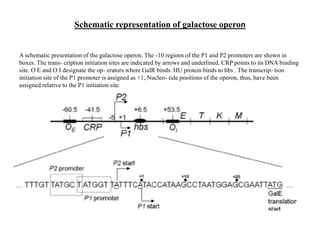
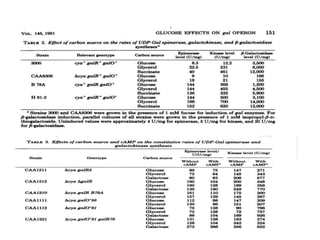
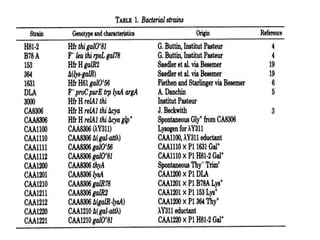
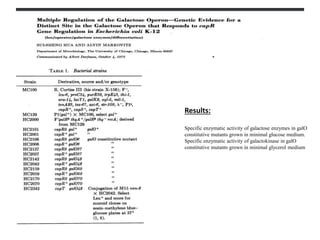
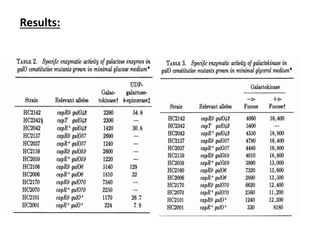
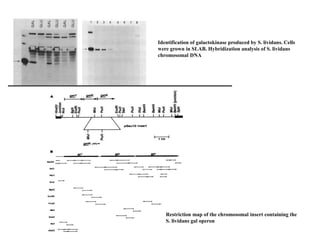
The gal operon in E. coli encodes enzymes essential for galactose metabolism and is regulated by various mechanisms, including the binding of repressor molecules to specific operators, which inhibits transcription. Key enzymes are involved in both the catabolism of D-galactose and the synthesis of precursors for complex carbohydrates. The operon's structure and regulation allow for coordinated gene expression, although mutations in the promoter can disrupt the functionality of all associated genes.