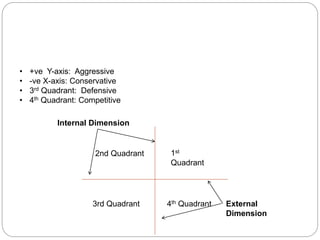
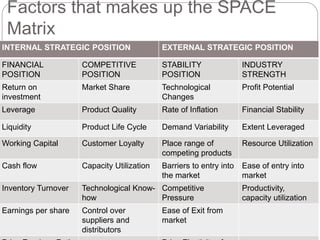
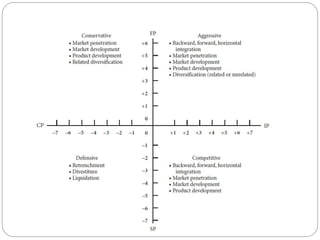
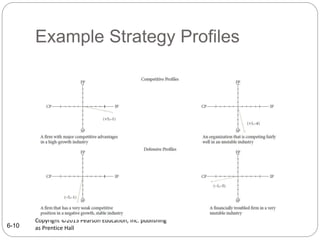
The document discusses the SPACE Matrix, a four-quadrant framework that indicates which type of strategies are most appropriate for an organization based on its strategic position. The matrix evaluates an organization across internal dimensions like financial position and competitive position, and external dimensions like stability position and industry position to place the organization in an aggressive, conservative, defensive, or competitive quadrant. Each quadrant suggests different types of strategies, such as using strengths aggressively for the aggressive quadrant or focusing on weaknesses for the defensive quadrant.

![Most important determinants of an organization’s
overall strategic position
1st
Quadrant
2nd Quadrant
3rd Quadrant 4th Quadrant
• Two Internal dimensions (financial position [FP] and competitive position
[CP])
• Two External dimensions (stability position [SP] and industry position [IP])
Internal Dimension
External
Dimension](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spacematrix-140527024233-phpapp01/85/Space-matrix-2-320.jpg)