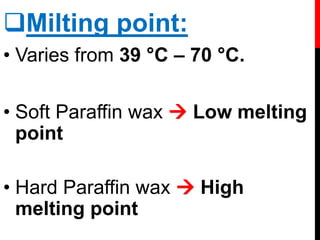
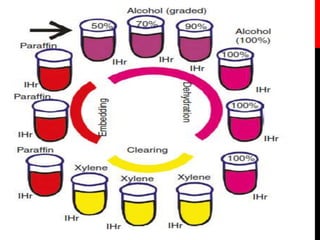
The document discusses the principles and techniques of tissue infiltration and embedding. It describes how clearing agents are removed from tissues through diffusion and replaced with molten embedding media like wax. The wax is then cooled to solidify and provide support for sectioning thin tissue samples. Several factors influence infiltration including tissue size, type, clearing agent used, and whether vacuum embedding is performed. Common embedding media include paraffin wax which provides good support but can cause shrinkage, and DMSO-supplemented wax which speeds infiltration. Both manual and automated processors are described.