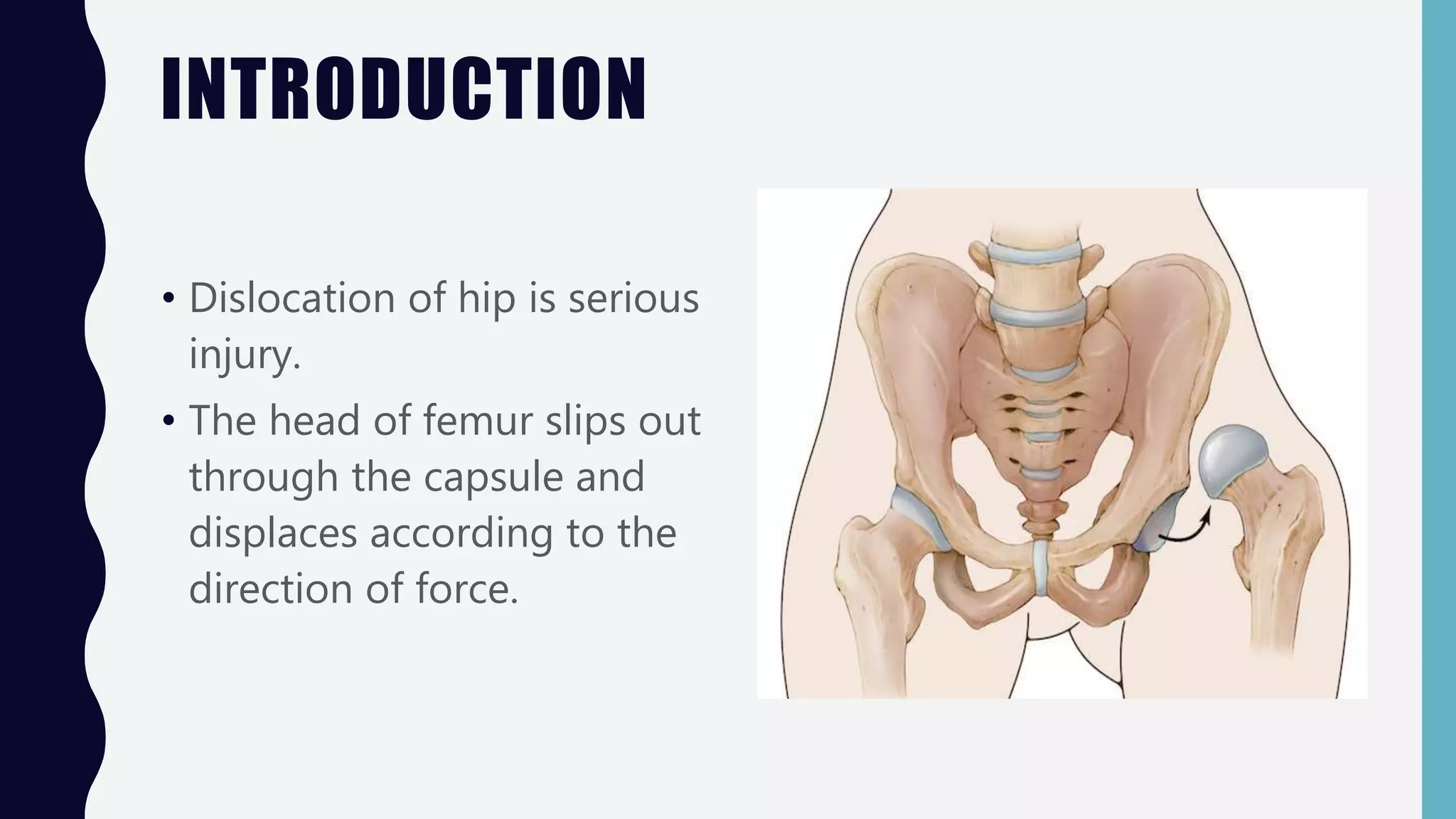
This document discusses different types of hip dislocations: posterior, anterior, and central. Posterior dislocation is the most common, occurring when the flexed and adducted femur is pushed backwards. It can be classified using Thompson-Epstein or Pipkin systems. Clinical signs include pain, limb position, and shortening. Treatment involves closed or open reduction and immobilization. Complications can include nerve injury, osteonecrosis, and arthritis. Anterior and central dislocations have similar but different mechanisms, clinical presentations, and treatments.