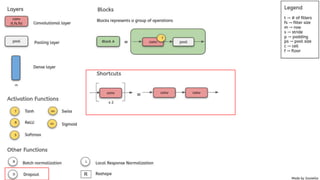
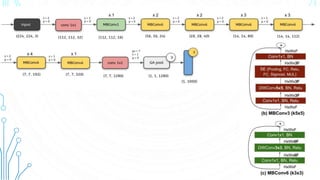
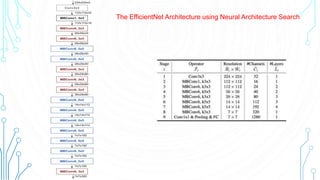
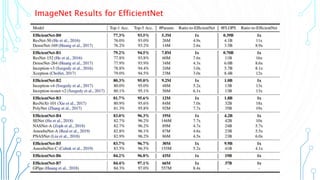
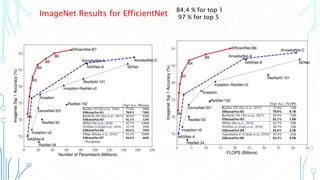
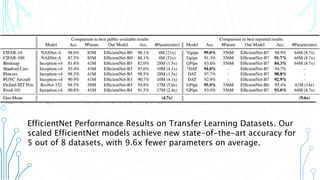
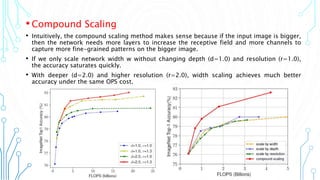
EfficientNet is a convolutional neural network architecture and scaling method that achieves state-of-the-art accuracy on image classification tasks using fewer parameters than previous models. The paper proposes a compound scaling method that scales up all dimensions (width, depth, resolution) of the model through continuous functions to balance accuracy and efficiency. Applying this method to a baseline model produces the EfficientNet models B0 through B7, with B7 achieving 84.4% top-1 accuracy on ImageNet using fewer parameters than previous best models. The paper also demonstrates that EfficientNet transfers well to other datasets, achieving new state-of-the-art results on 5 out of 8 datasets tested.





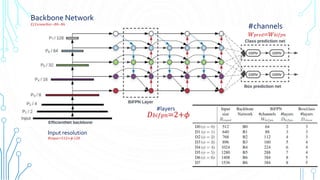
![14
Backbone network
Same width/depth scaling coefficient of EfficientNet B0 to B6
BiFPN network ( Bi-directional Feature Pyramid Network )
Exponentially grow BiFPN width 𝑊 𝑏𝑖𝑓𝑝𝑛(#channels), but linearly increase depth
𝐷b𝑖𝑓𝑝𝑛(#layers) since depth needs to be rounded to small.
𝑊 𝑏𝑖𝑓𝑝𝑛=64∙1.35 𝜙,𝐷 𝑏𝑖𝑓𝑝𝑛=2+𝜙
Box/class prediction network
Fix their width to always the same as BiFPN (i.e., 𝑊 𝑝𝑟𝑒𝑑=𝑊 𝑏𝑖𝑓𝑝𝑛
But, linearly increase the depth(#layers) using equation:
𝐷𝑏𝑜𝑥 = 𝐷𝑐𝑙𝑎𝑠𝑠 = 3 + [𝜙/3]
Input image resolution
Since feature level 3 - 7 are used in BiFPN , the input resolution must be dividable by
128
𝑅𝑖𝑛𝑝𝑢𝑡=512+𝜙∙128](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/efficientnet-201124090647/85/EfficientNet-14-320.jpg)