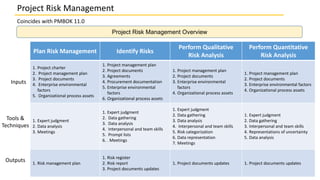
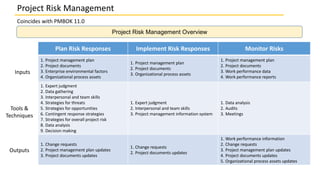
The document discusses project risk management as it coincides with PMBOK 11.0. It outlines the 7 processes of project risk management according to PMBOK which are: plan risk management, identify risks, perform qualitative risk analysis, perform quantitative risk analysis, plan risk responses, implement risk responses, and monitor risks. It also discusses key concepts, trends, considerations for tailoring, and considerations for agile environments.