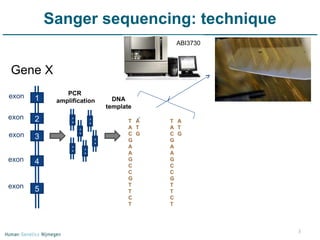
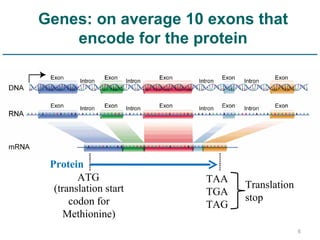
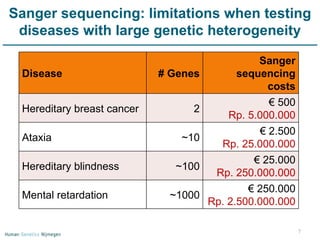
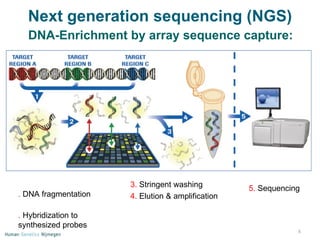
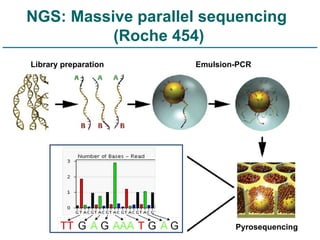
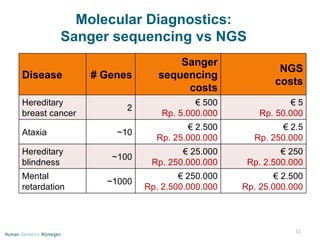
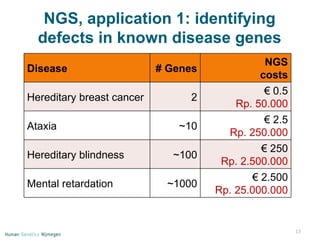
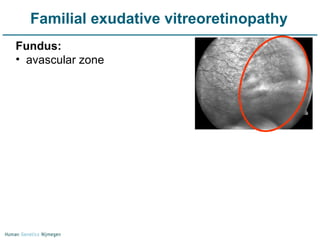
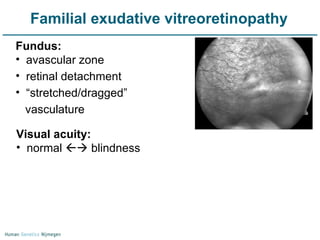
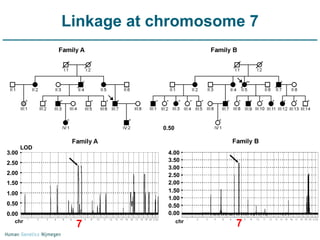
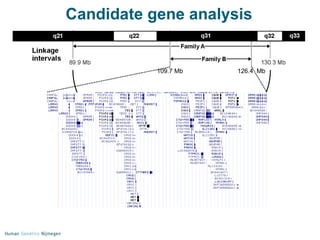
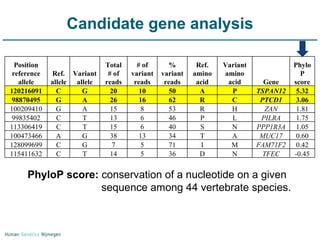
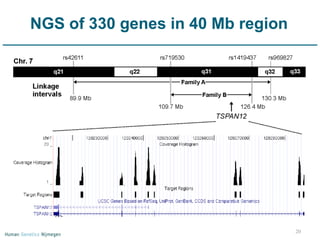
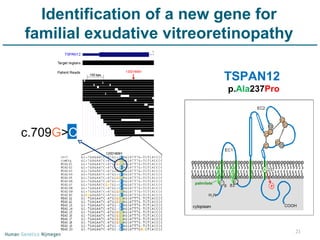
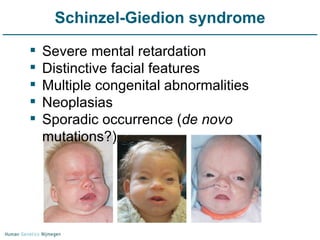
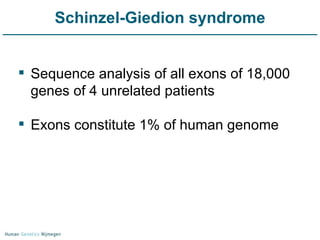
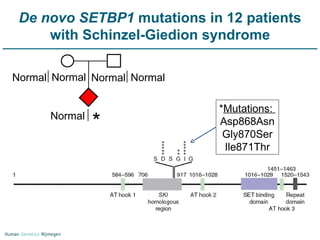
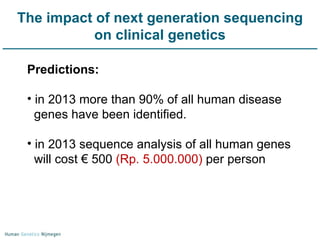
Next generation sequencing (NGS) provides a 1000-fold increase in sequencing output and a 100-fold reduction in cost compared to Sanger sequencing. This allows for large-scale sequencing of genes and genomes to identify genetic defects underlying human diseases. The document describes applications of NGS in clinical genetics such as sequencing known disease genes, identifying new disease genes, sequencing whole genomes, and sequencing all human genes in patients. It also discusses future predictions and challenges regarding use of NGS in clinical genetics.