Embed presentation
Downloaded 98 times


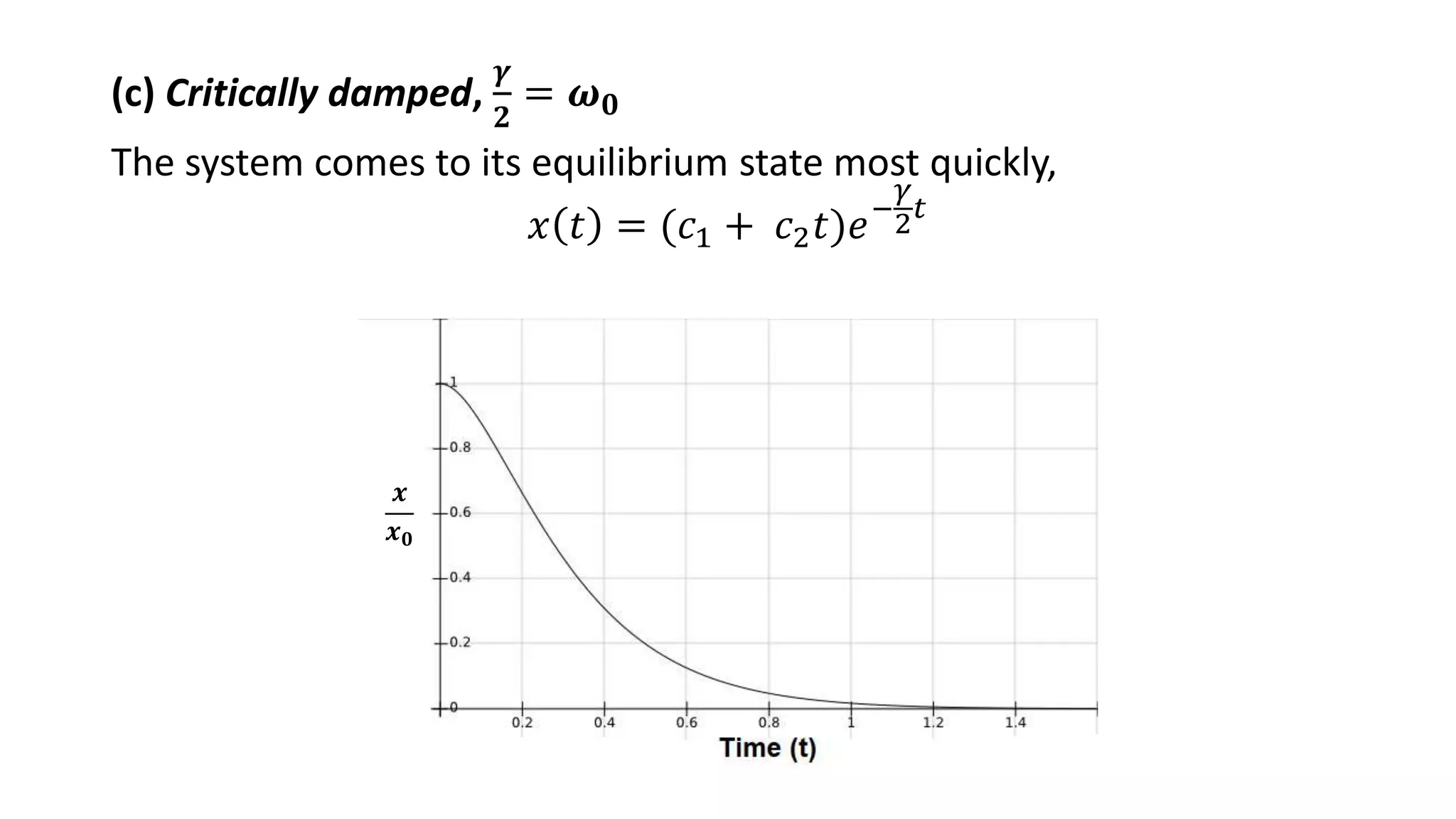




The document discusses the concepts of simple and damped harmonic oscillators, detailing their equations of motion and solutions. It categorizes damped oscillators into three types: overdamped, underdamped, and critically damped, each with distinct behavior in relation to equilibrium states. Additionally, it highlights the application of damped oscillators in systems such as car suspension.
Introduction to damped and simple harmonic oscillators, methods of dampening, and applications.
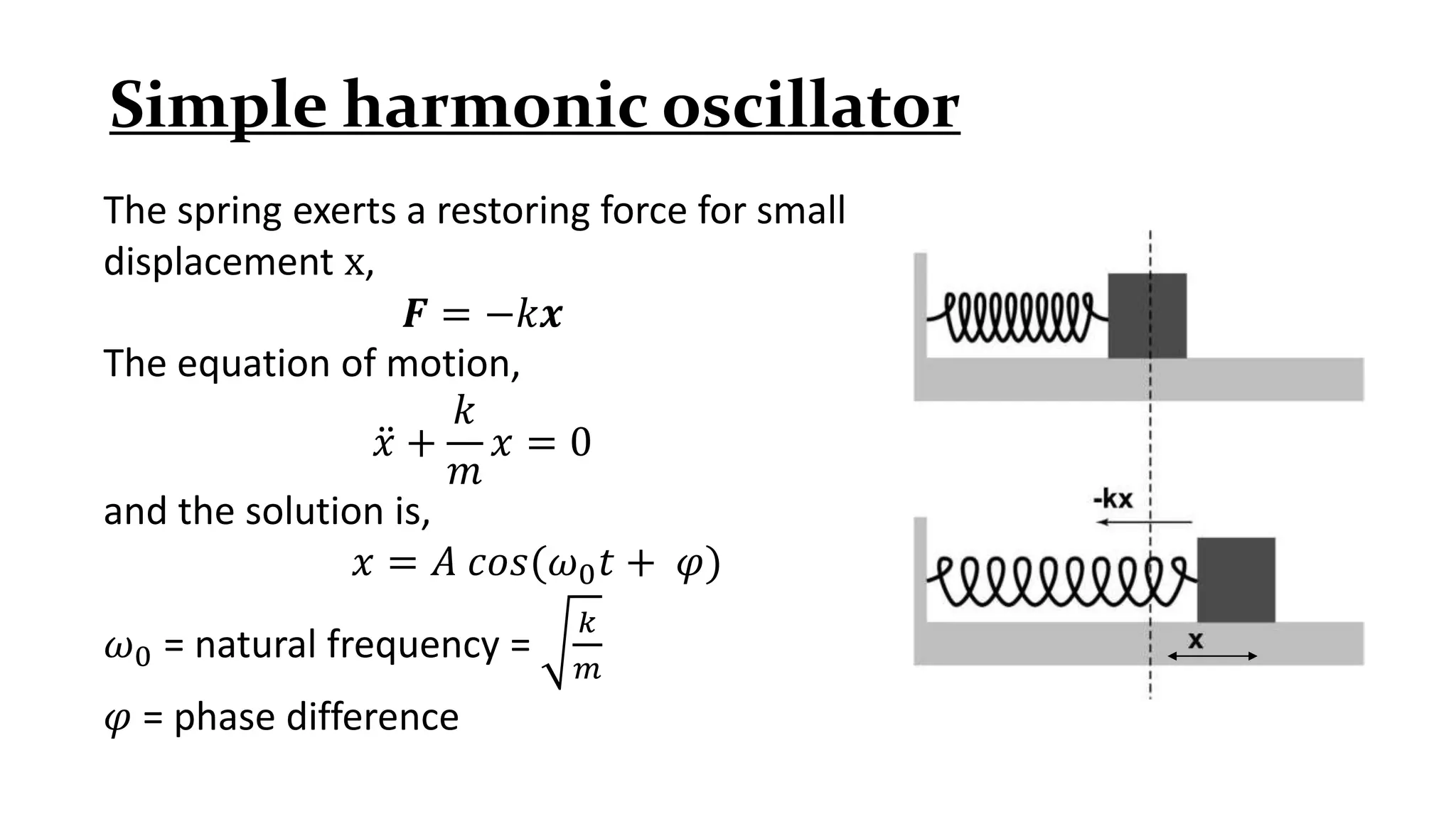
Explains simple harmonic oscillation, restoring forces, equations of motion, and natural frequency.
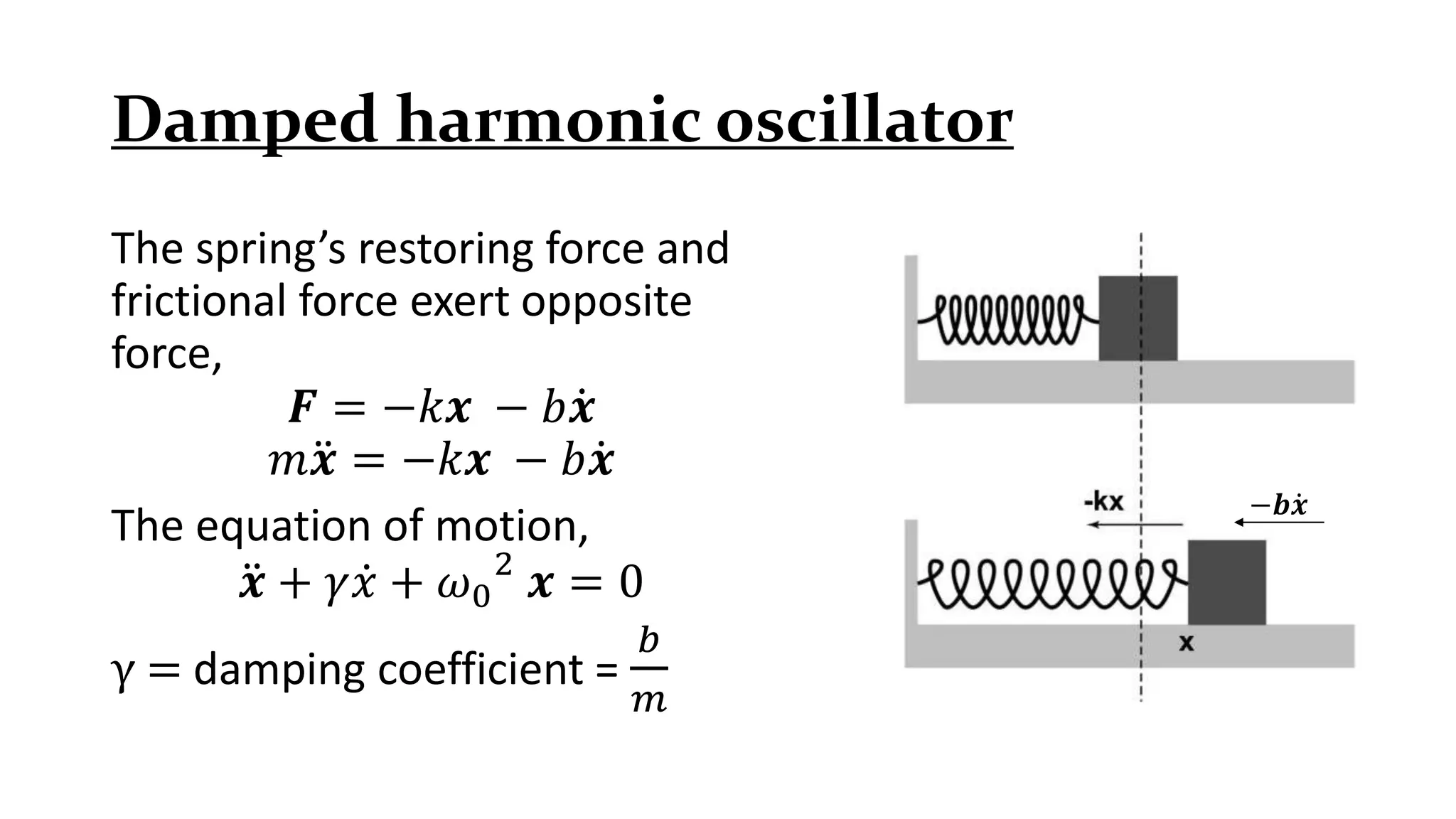
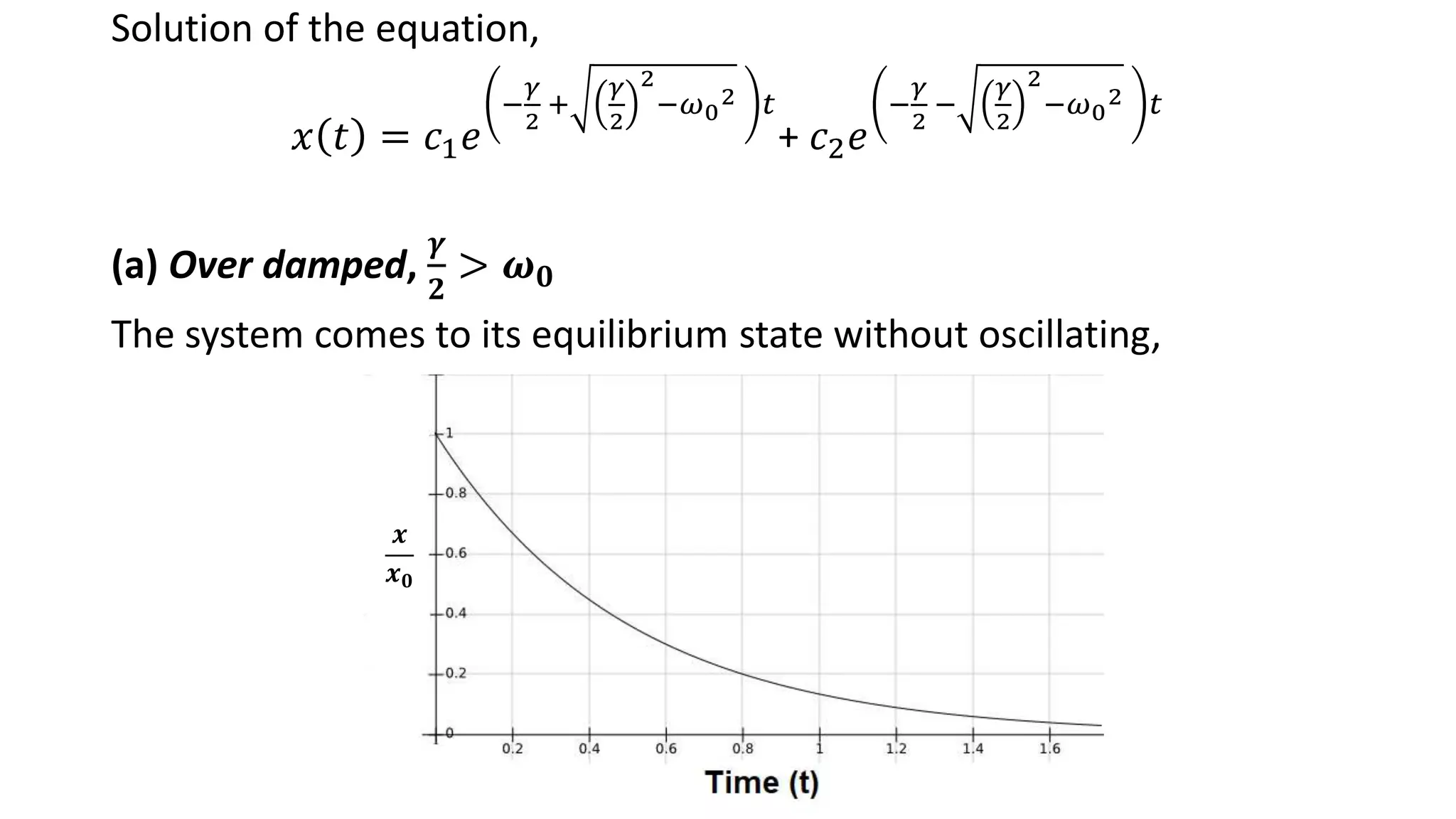
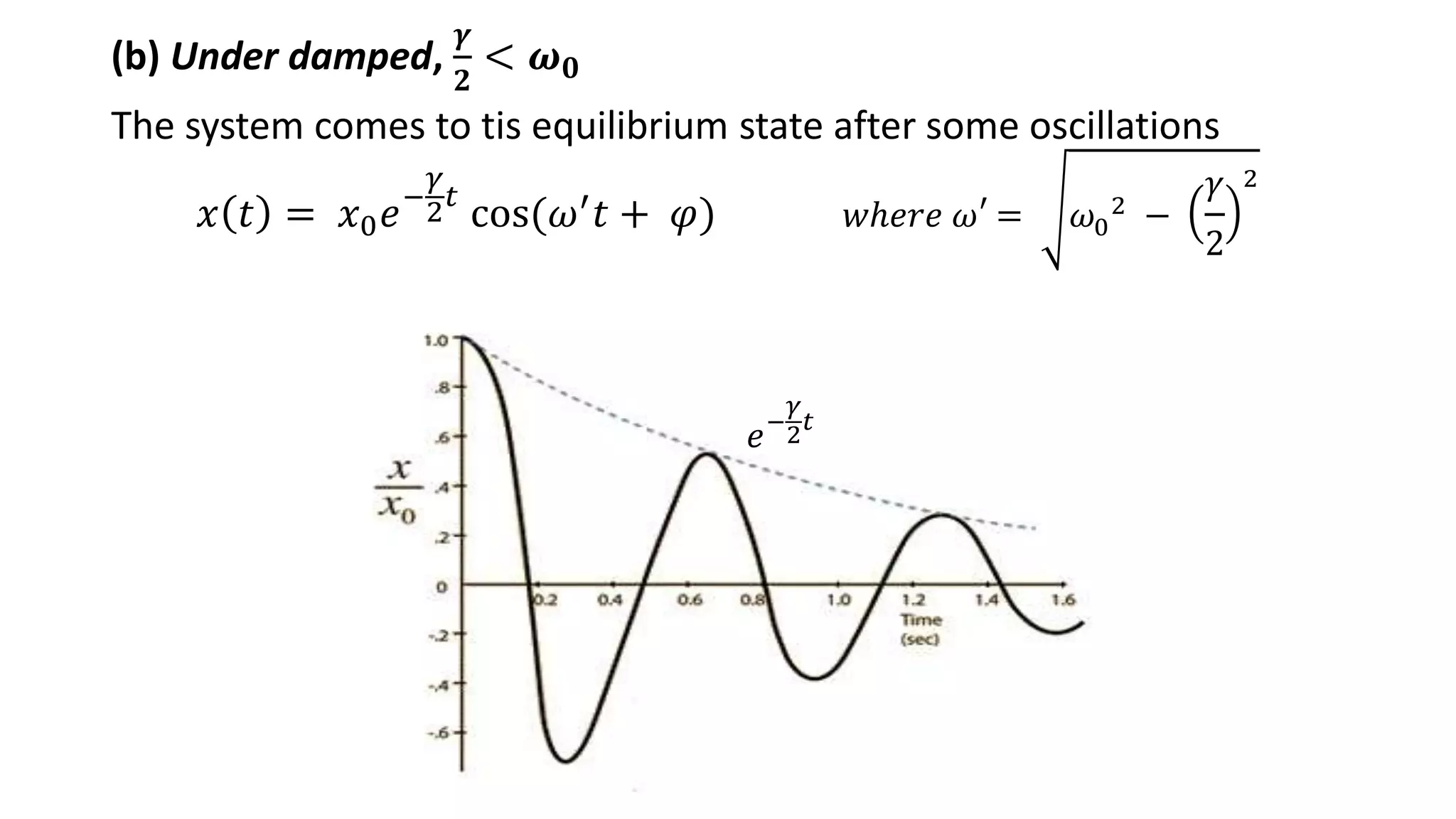
Details on damped harmonic oscillators, types: over damped, under damped, critically damped, and their mathematical solutions.
Discusses the practical application of damped harmonic oscillators, specifically in car suspension systems.
Closing remarks and thank you.










