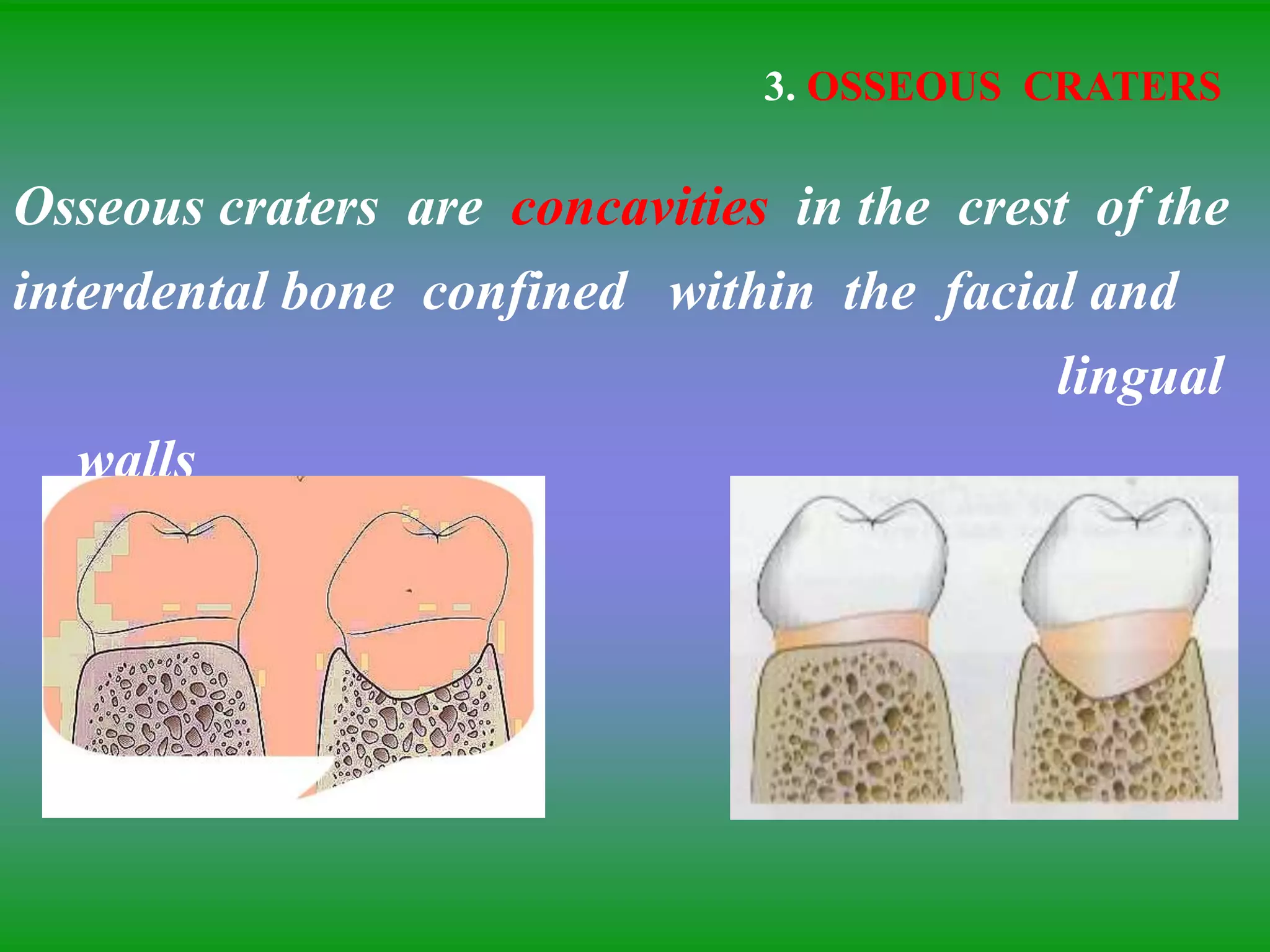
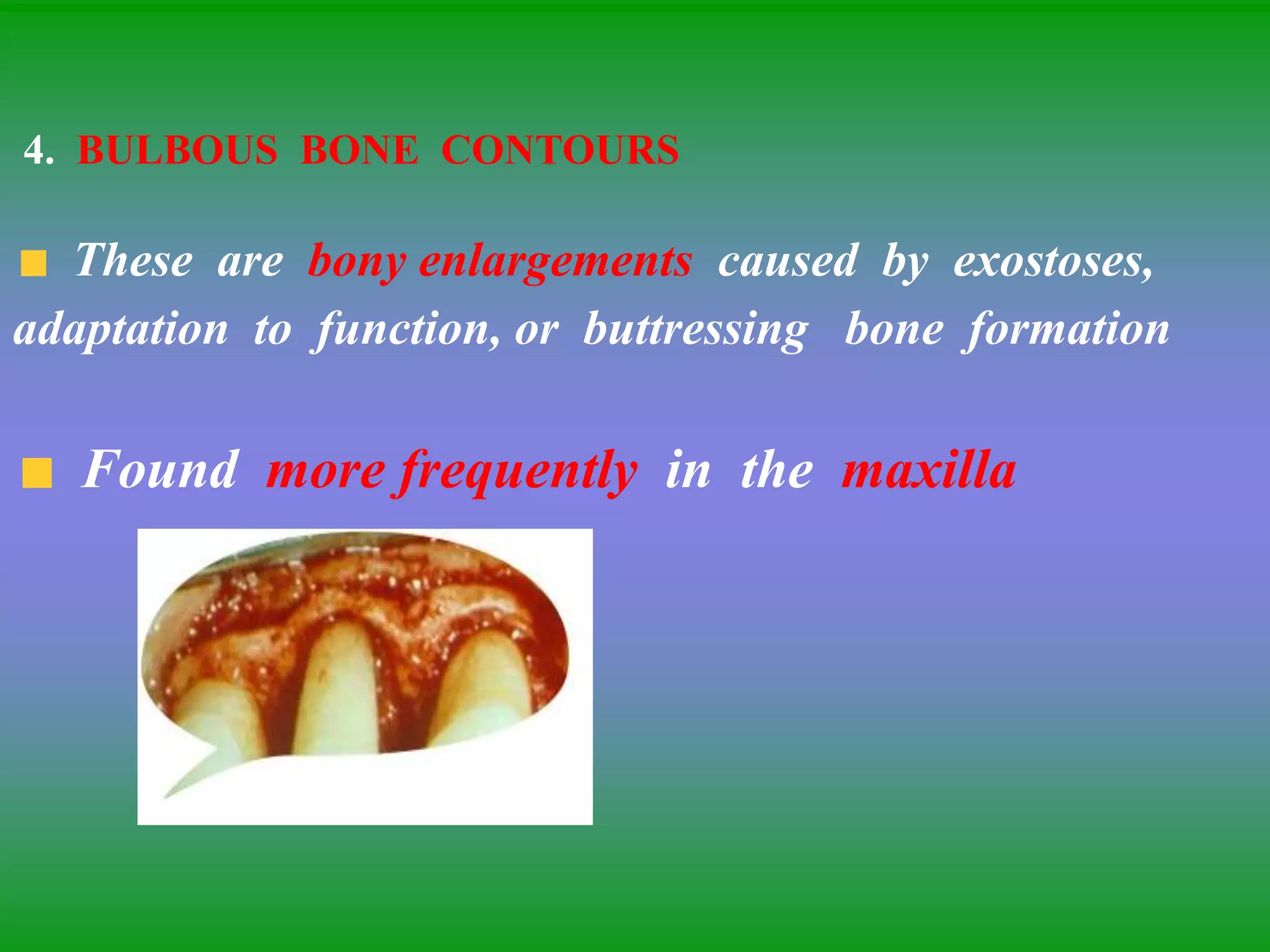
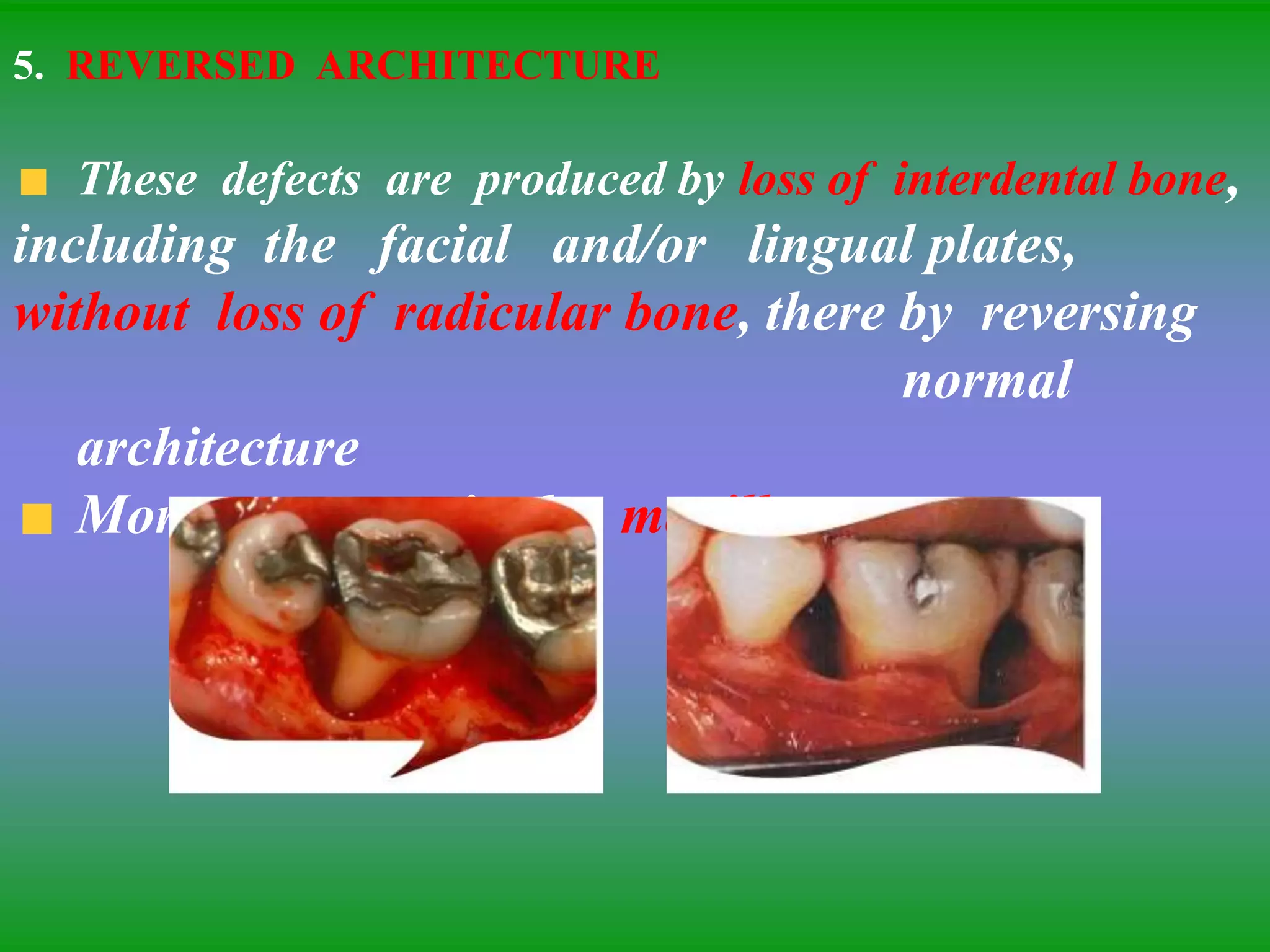
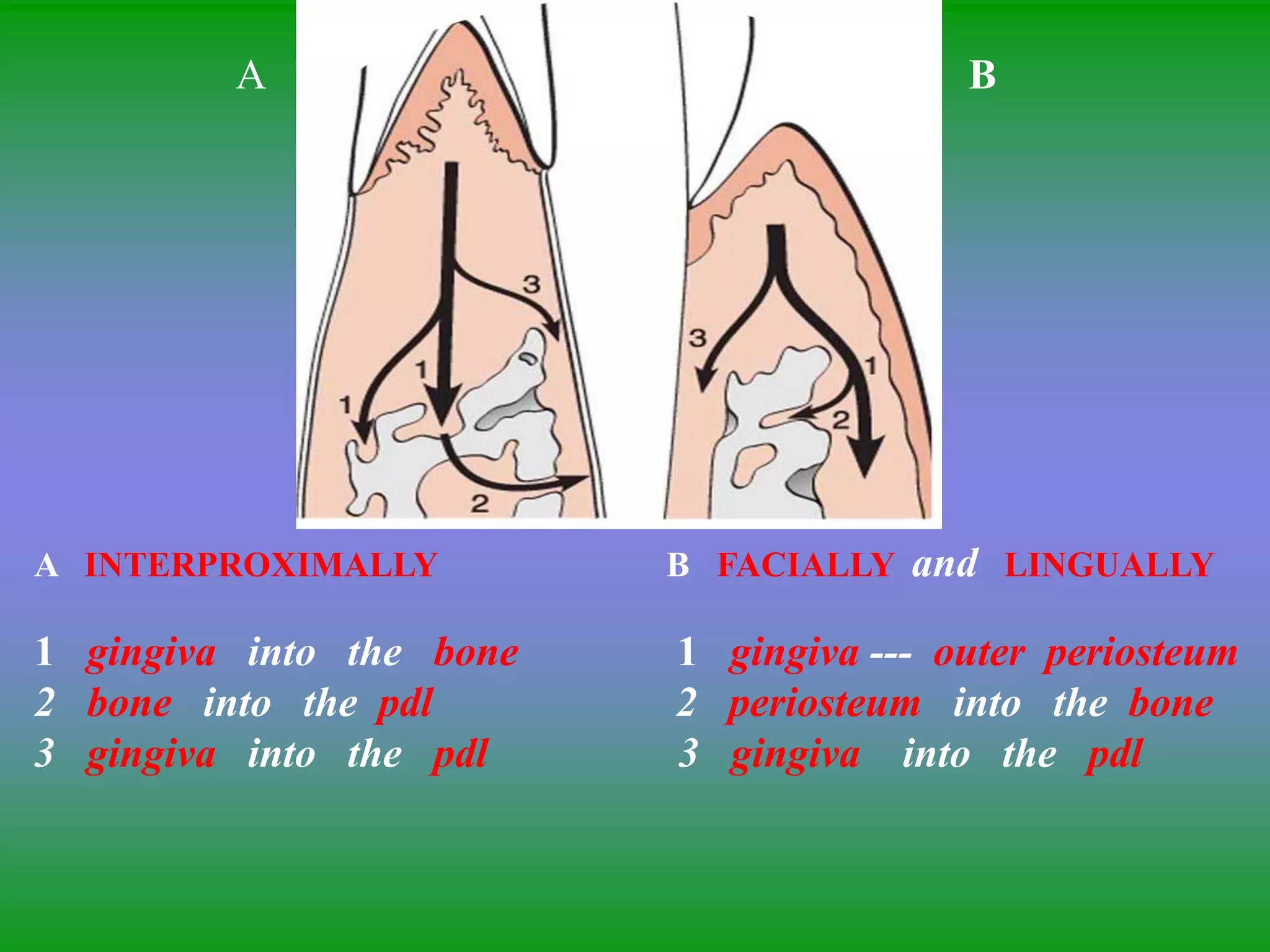
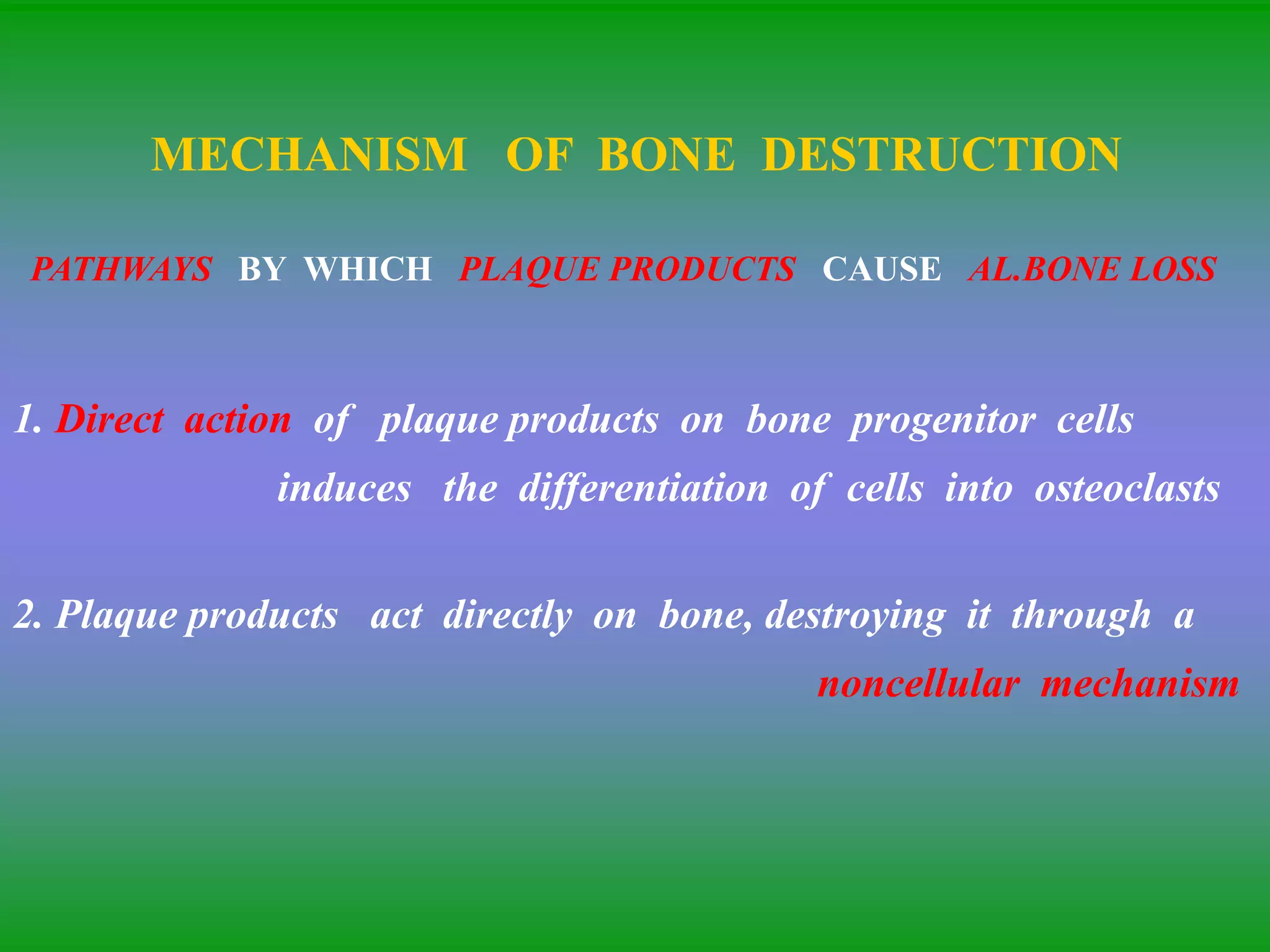
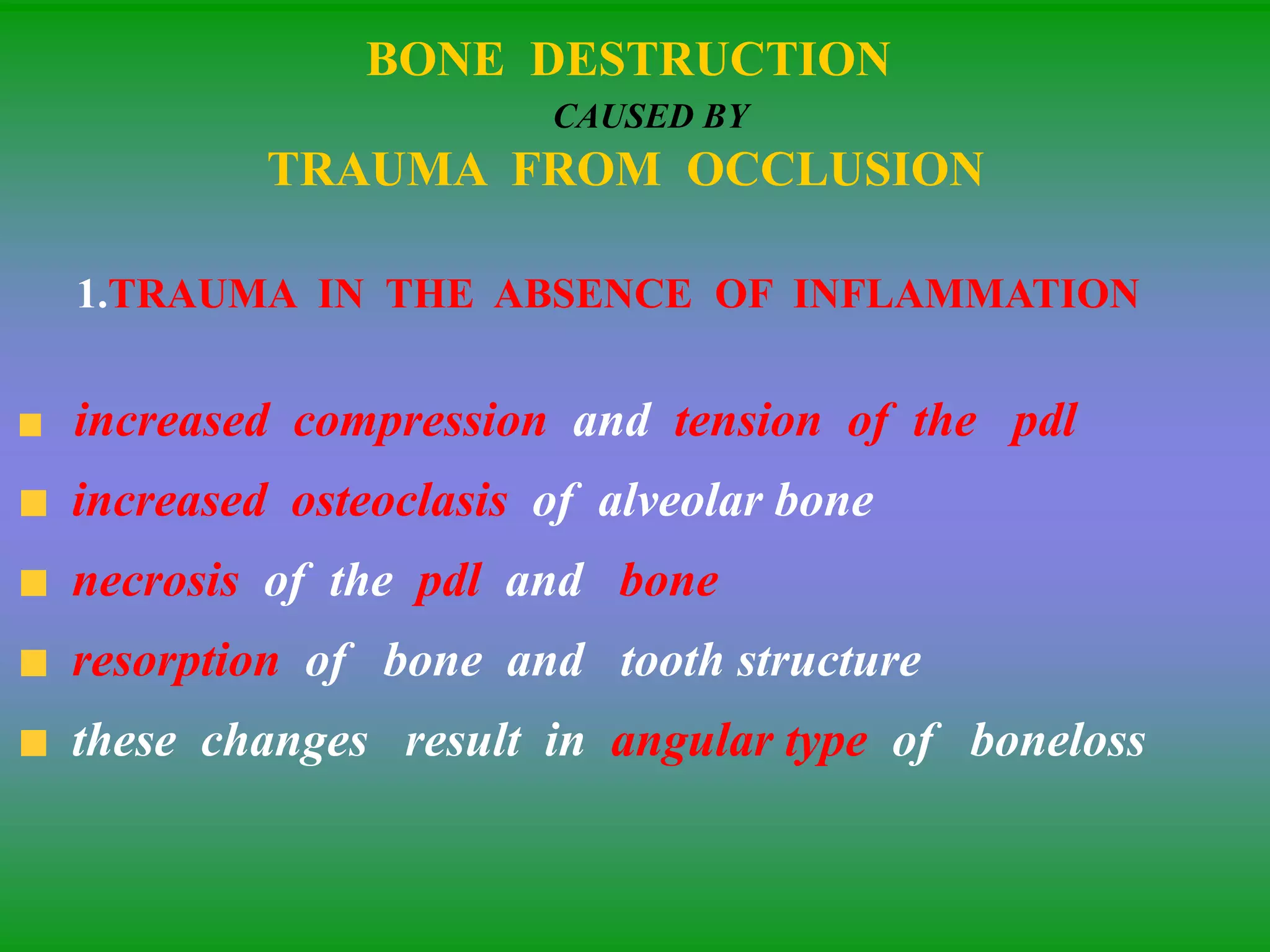
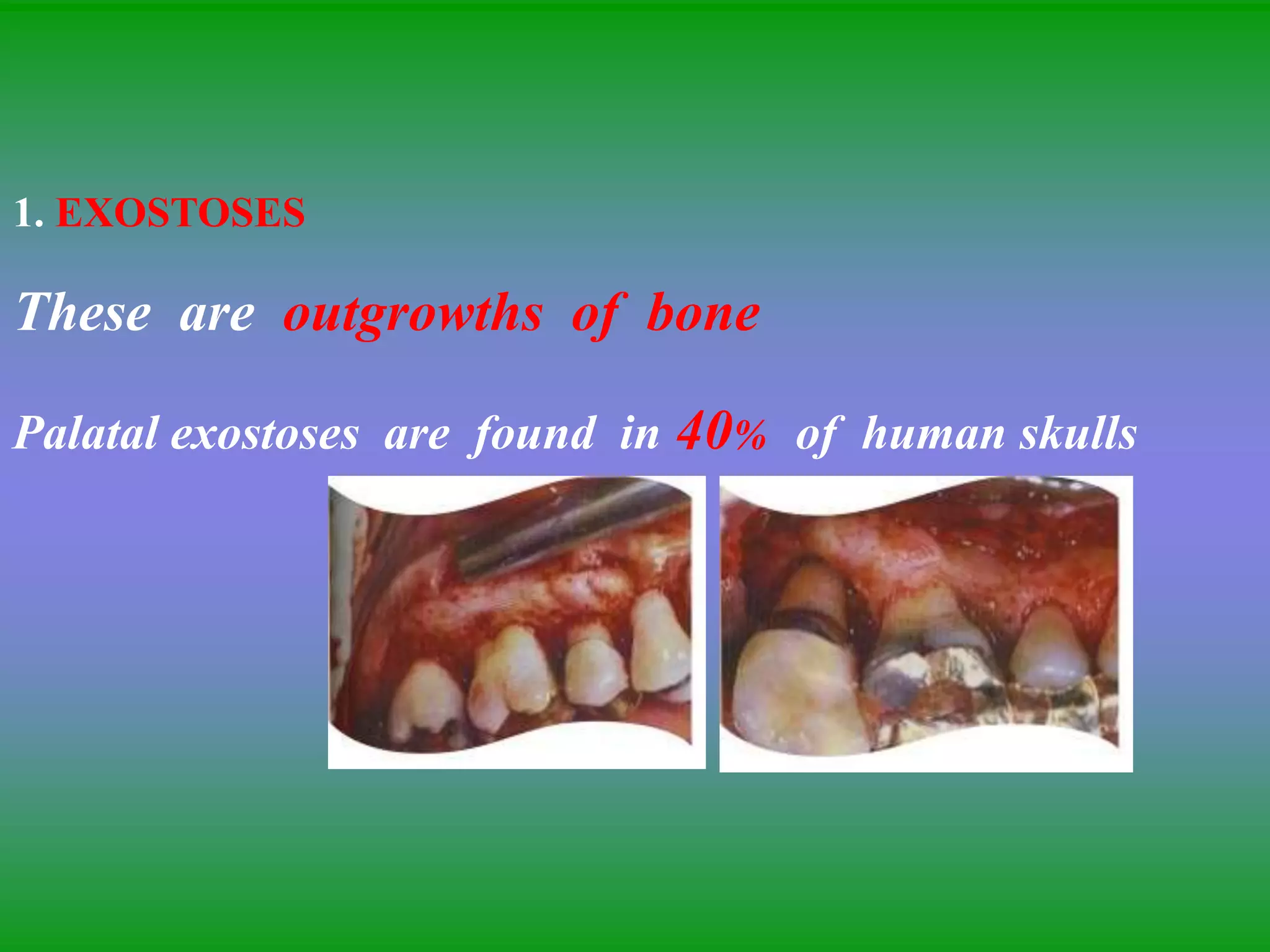
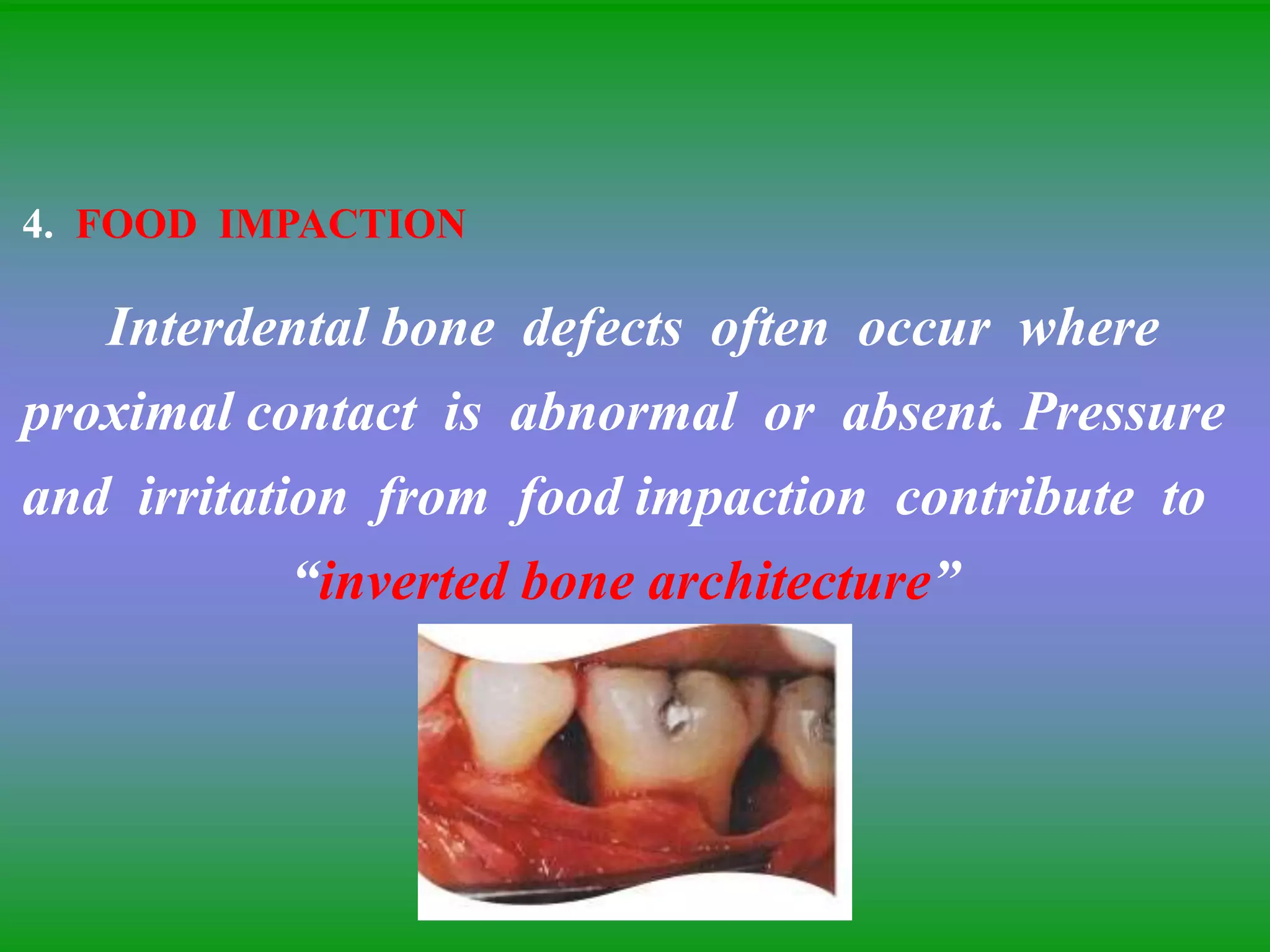
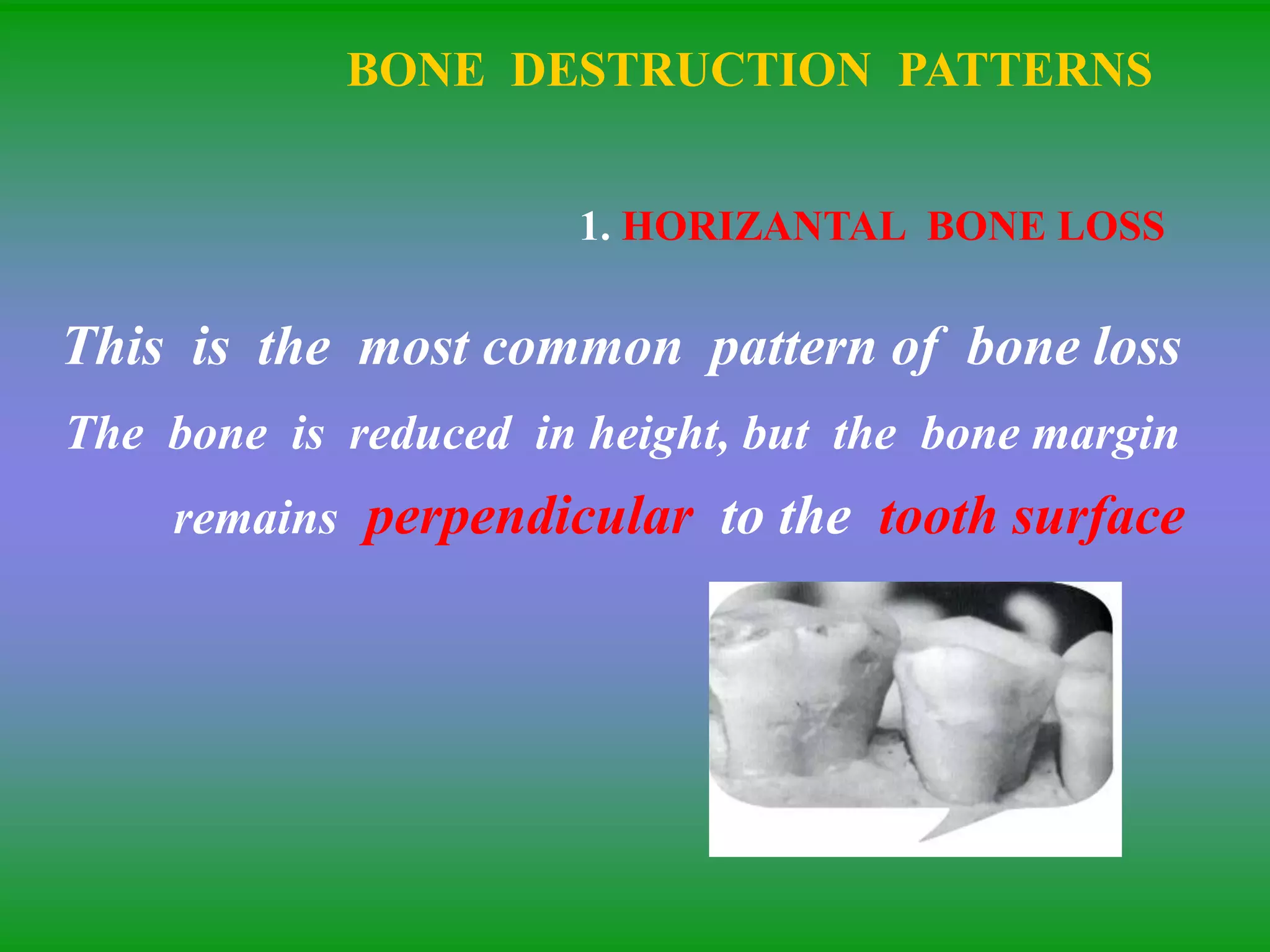
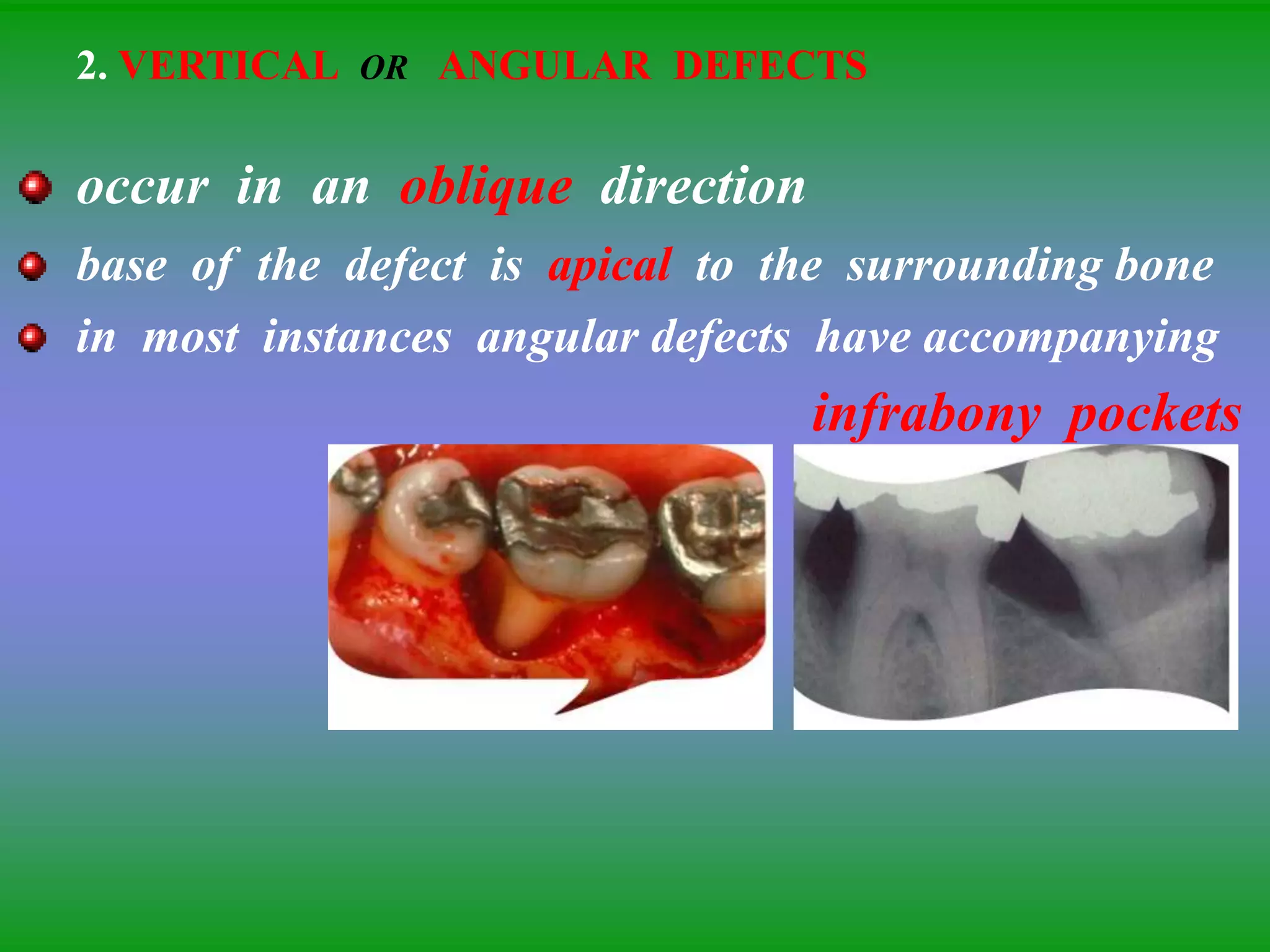
This document summarizes the key aspects of periodontitis and bone destruction in periodontal disease. It discusses that periodontitis is an infectious disease involving the destruction of alveolar bone, which leads to tooth loss. Bone destruction occurs through two pathways - interproximally as inflammation spreads from the gingiva into the bone through blood vessels, and facially/lingually as inflammation penetrates from the gingiva directly into the bone. A variety of local and systemic factors can influence the balance between bone formation and resorption in periodontal disease.















![BONE FORMATION IN PERIODONTAL DISEASE
Areas of bone formation are also found
immediately adjacent to sites of active bone
resorption to reinforce the remaining bone
[buttressing bone formation]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bonelossandpatternsofbonedestruction-220827091109-901b538b/75/BONE-LOSS-AND-PATTERNS-OF-BONE-DESTRUCTION-ppt-19-2048.jpg)

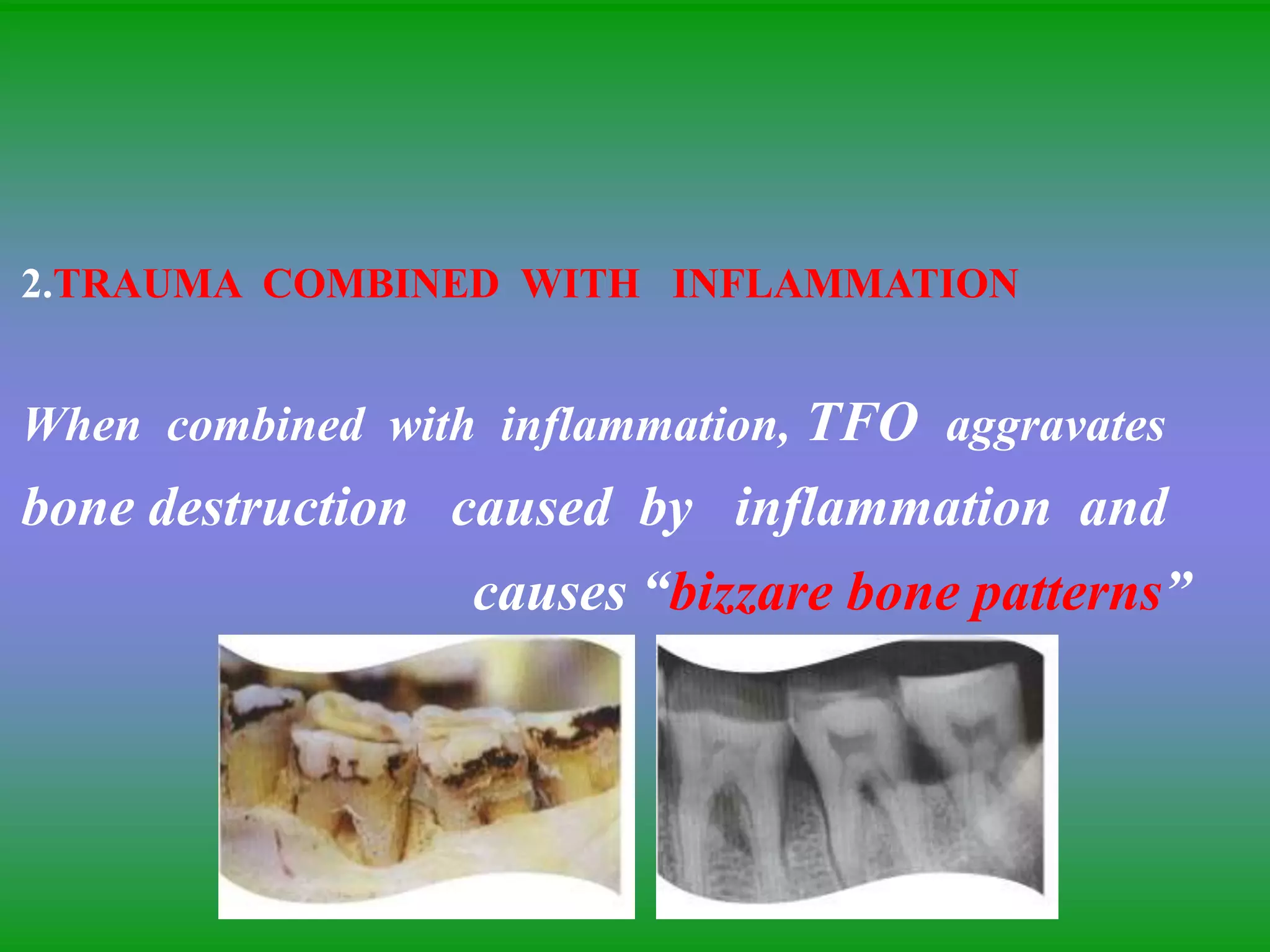


![2. TRAUMA FROM OCCLUSION
TFO may cause thickening of cervical margin
of alveolar bone or a change in the morphology
of the bone [e.g., angular defects and buttressing bone]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bonelossandpatternsofbonedestruction-220827091109-901b538b/75/BONE-LOSS-AND-PATTERNS-OF-BONE-DESTRUCTION-ppt-26-2048.jpg)
![3. BUTTRESSING BONE FORMATION [lipping]
Bone formation occurs in an attempt to buttress
bony trabaculae weakened by resorption
When it occurs within the jaw, it is termed as
“central buttressing bone formation”
when it occurs on the external surface, it is referred as
“peripheral buttressing bone formation”
which in turn cause bulging of the bone contour, termed
“lipping”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bonelossandpatternsofbonedestruction-220827091109-901b538b/75/BONE-LOSS-AND-PATTERNS-OF-BONE-DESTRUCTION-ppt-27-2048.jpg)


![THREE BONY WALLS
distal[1] lingual[2] and facial[3]
TWO -WALL DEFECT
distal[1] lingual[2]
ONE -WALL DEFECT
distal wall only[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bonelossandpatternsofbonedestruction-220827091109-901b538b/75/BONE-LOSS-AND-PATTERNS-OF-BONE-DESTRUCTION-ppt-33-2048.jpg)