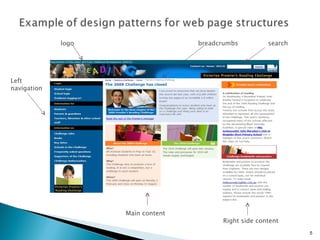
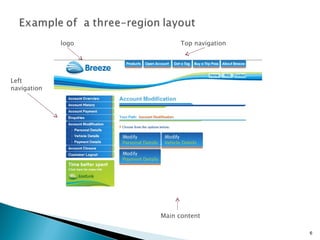
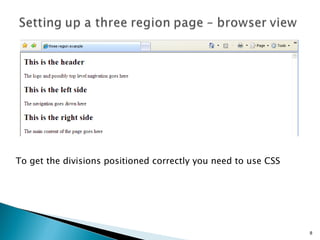
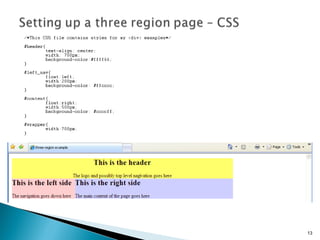
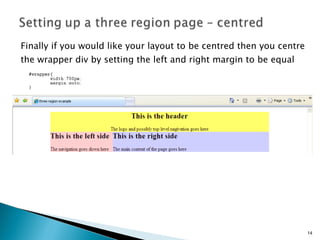
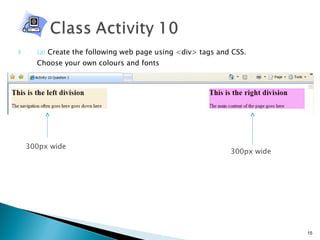
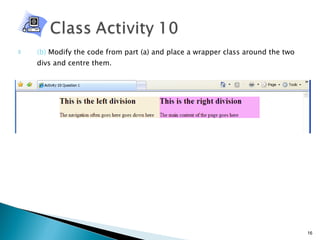
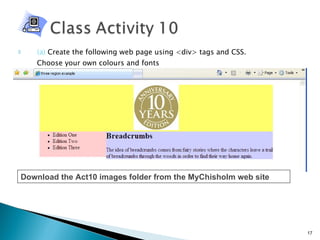
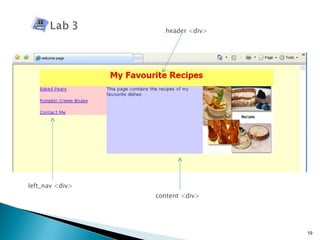
The document discusses using <div> tags and CSS for page layout instead of tables. <div> tags define sections of an HTML document and are easy to style with CSS. CSS properties like float allow elements to be positioned and other elements to flow around them. A common layout uses <div> tags for the logo, navigation, and main content sections.