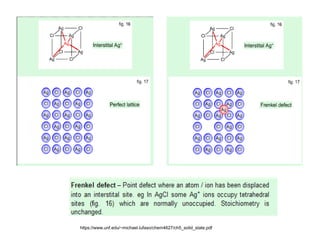
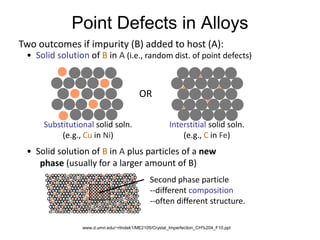
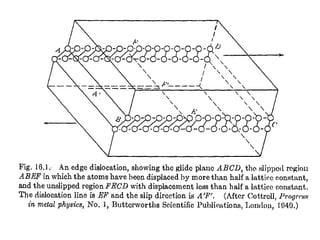
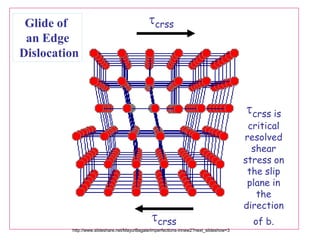
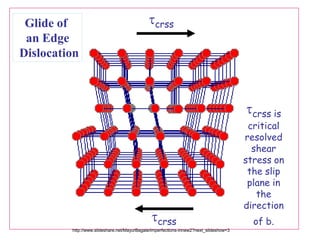
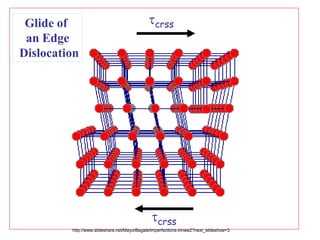
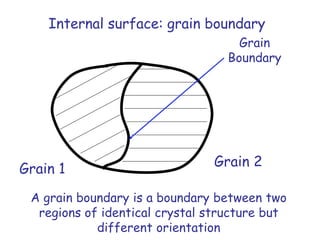
Defects in solids can be classified based on their dimensionality. Point defects are zero-dimensional and include vacancies, impurities, and Frenkel and Schottky defects. Line defects are one-dimensional and include dislocations. Surface and interface defects are two-dimensional, including grain boundaries. Three-dimensional defects include twins and precipitates. Dislocations are linear defects associated with mechanical deformation that influence properties like strength. Grain boundaries separate crystalline regions with different orientations.