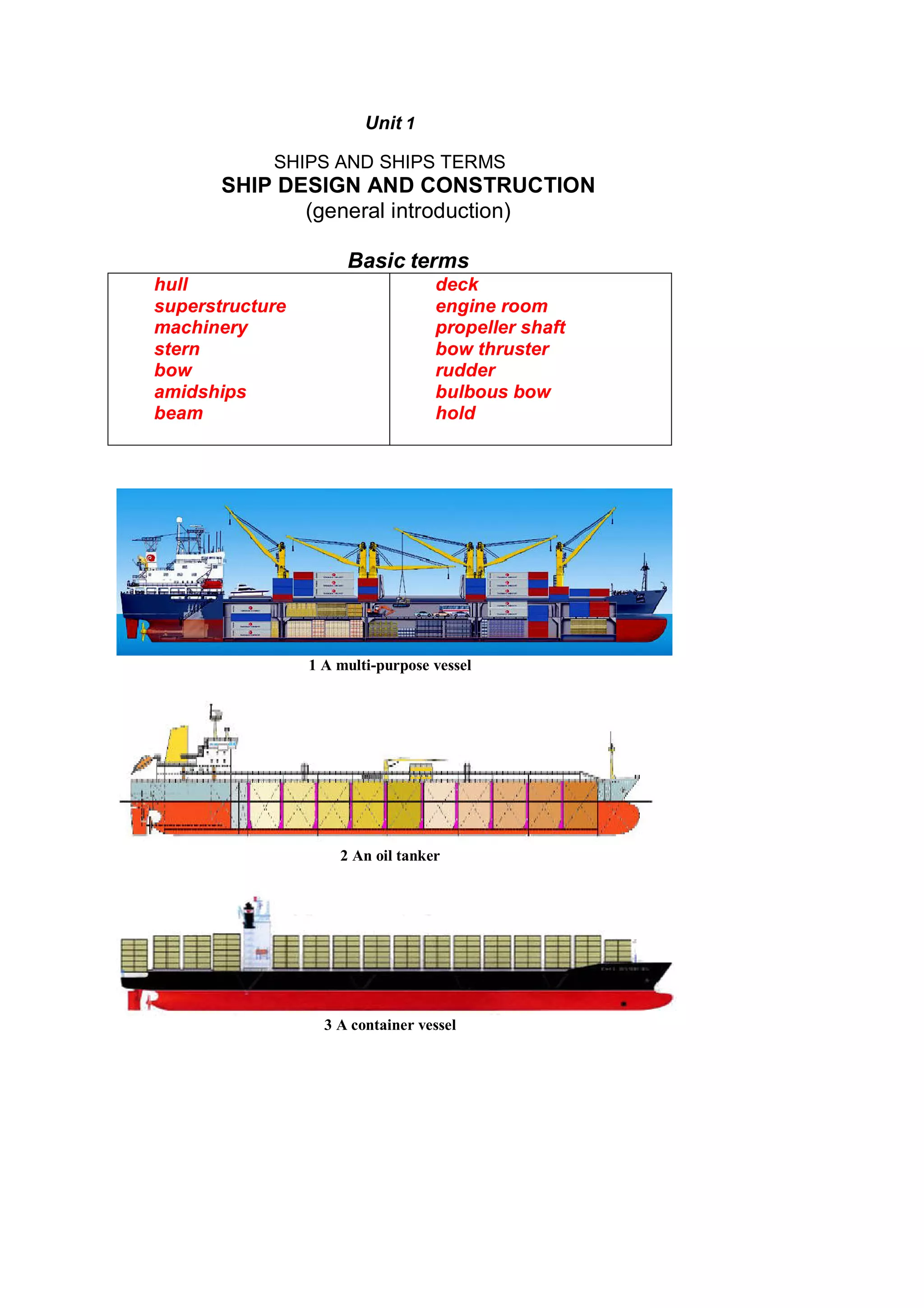
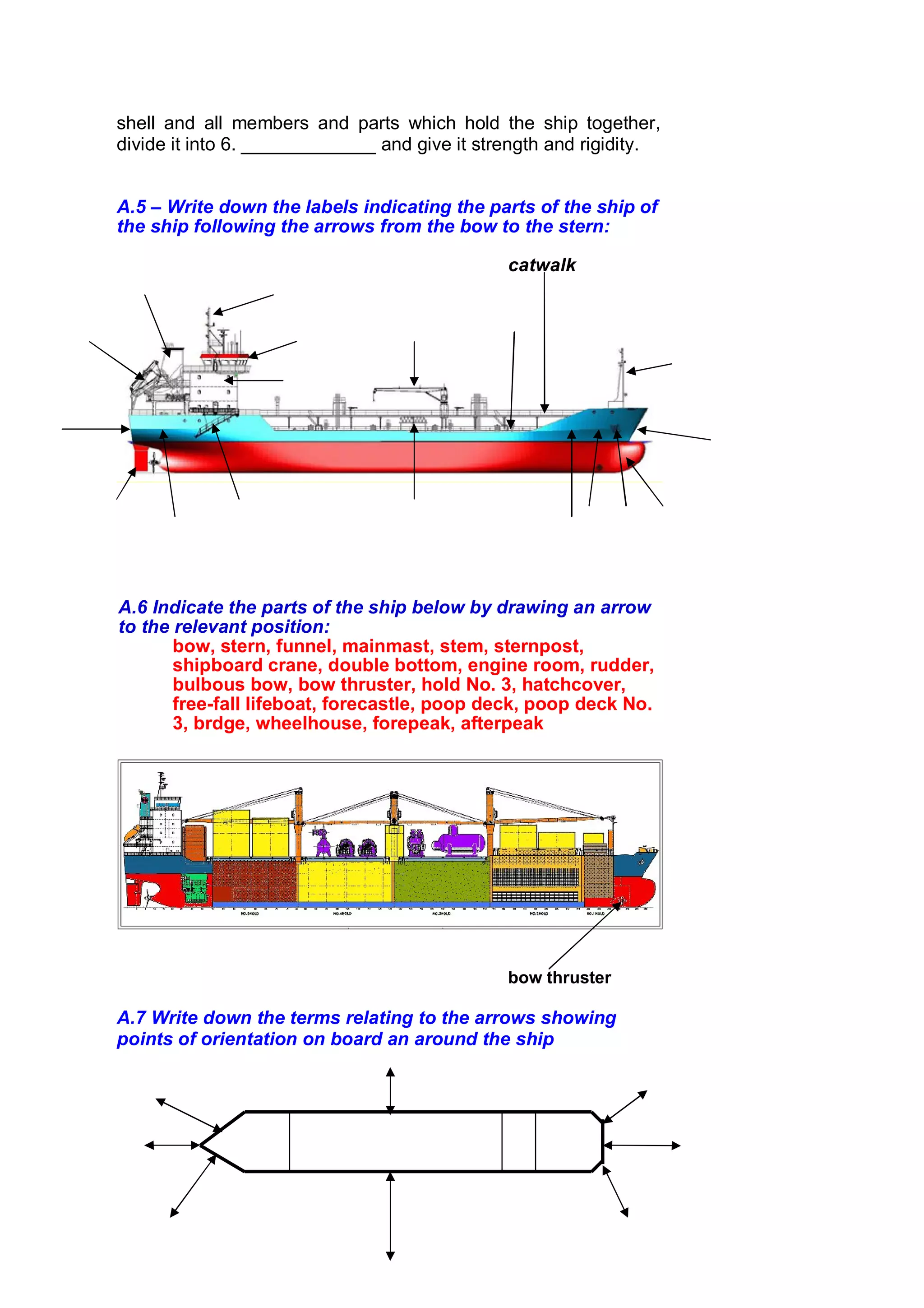
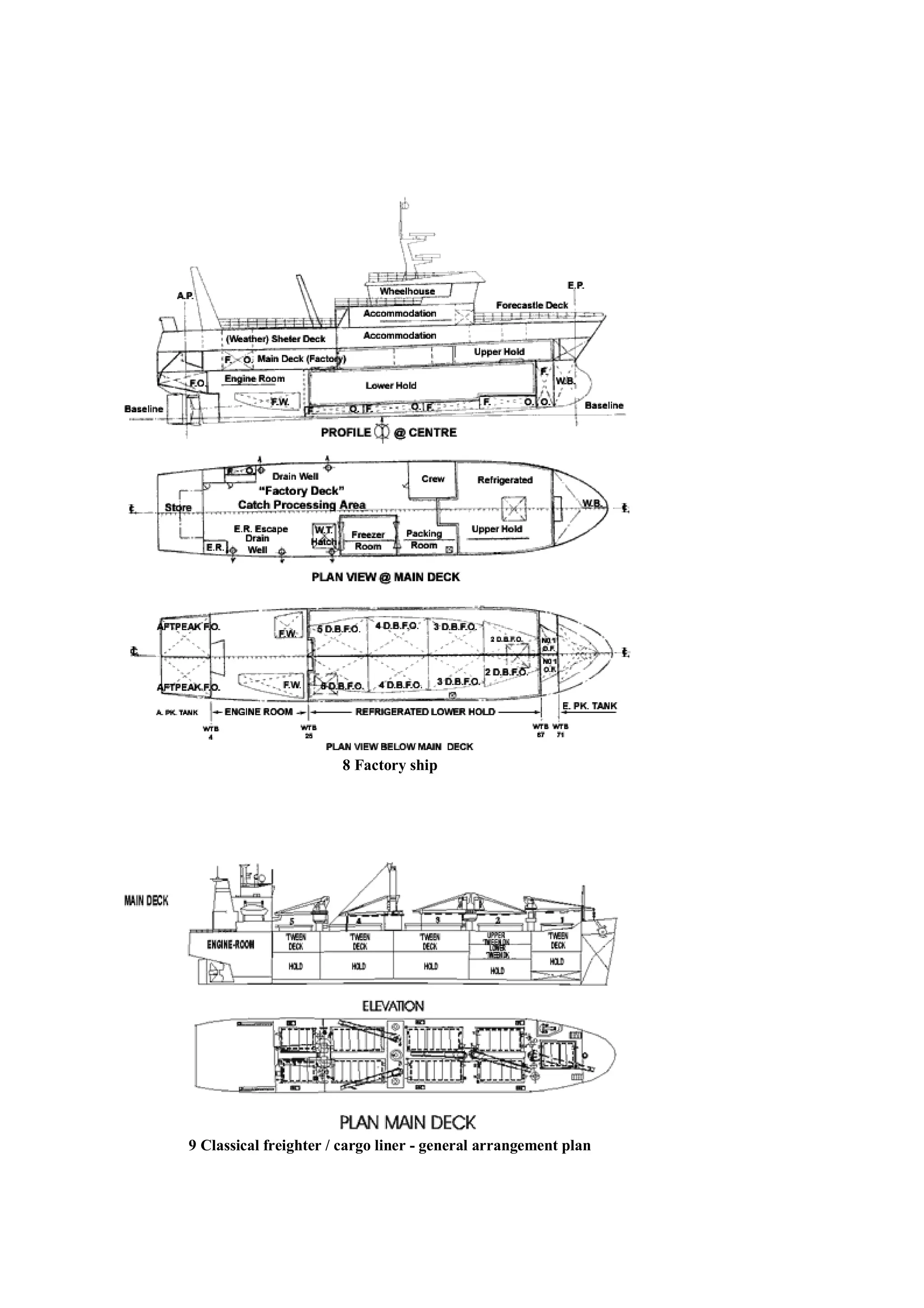
The document provides information about ship design and construction. It defines common ship terms like hull, superstructure, machinery, stern, bow, amidships, beam, deck, engine room, propeller shaft, bulbous bow, hold. It describes the roles of the naval architect, navigating officer and marine engineer in ship design. It explains the two main parts of a ship are the hull and machinery. It provides details about locations on a ship like stern, bow, amidships and common directional terms. It also describes ship types and general arrangements depending on intended cargo and trade.