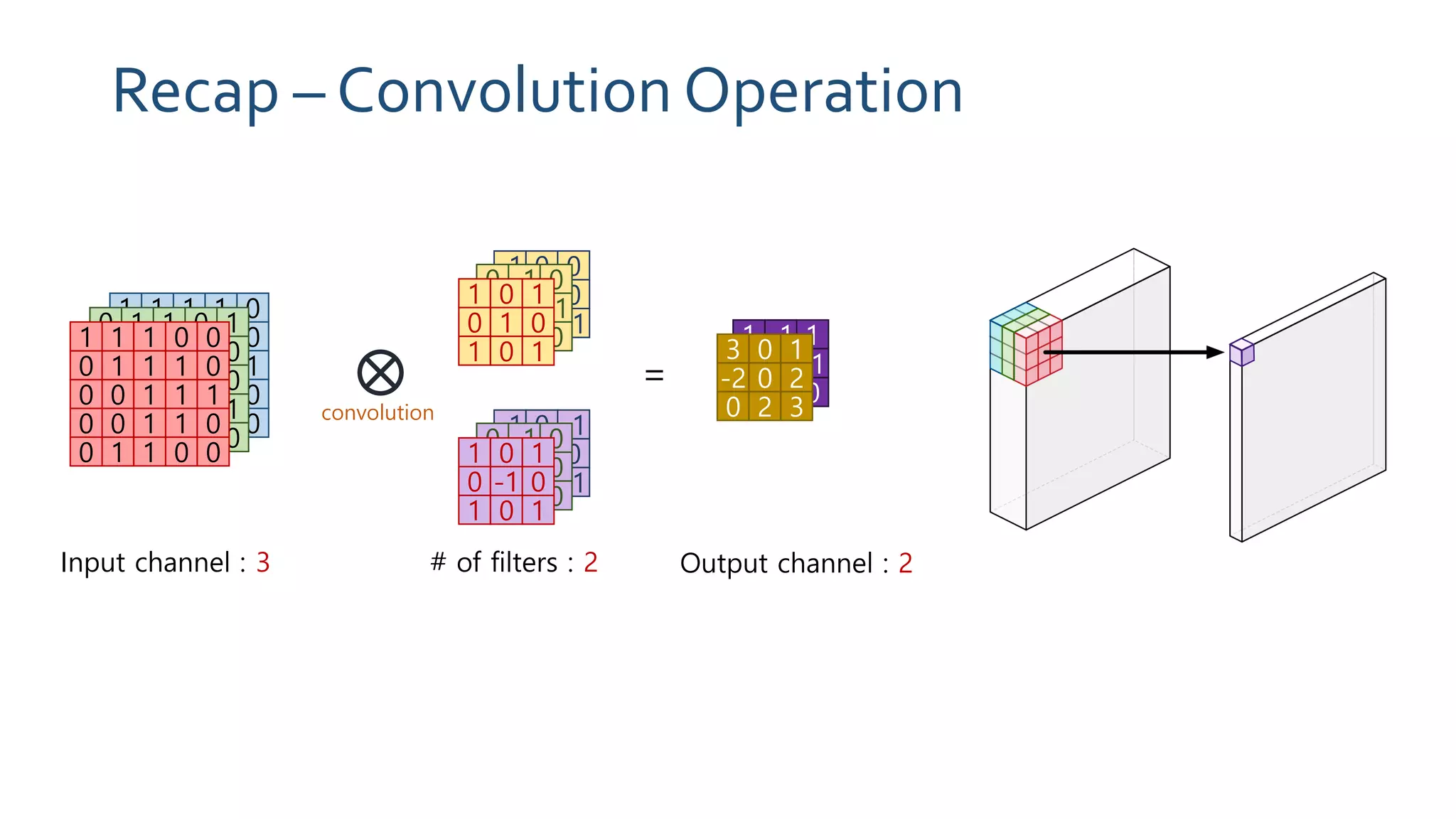
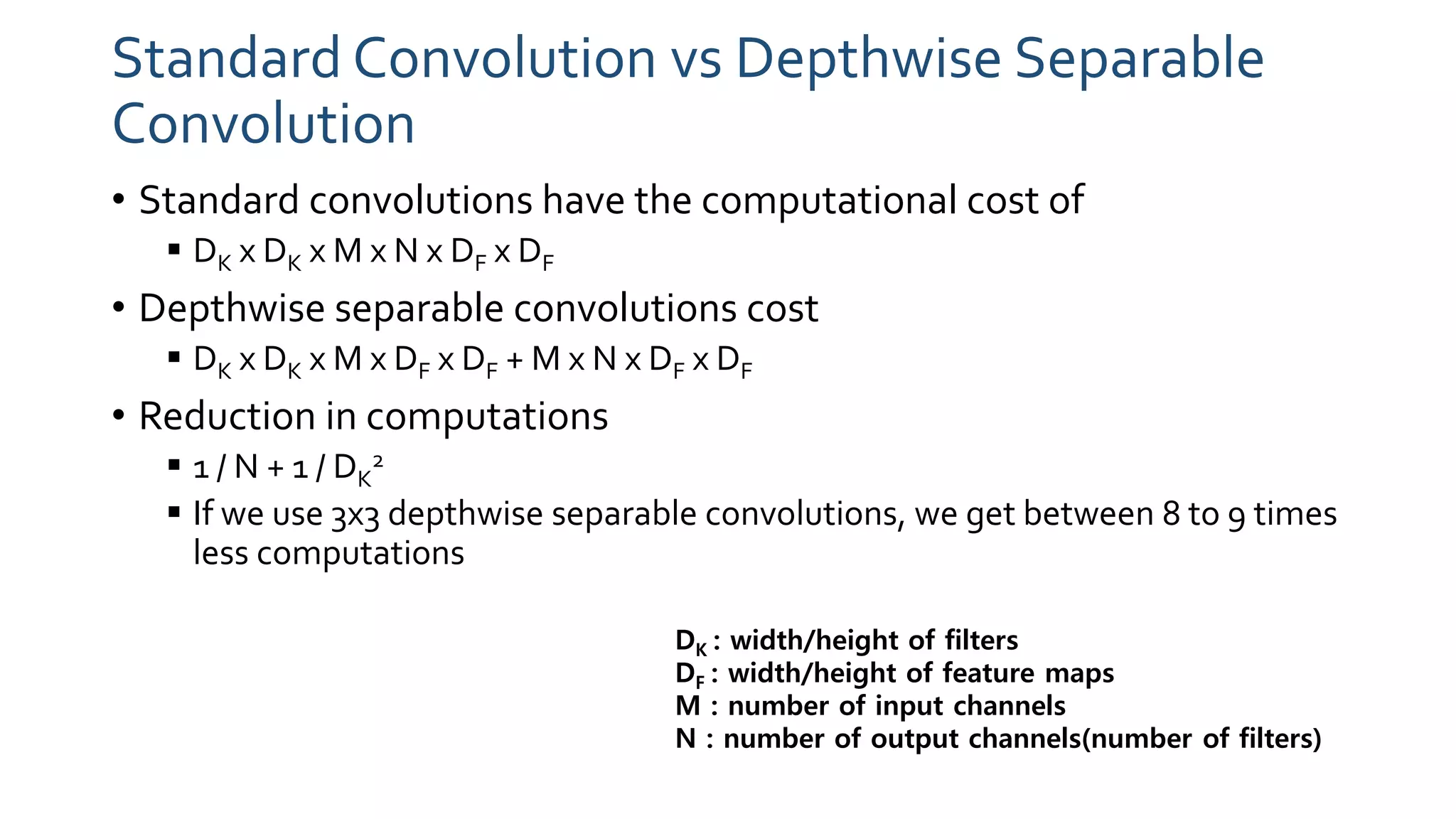
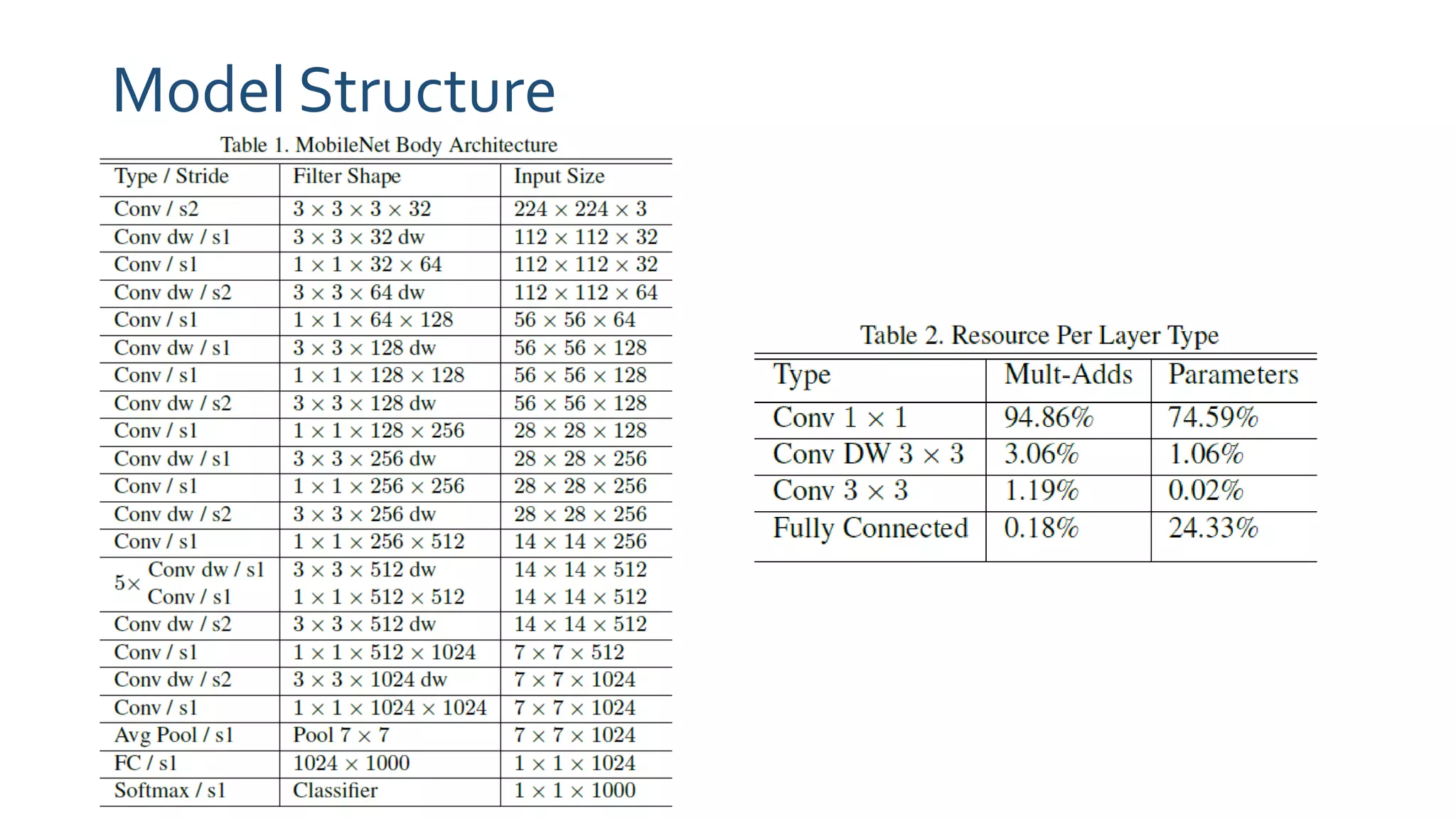
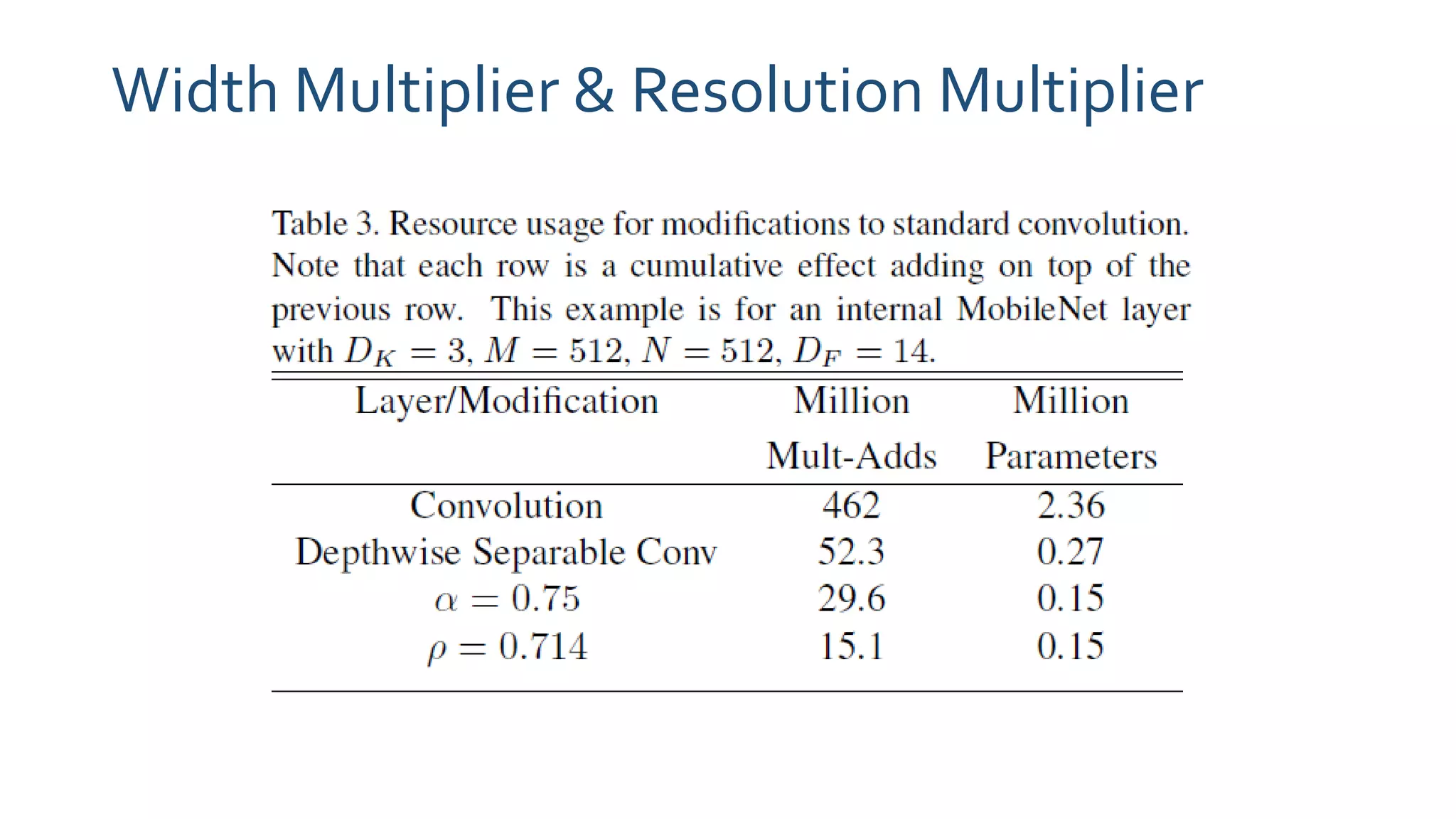
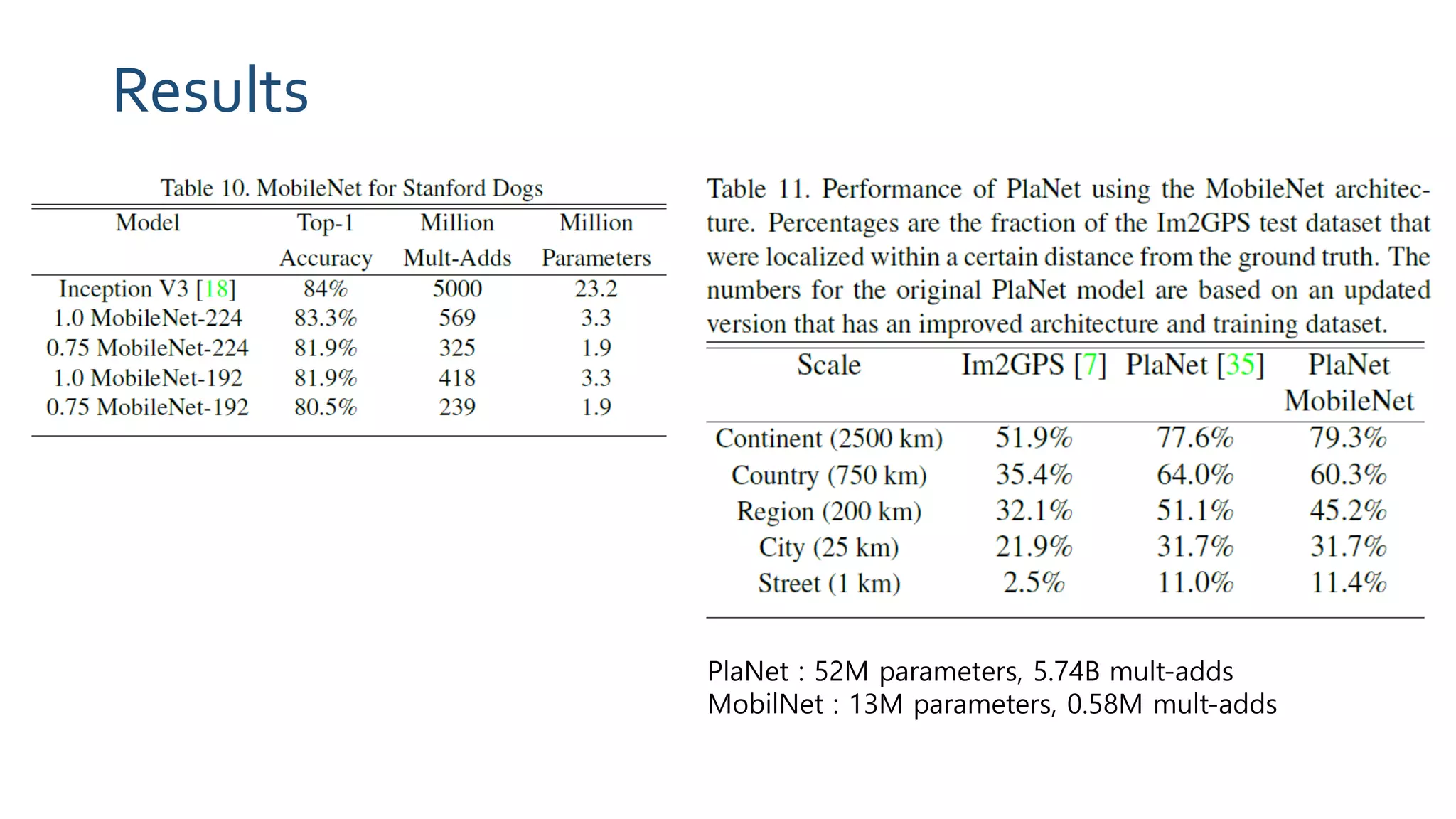
The document discusses MobileNets, a framework for efficient convolutional neural networks aimed at mobile vision applications, emphasizing the need for low power, real-time performance, and small model sizes in safety-critical gadgets. Key techniques for optimizing small deep neural networks include removing fully-connected layers, kernel and channel reduction, depthwise separable convolutions, and varying hyperparameters like width and resolution multipliers. Depthwise separable convolutions significantly reduce computational costs while maintaining performance, making them suitable for resource-constrained environments.