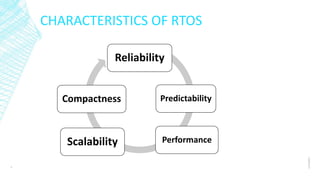
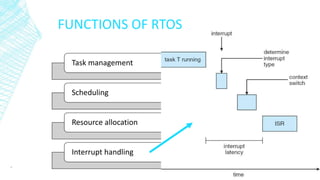
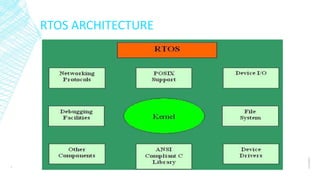
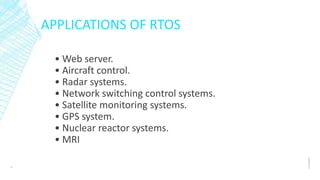
Real-time operating systems (RTOS) are specialized operating systems designed to run applications with precise timing and high reliability. An RTOS is single-tasked compared to general purpose OSs which run multiple tasks simultaneously. There are three main types of RTOS: hard, firm, and soft. An RTOS provides functions like task management, scheduling, resource allocation, and interrupt handling. Common applications of RTOS include web servers, aircraft control systems, medical devices, and industrial automation.







![REFERENCES
[1] National Instrument, (2013, Nov.22), What is a Real-Time Operating
System (RTOS)? Available: http://www.ni.com/white-paper/3938/en/
[2] H.ARORA, (2012, FEB.6), what is RTOS? Real Time Operating
Systems Basics , Available: http://www.thegeekstuff.com/2012/02/rtosbasics/
[3] W.Cedeo and P.Laplante, (2015), An Overview of Real-Time Operating
Systems, Available: http://jla.sagepub.com/content/12/1/40.full
[4] Pantech solutions, REAL TIME OPERATING SYSTEM (RTOS)
CONCEPTS, India.
[5] silberchatz, glaving and Gange,Operating system concepts 8th
ed.USA:2009.
[6] Renesas Electronics Corporation,(2010, Jan.4),General RTOS
Concepts, Available: http://www.renesas.com
1/14/2017
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rtos-presentation-170114080326/85/RTOS-Real-Time-Operating-Systems-12-320.jpg)