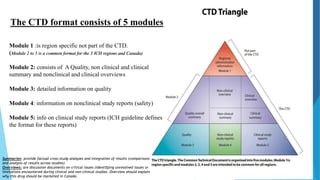
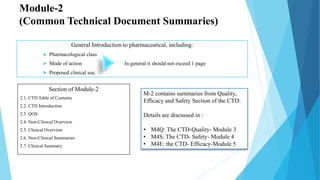
The document provides an overview of the Common Technical Document (CTD), which was created through collaboration between the European Medicines Agency, US Food and Drug Administration, and Japan's Ministry of Health to standardize the submission format for new drug applications. The CTD consists of 5 modules, with Module 1 containing region-specific information and Modules 2 through 5 containing common quality, non-clinical, and clinical summaries and reports. The goals of the CTD were to create a more consistent application format that streamlines review, facilitates information exchange, and reduces the resources needed for global drug registration.