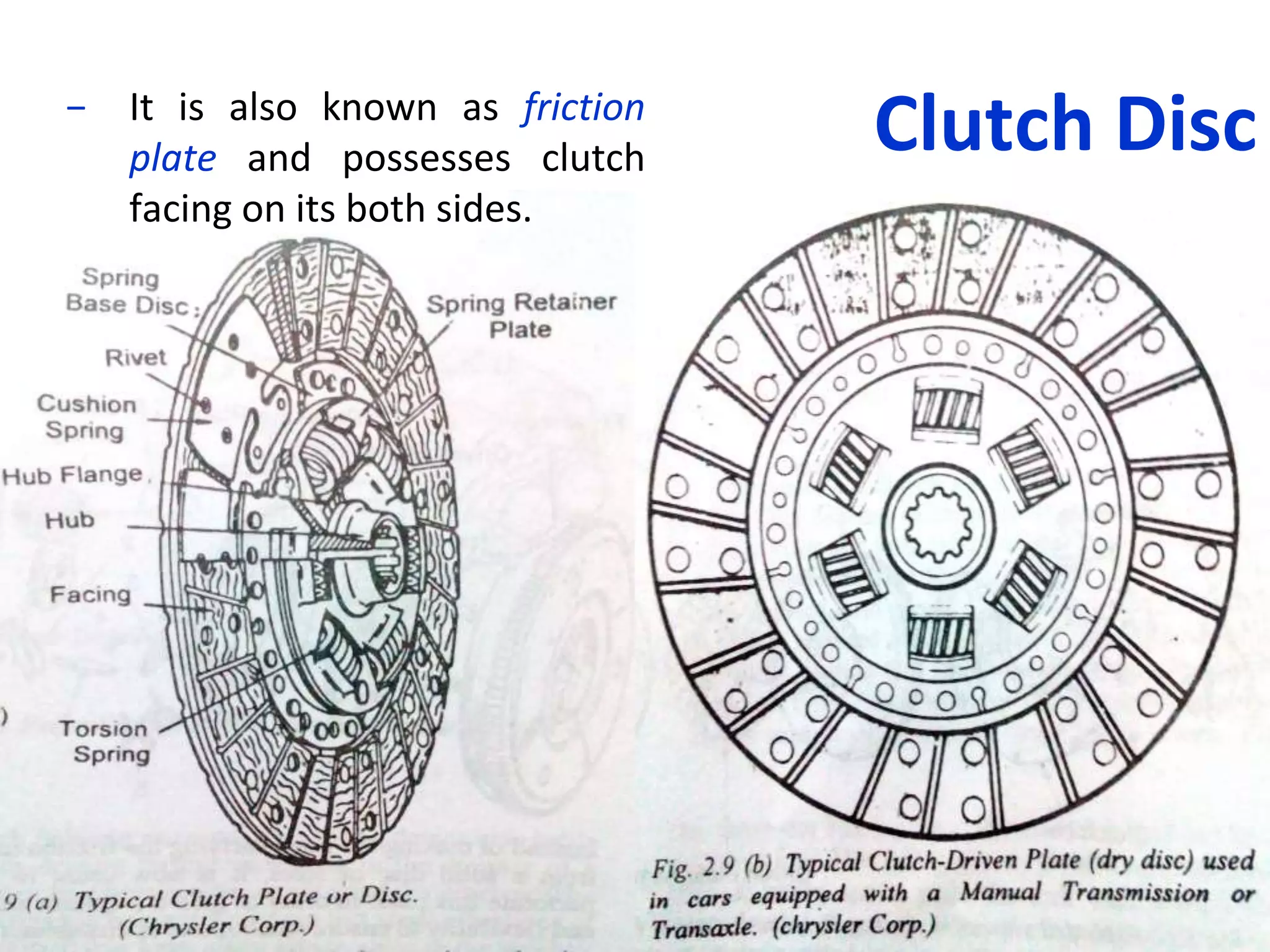
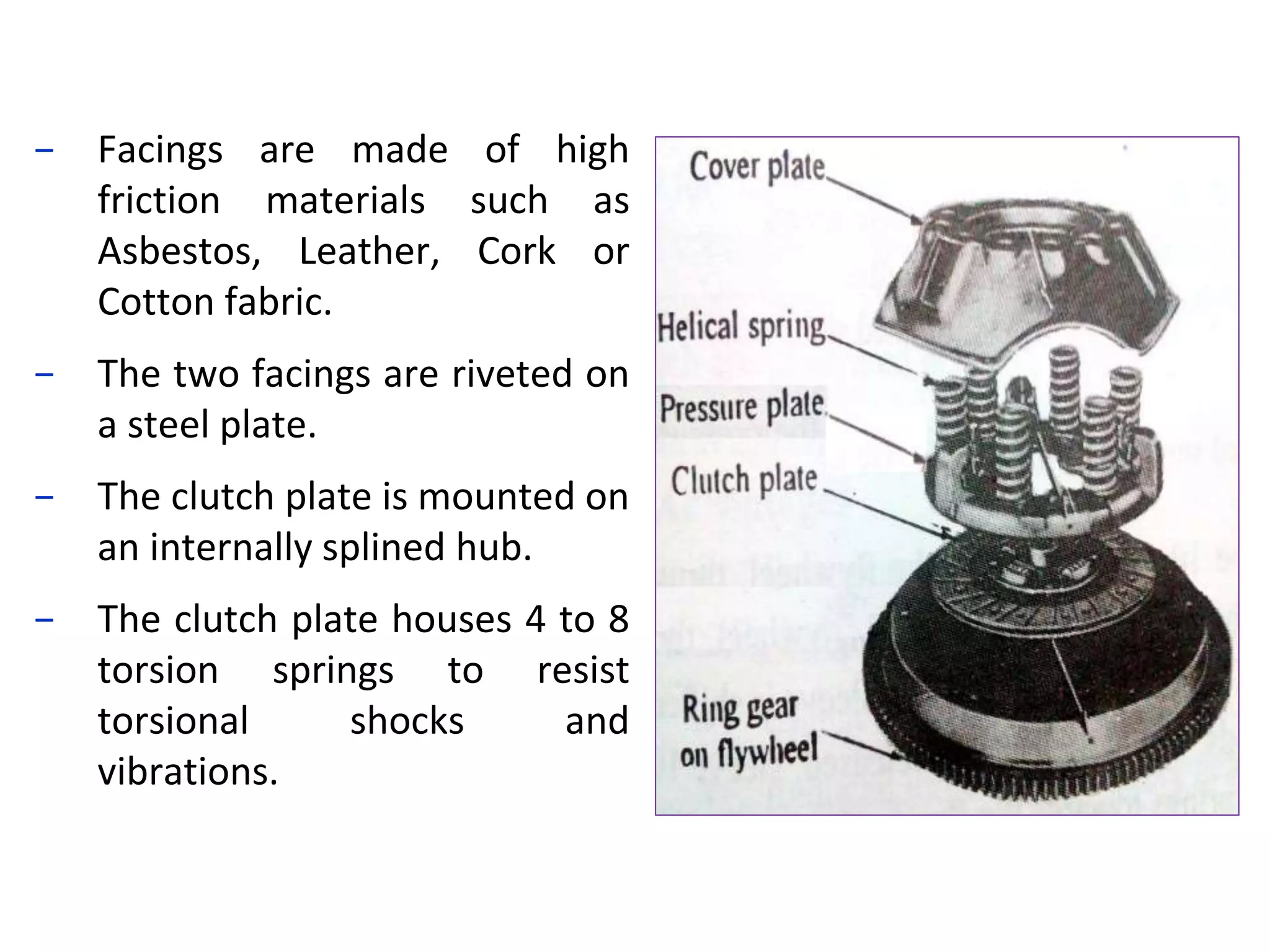
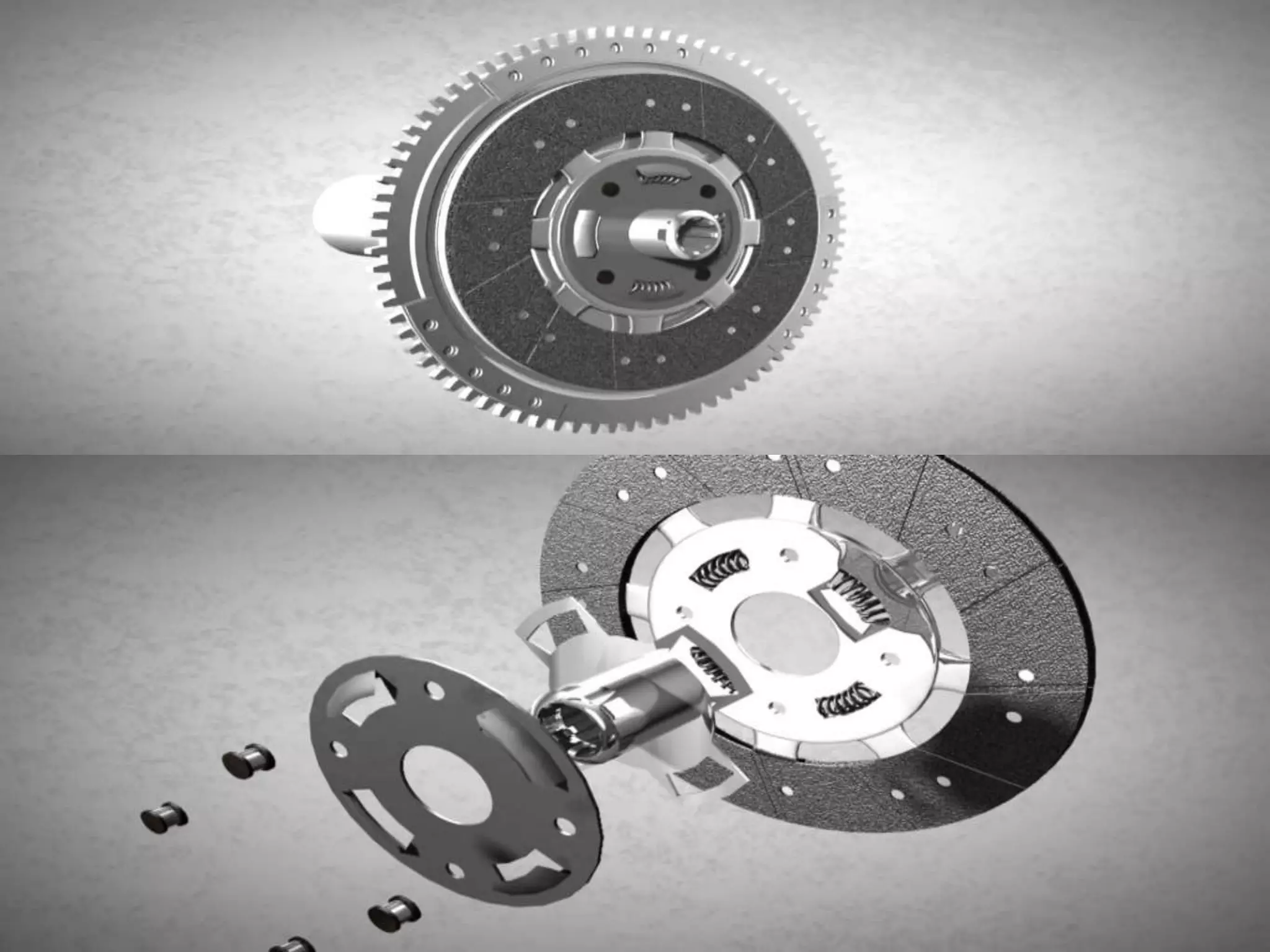
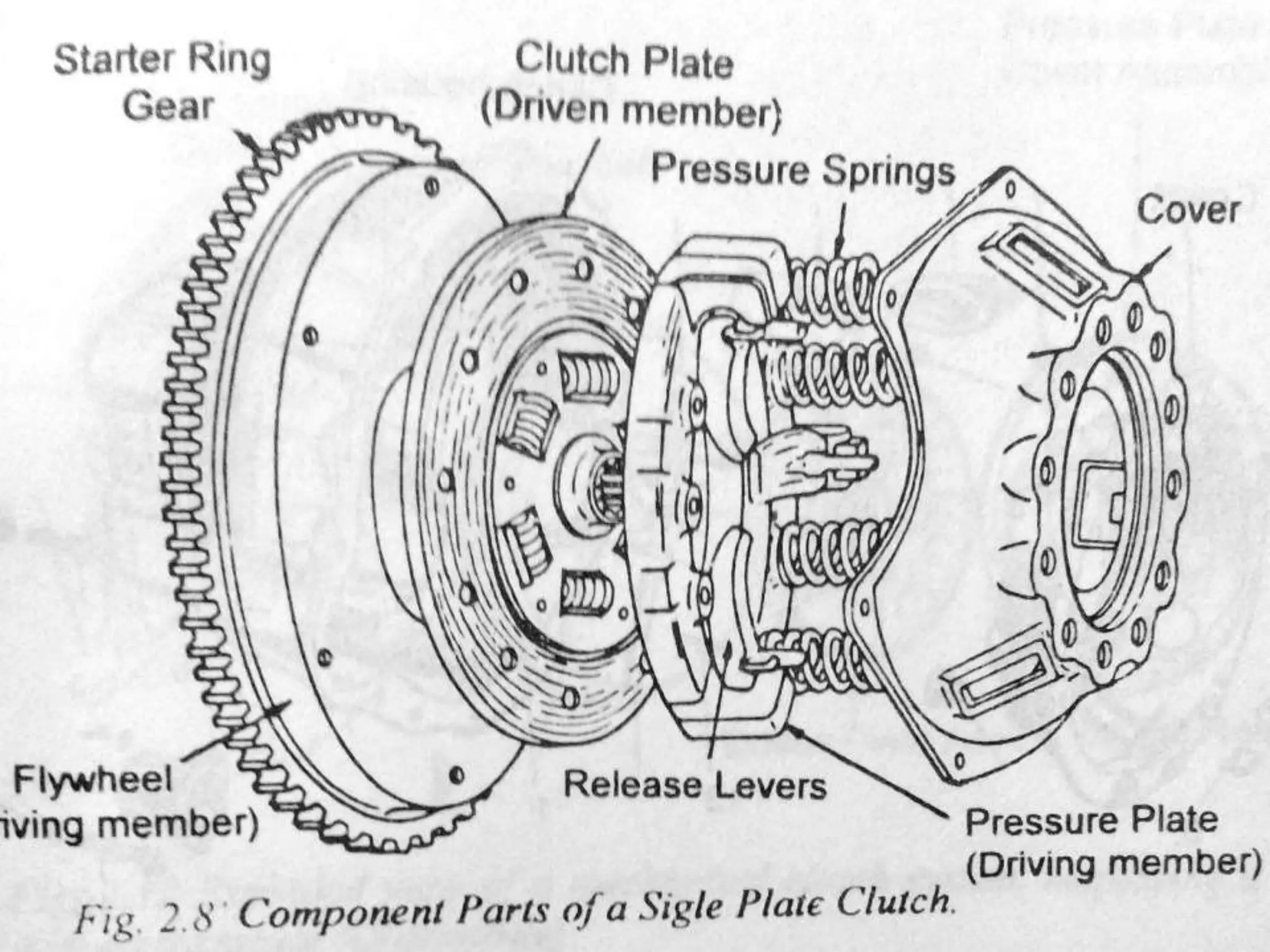
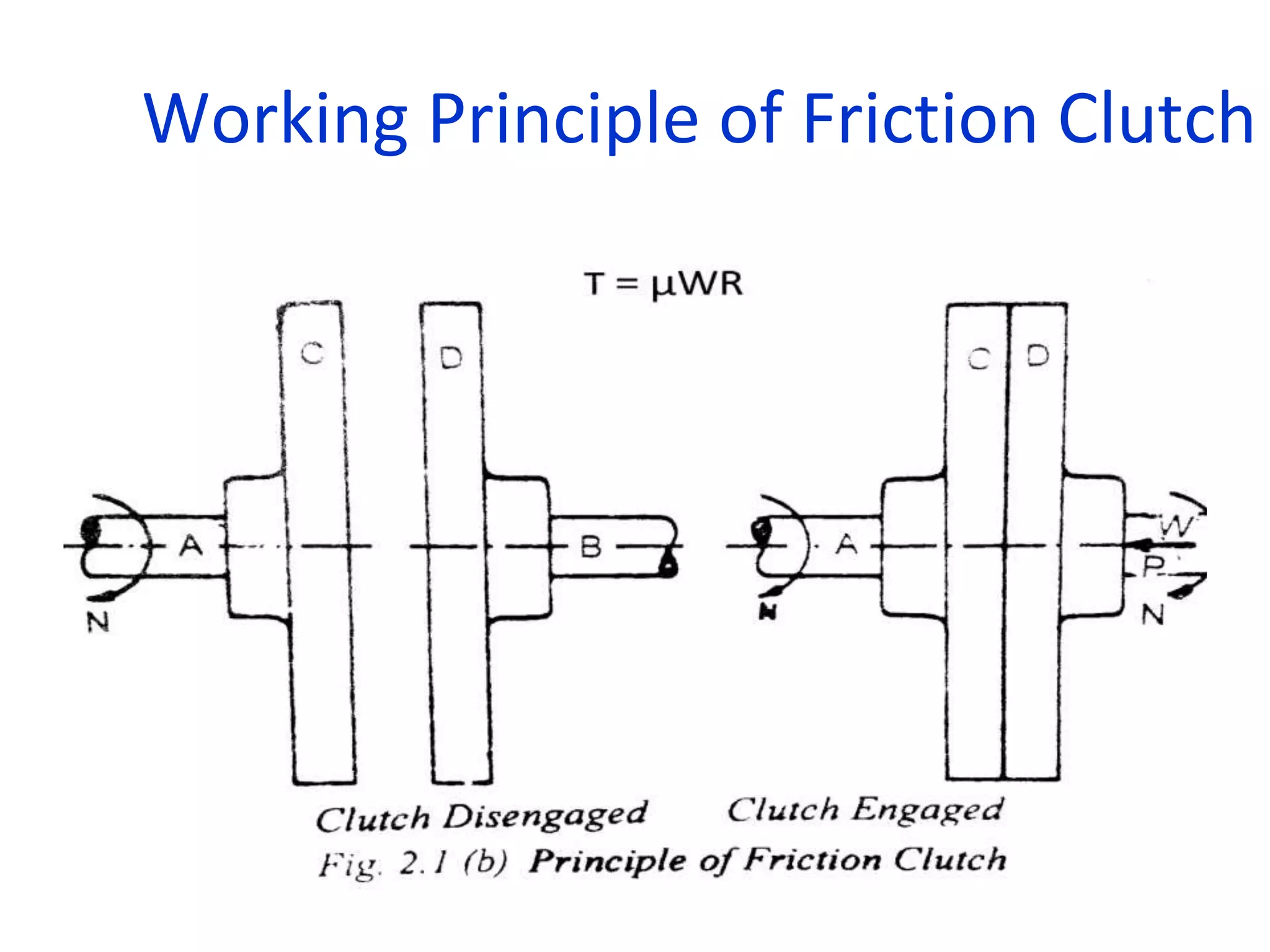
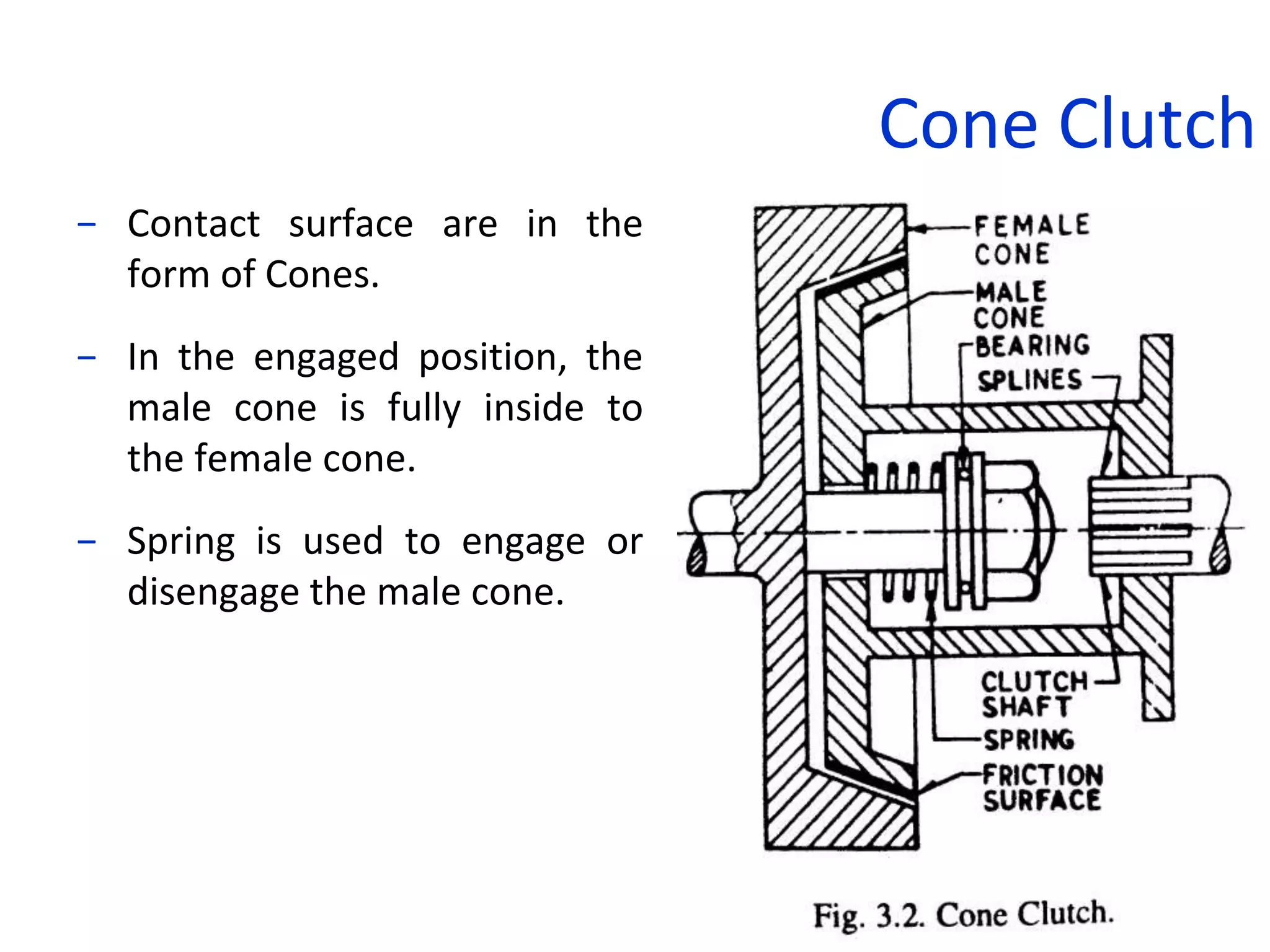
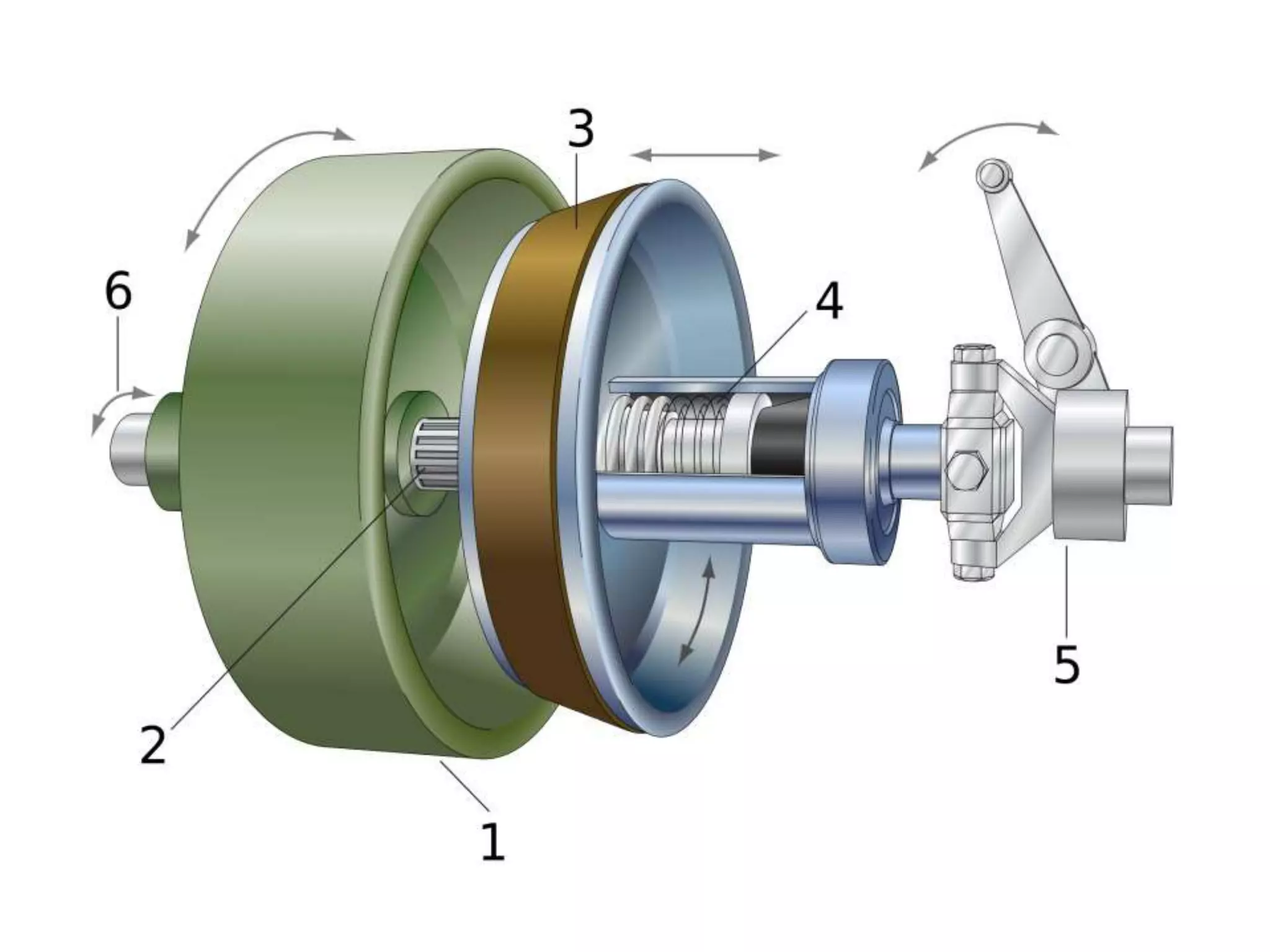
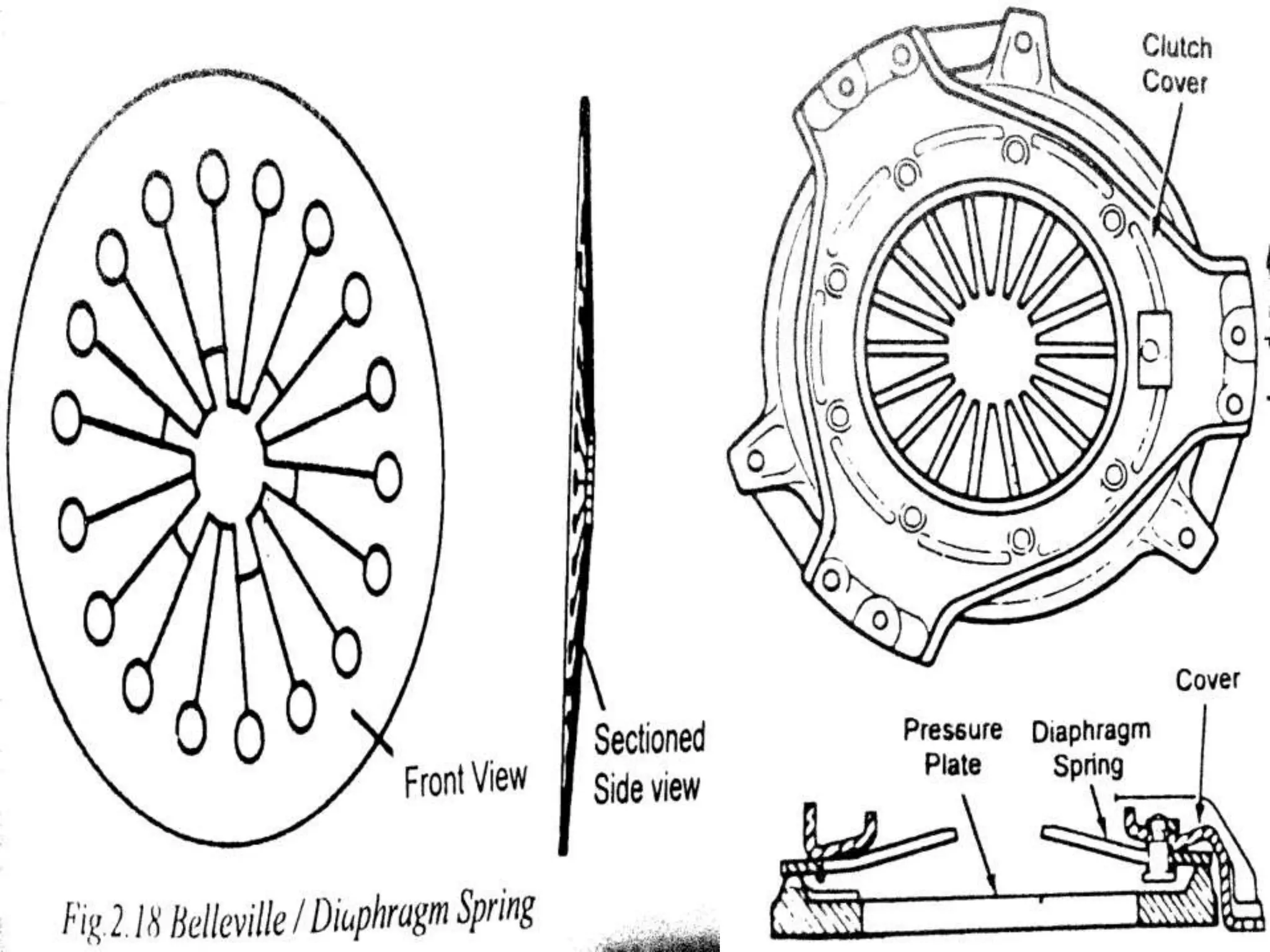
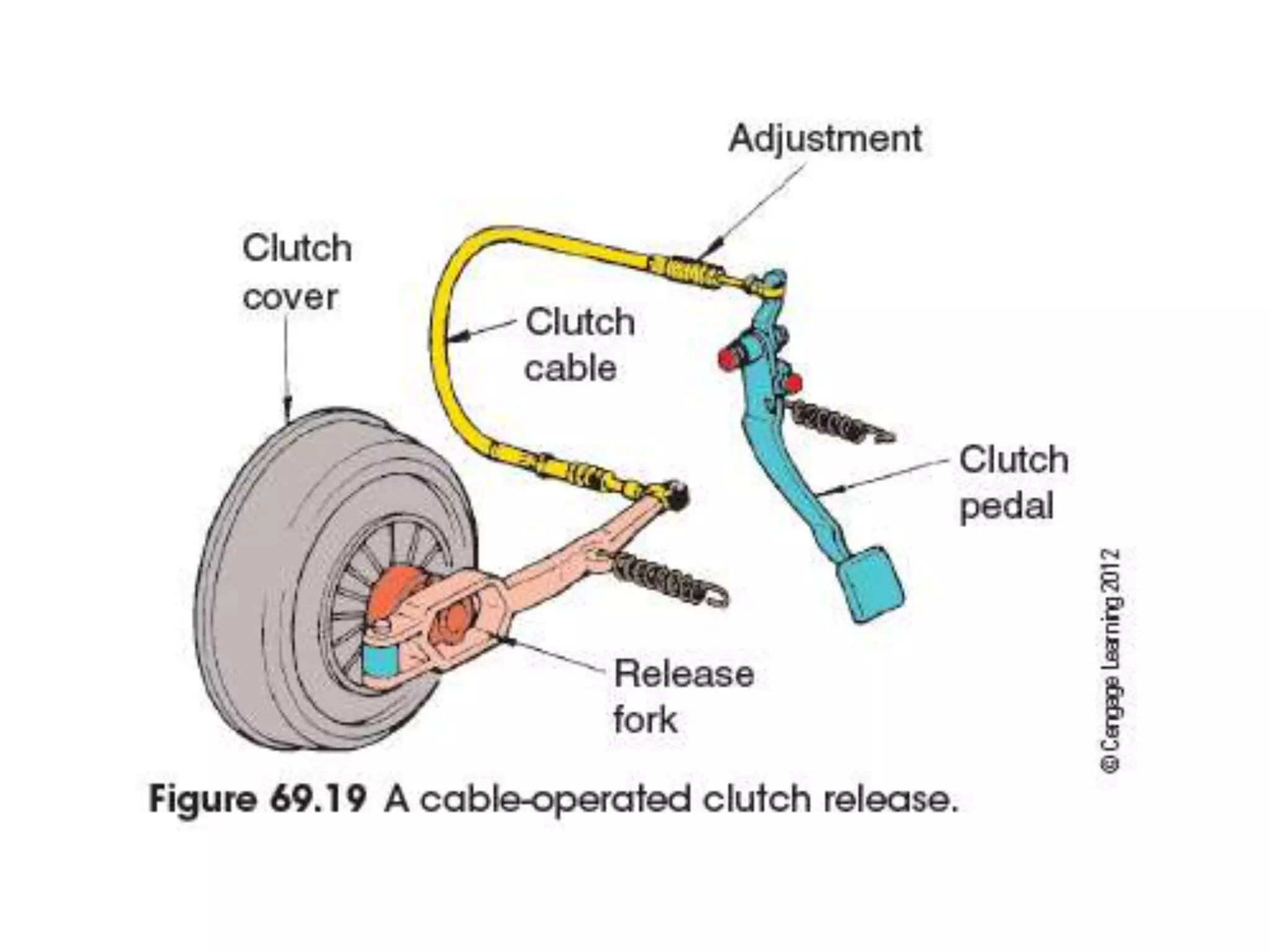
The document discusses clutches, which are intermediate mechanisms placed between the flywheel and gearbox in vehicles. Clutches allow the rotary motion of the shafts to be engaged and disengaged through friction, and serve several purposes: allowing power to flow from the engine to gearbox, enabling changing of gears by engaging and disengaging the gearbox, and allowing the vehicle to be put in neutral. Effective clutches require gradual engagement, effortless operation, heat dissipation, vibration damping, resistance to slipping, and ability to transmit full torque. The main parts of a clutch are the flywheel, friction disc, pressure plate, pressure springs, and release mechanism.