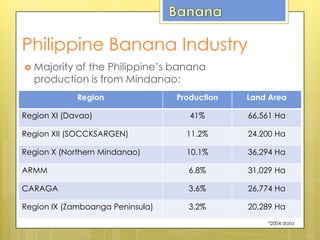
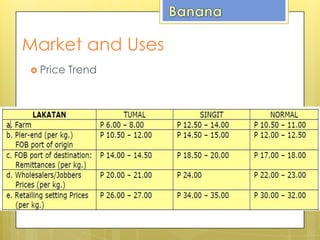
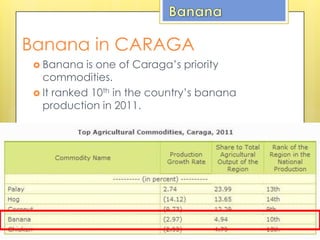
Bananas are an important crop for the Philippines. The country is the fourth largest producer and exporter of bananas worldwide. Around 5.9 million farm households depend on banana production as their primary source of income. The banana industry is also the leading export earner for Filipino farmers. Major varieties produced are Cavendish, lakatan, and latundan, with Cavendish and banana chips being the leading exports. Banana production is concentrated in Mindanao, which accounts for over 60% of the country's total banana output.