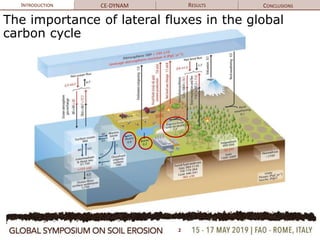
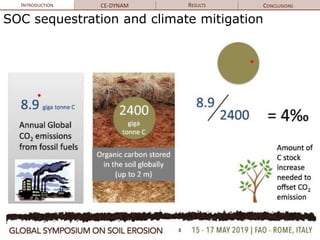
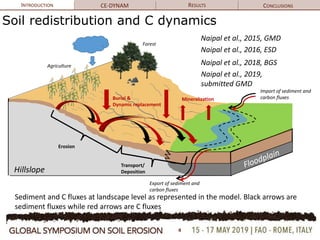
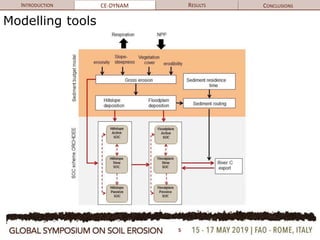
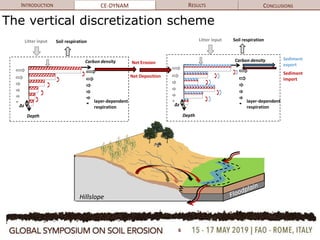
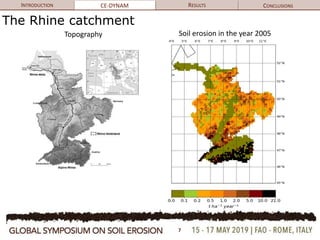
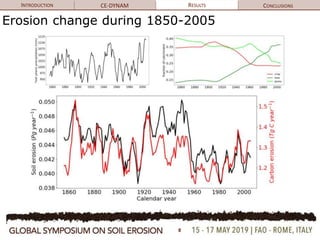
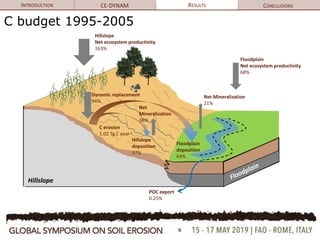
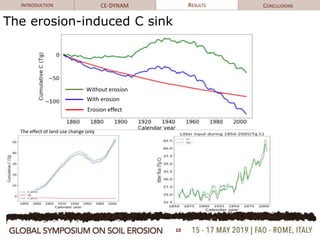
The document discusses soil erosion modeling tools and their significance in understanding soil carbon dynamics and the global carbon cycle. It highlights the importance of lateral fluxes and the cumulative effect of soil erosion as a carbon sink, which amounts to 90 Tg by the end of the observed period. Key factors influencing this sink include climate change, land use change, and the burial of eroded carbon in floodplains.