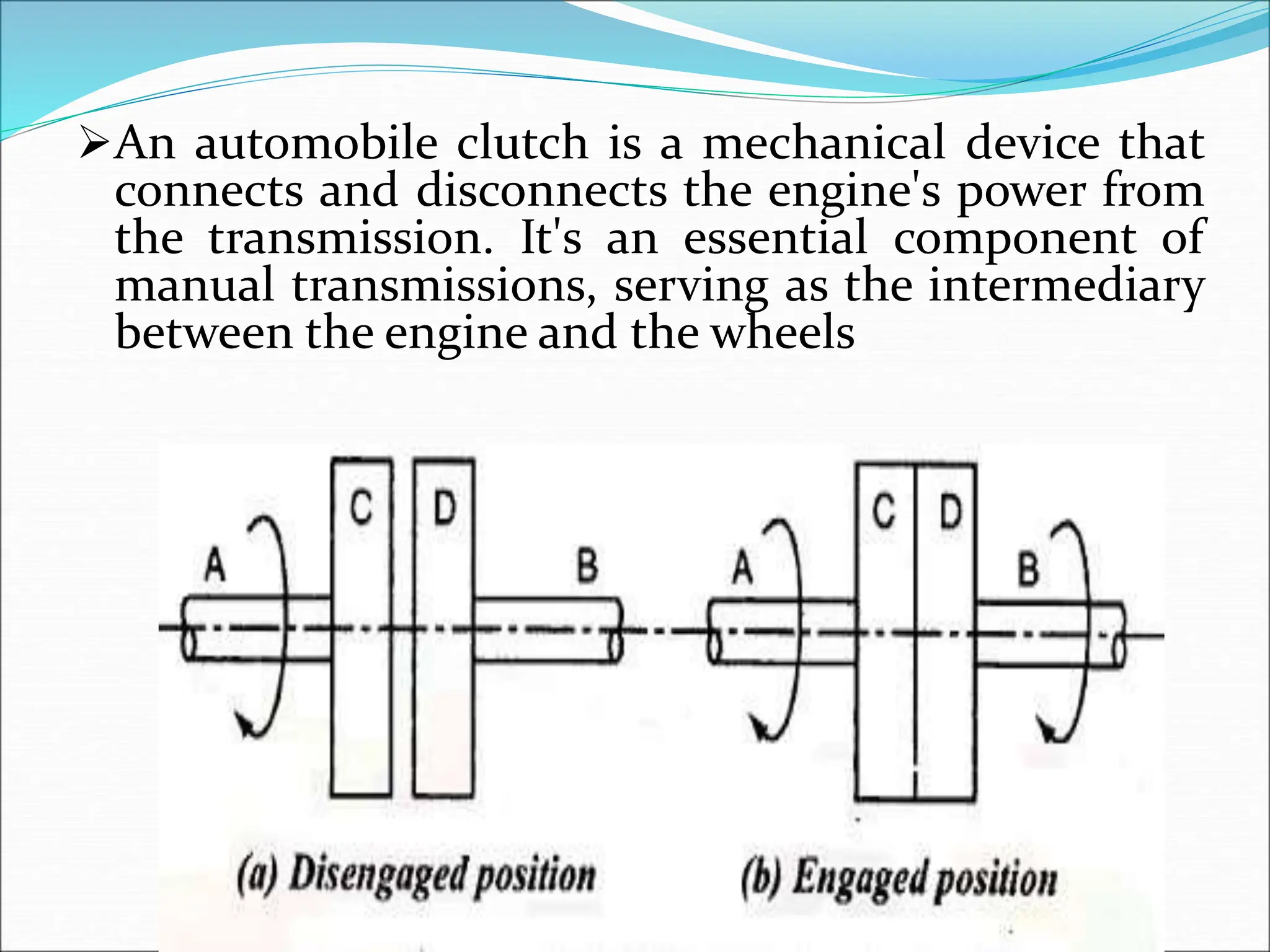
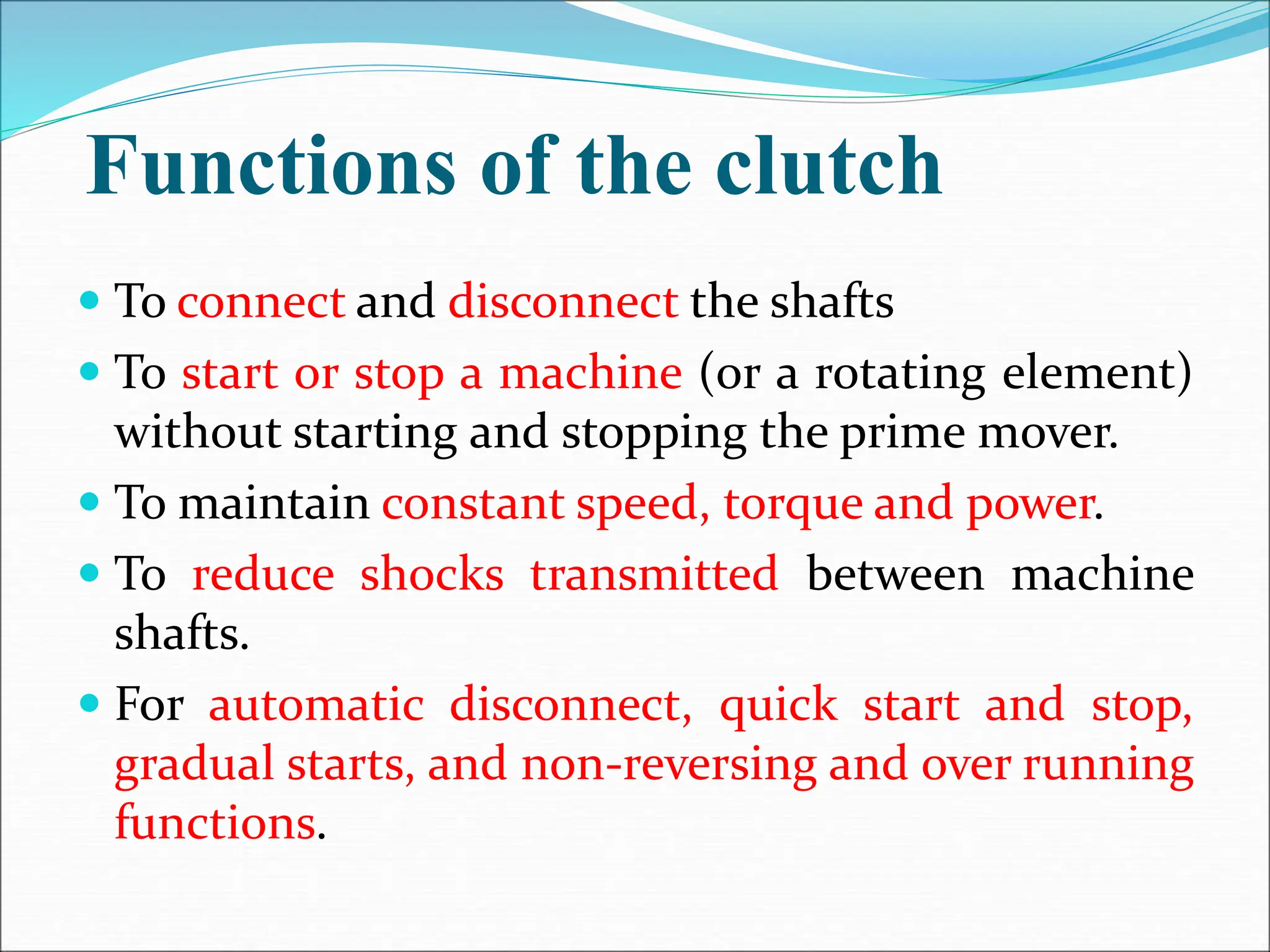
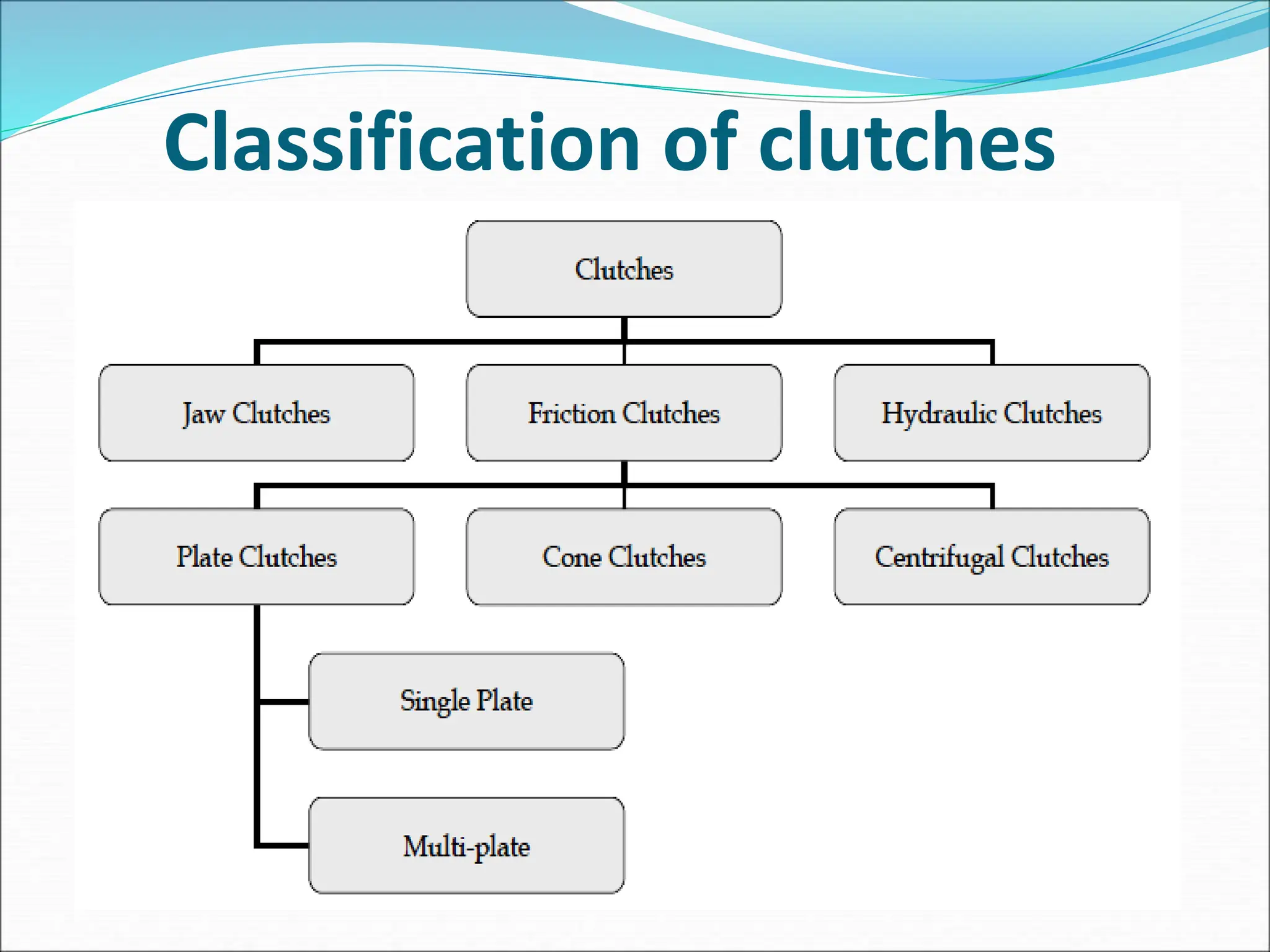
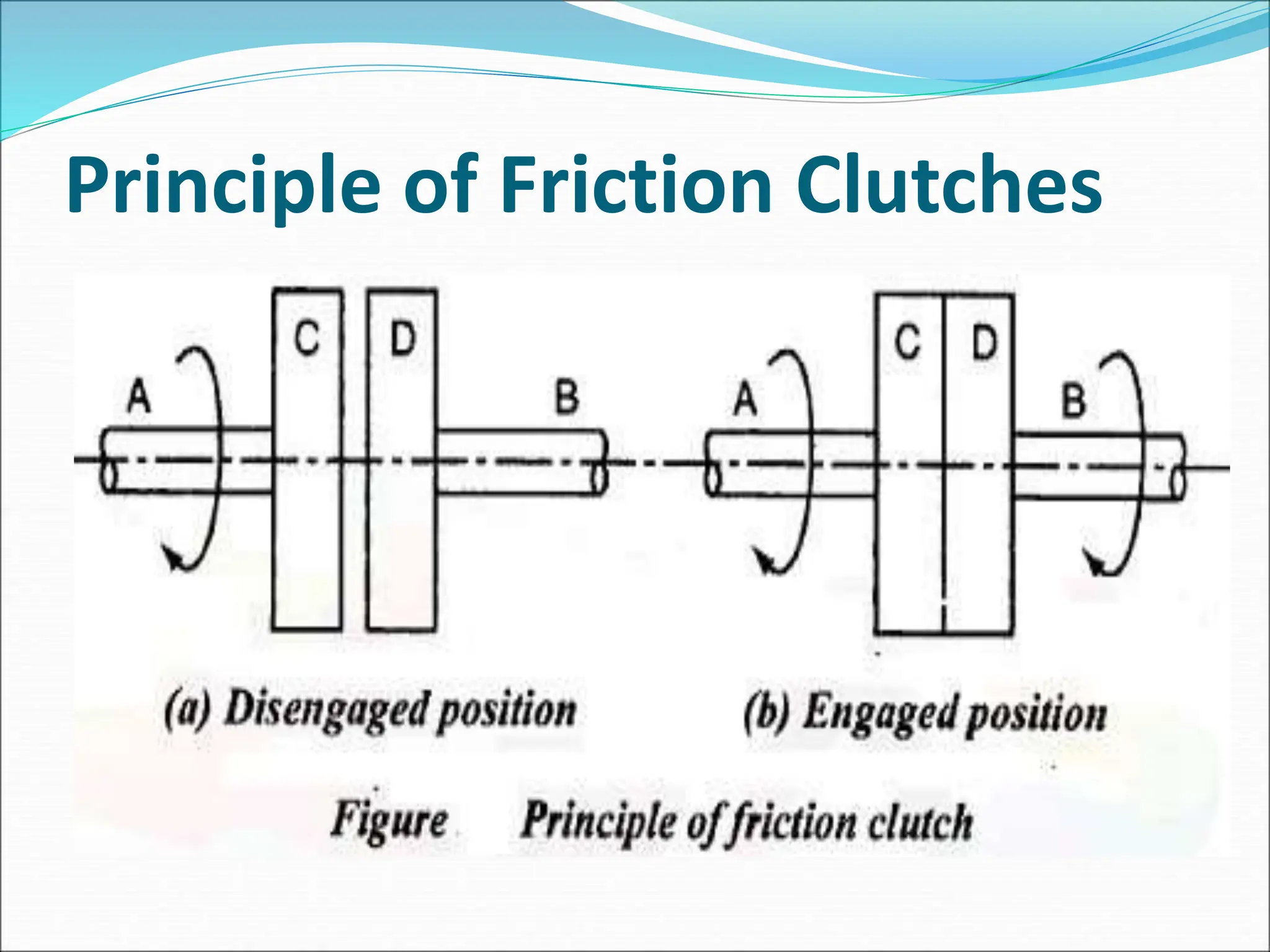
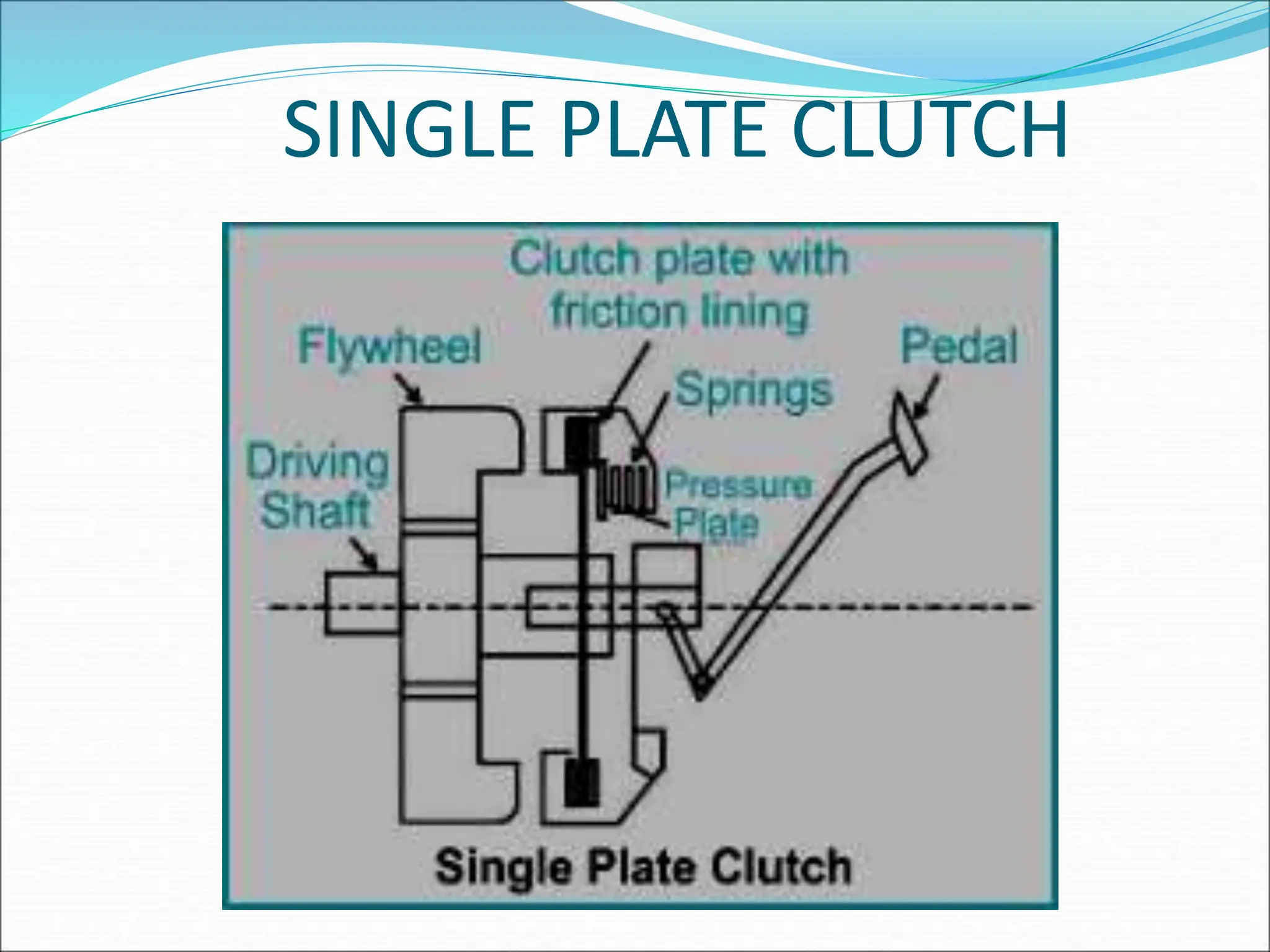
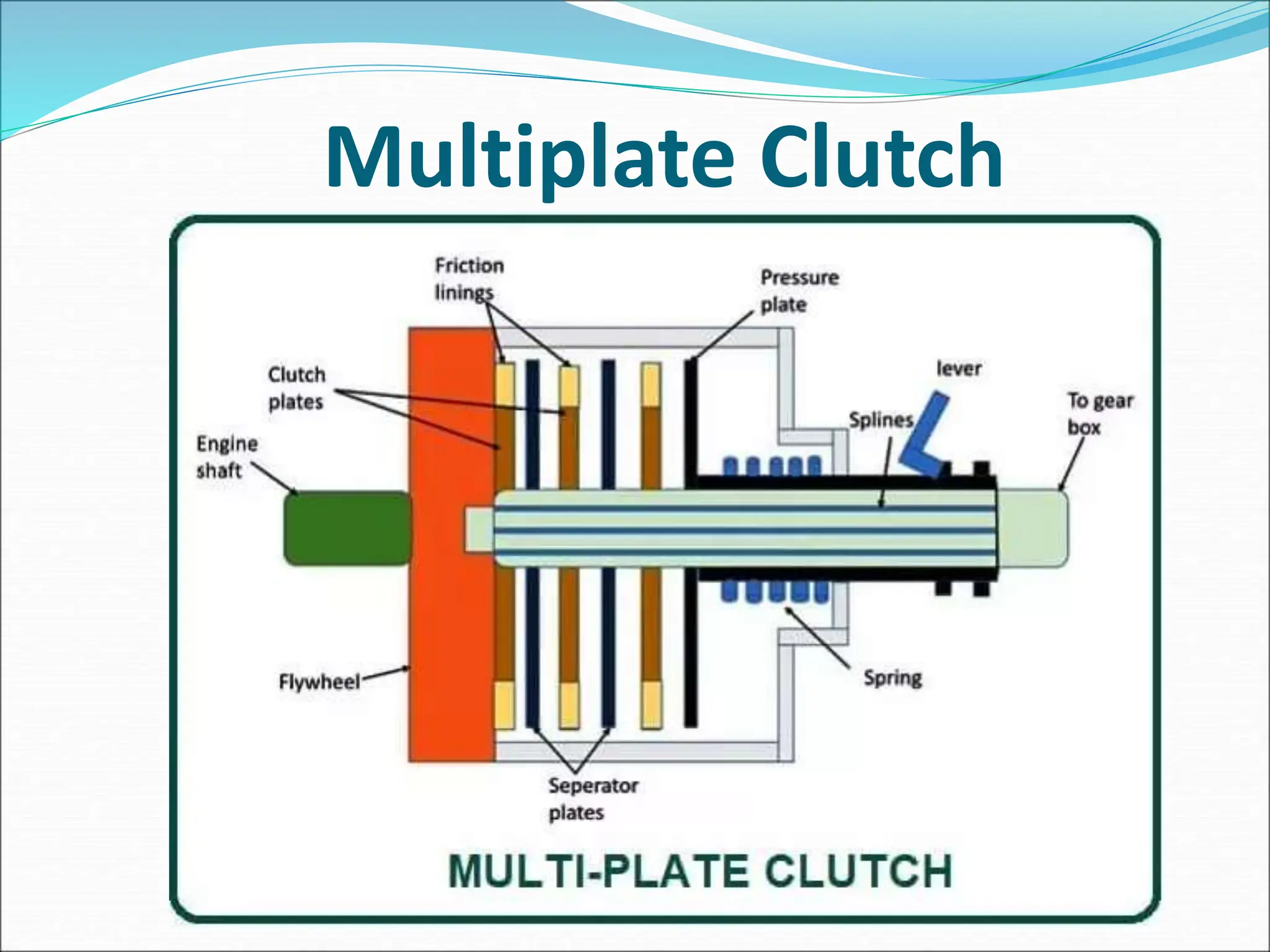
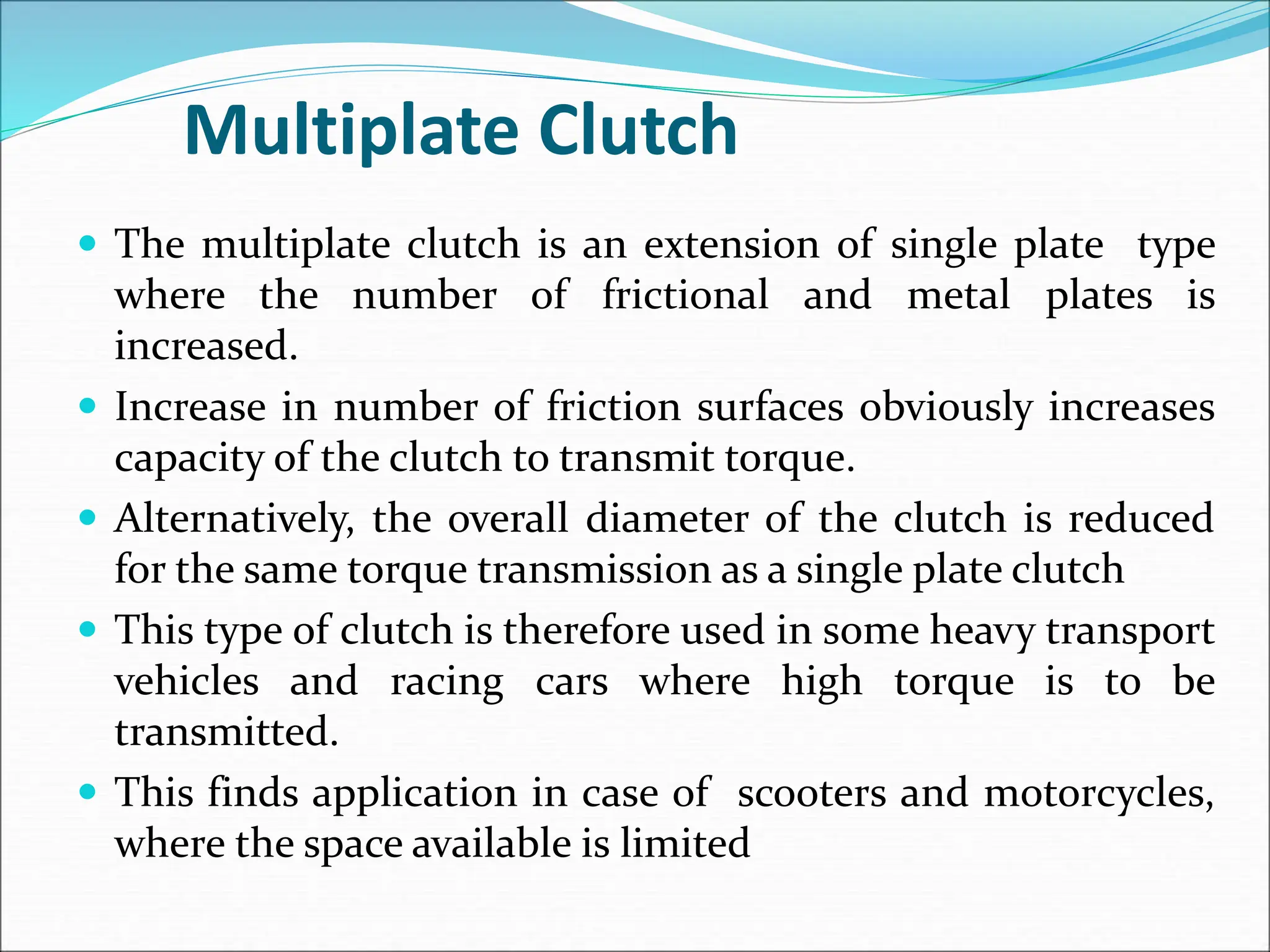
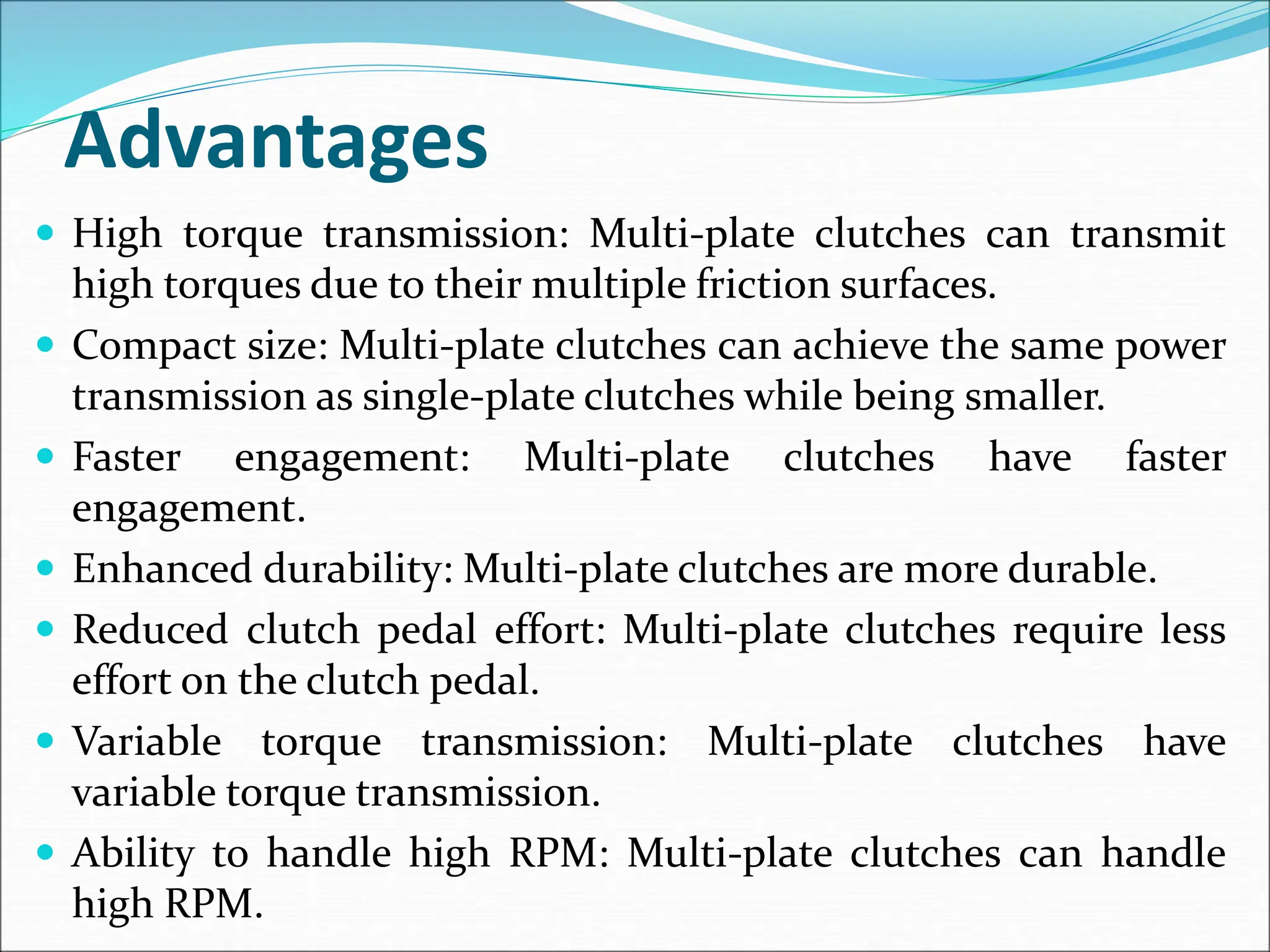
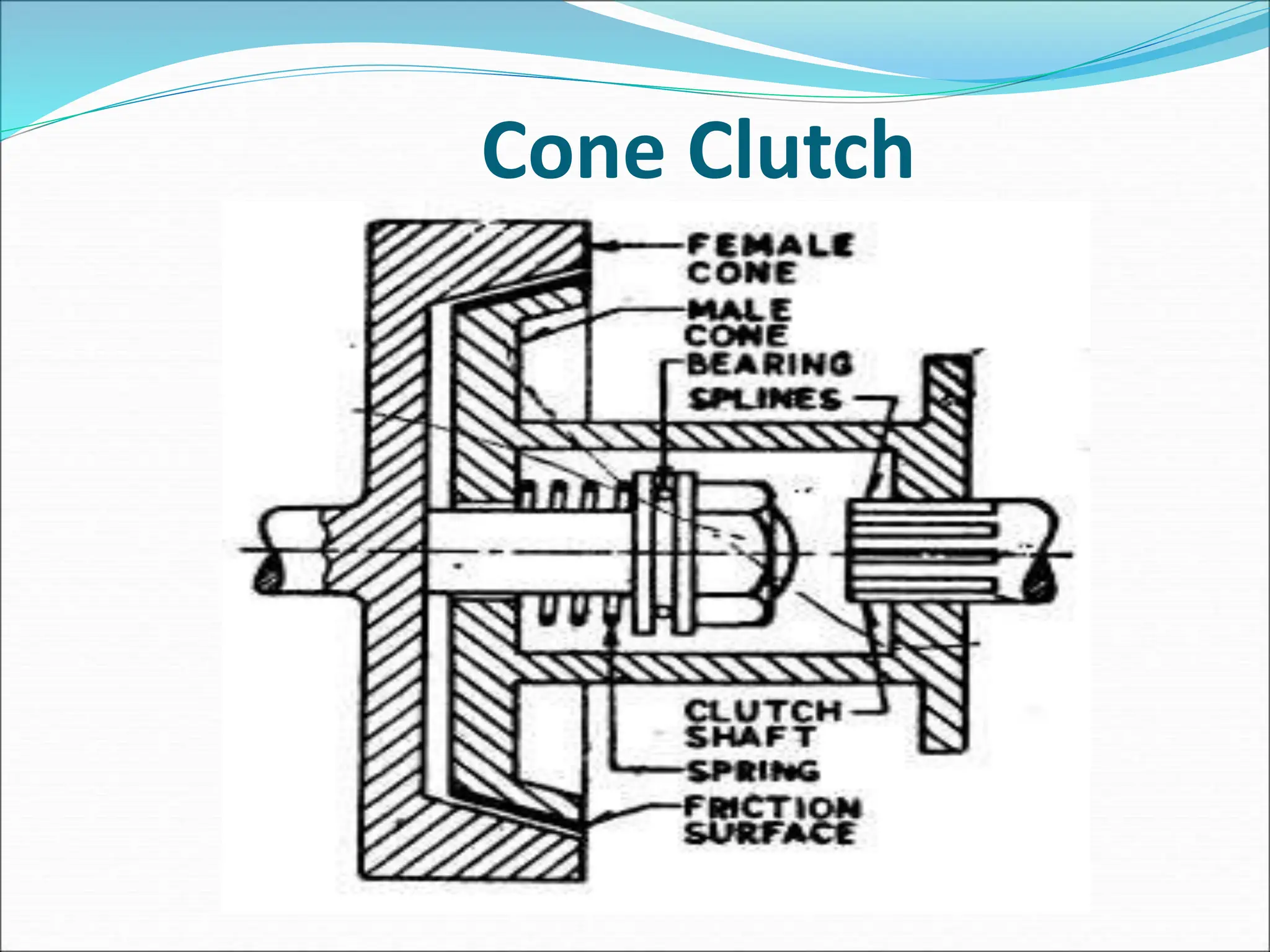
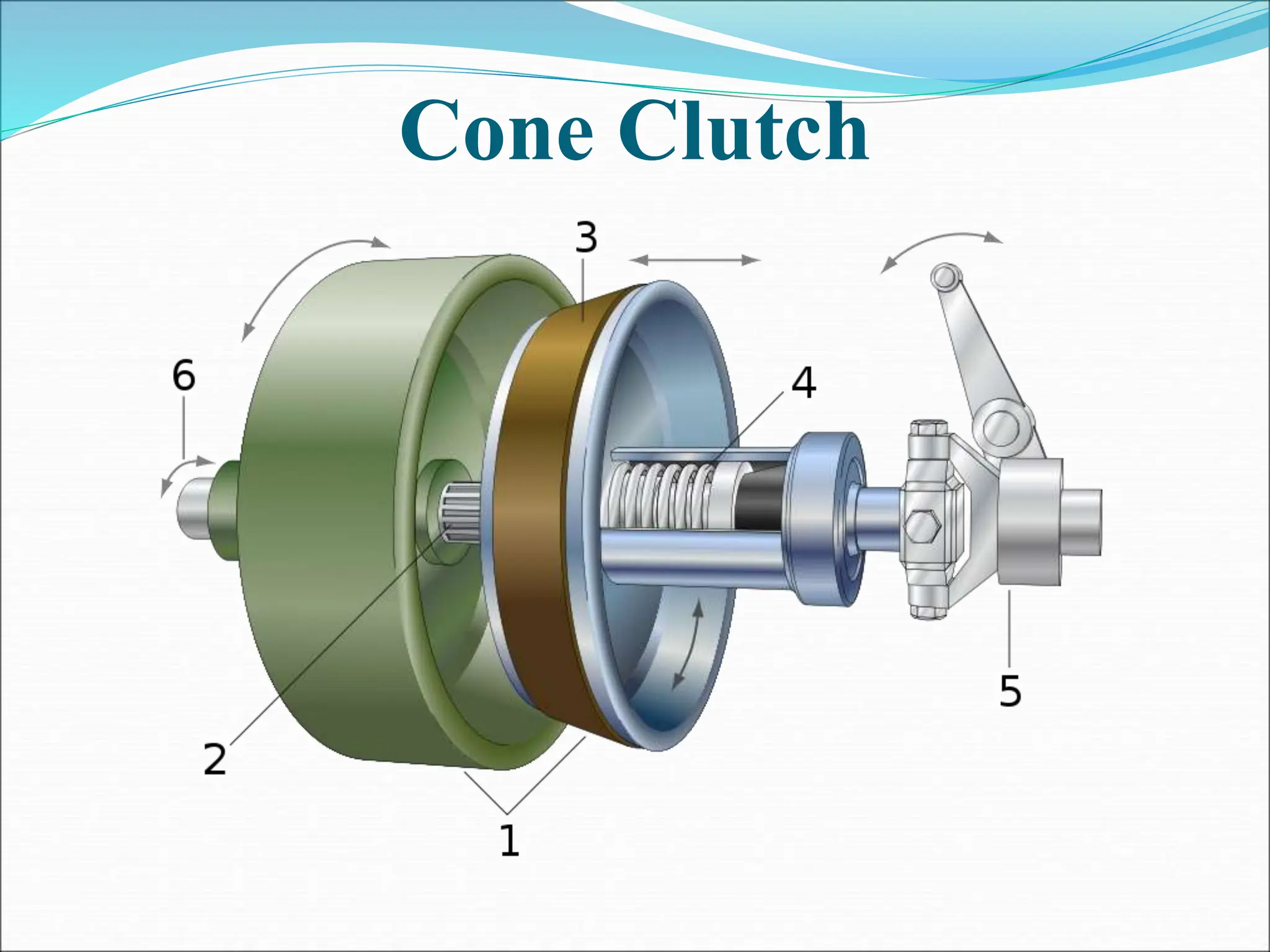
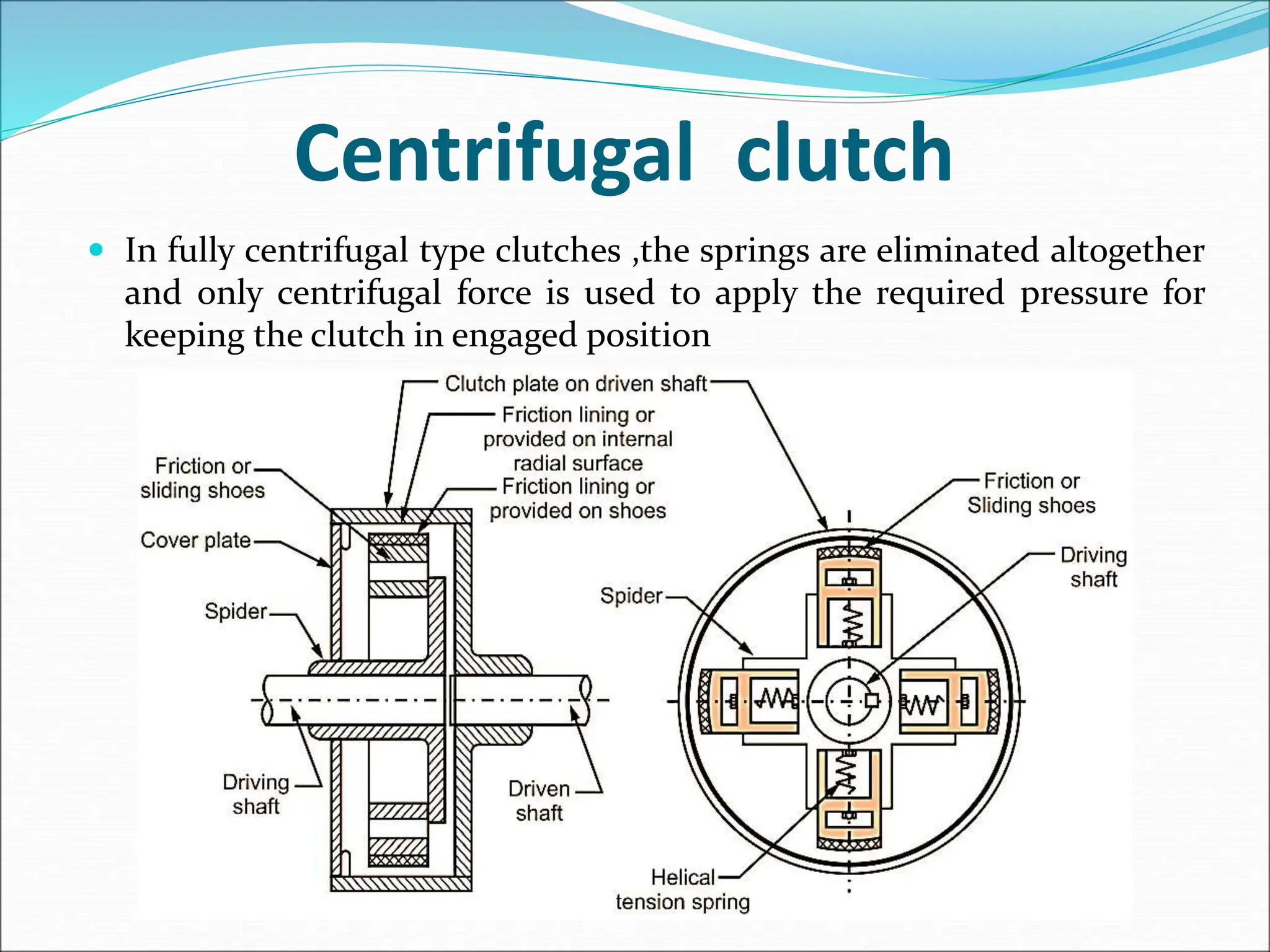
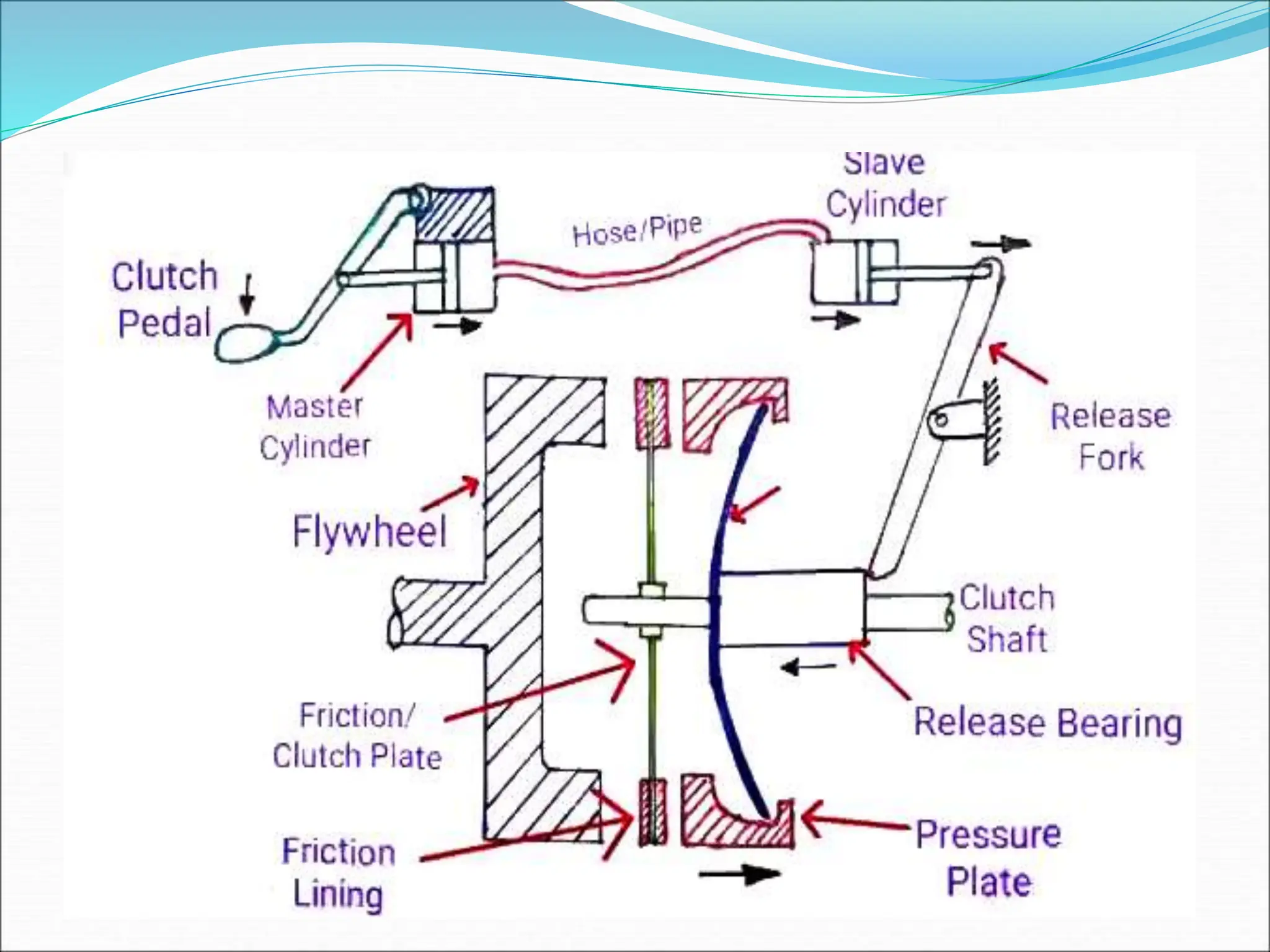
The document discusses different types of clutches used in vehicles. It describes the functions and basic principles of operation for clutches in general. It then provides details on specific clutch types, including single plate clutches, multi-plate clutches, cone clutches, centrifugal clutches and their relative advantages and disadvantages. For example, multi-plate clutches can transmit higher torque but are more complex and expensive than single plate clutches. Centrifugal clutches engage automatically based on engine speed but offer limited control over engagement.