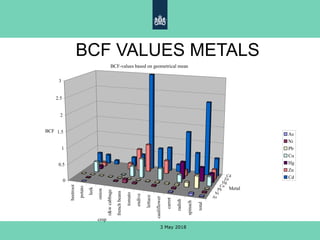
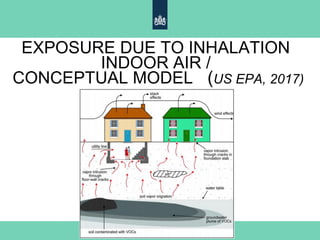
The document discusses the risks associated with soil pollution and its impact on food safety and human health, highlighting exposure pathways such as ingestion, dermal contact, and inhalation. It details various methodologies for assessing exposure and risk, including biomonitoring and mathematical models. The text emphasizes the need for harmonized risk assessment tools while allowing for flexibility based on geographical and cultural contexts.