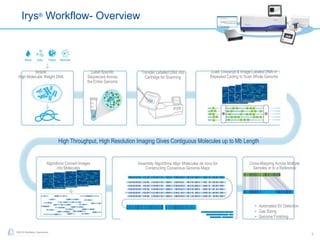
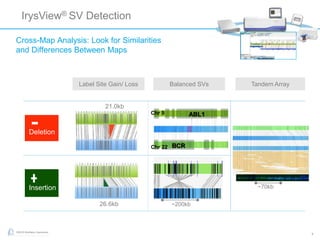
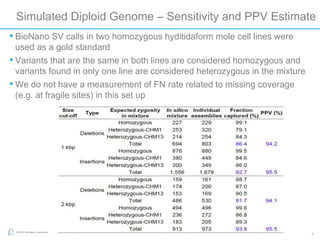
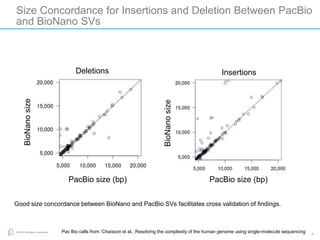
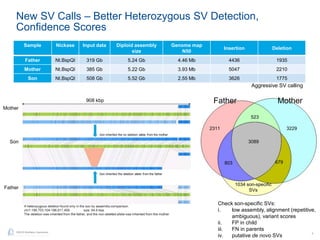
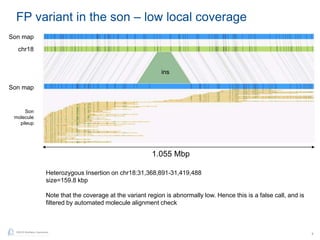
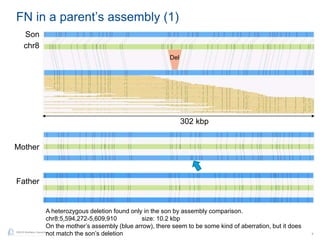
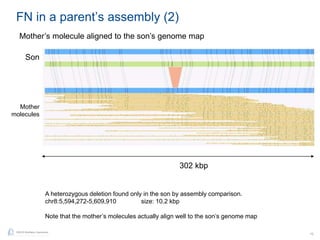
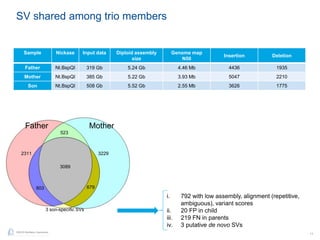
The document discusses updates to genome mapping technology. It describes how high-throughput, high-resolution imaging can generate contiguous DNA molecules up to megabase lengths. Labeled DNA is imaged repeatedly to scan the entire genome. Genome maps can be used to discover structural variants by comparing patterns of labeled sequences. Genome maps can also be used as scaffolds to align sequencing contigs. The document provides examples of detecting insertions, deletions, and other structural variants between samples or to a reference genome. It also discusses using genome maps to validate structural variants found through other methods like PacBio sequencing.