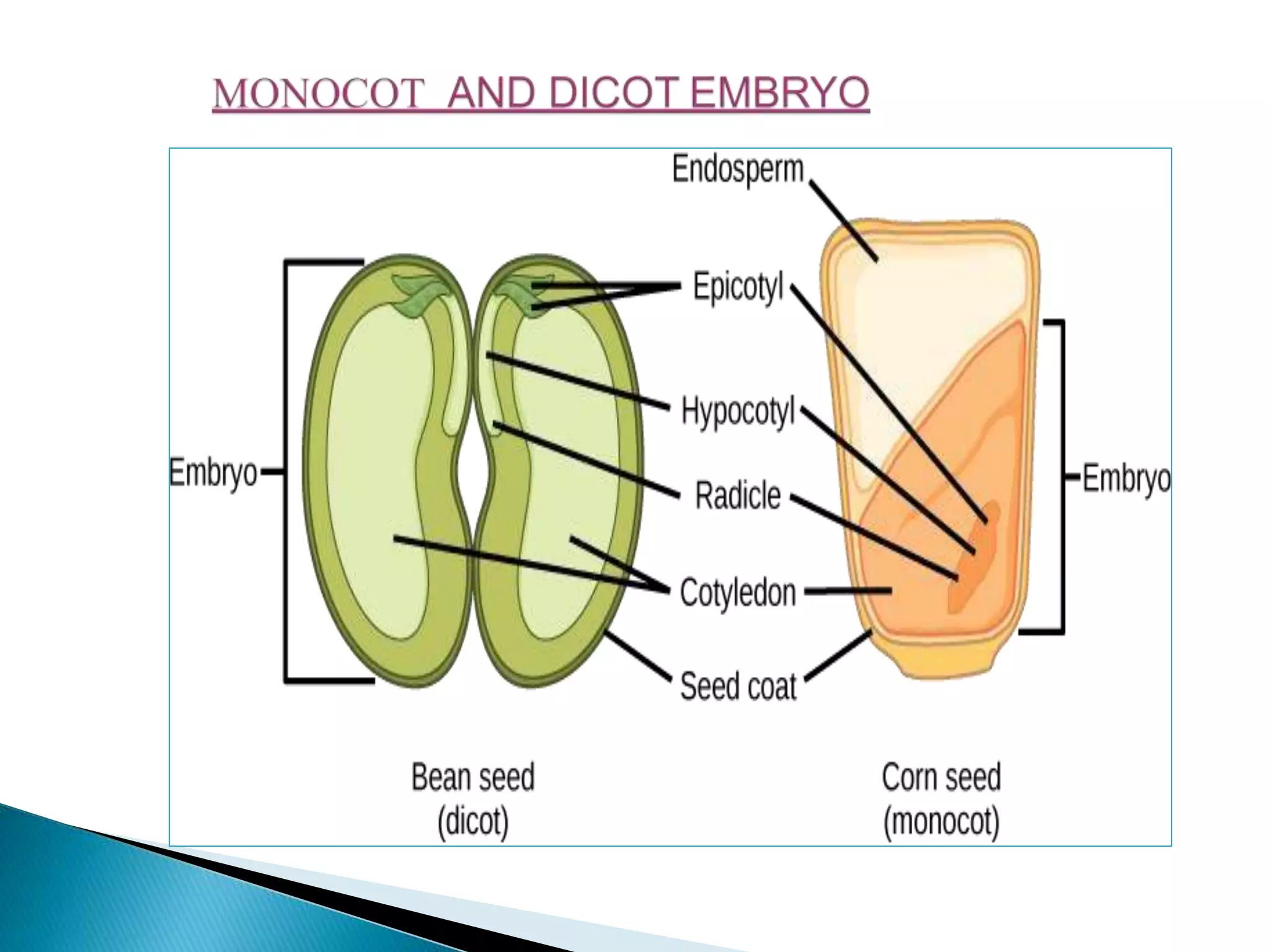
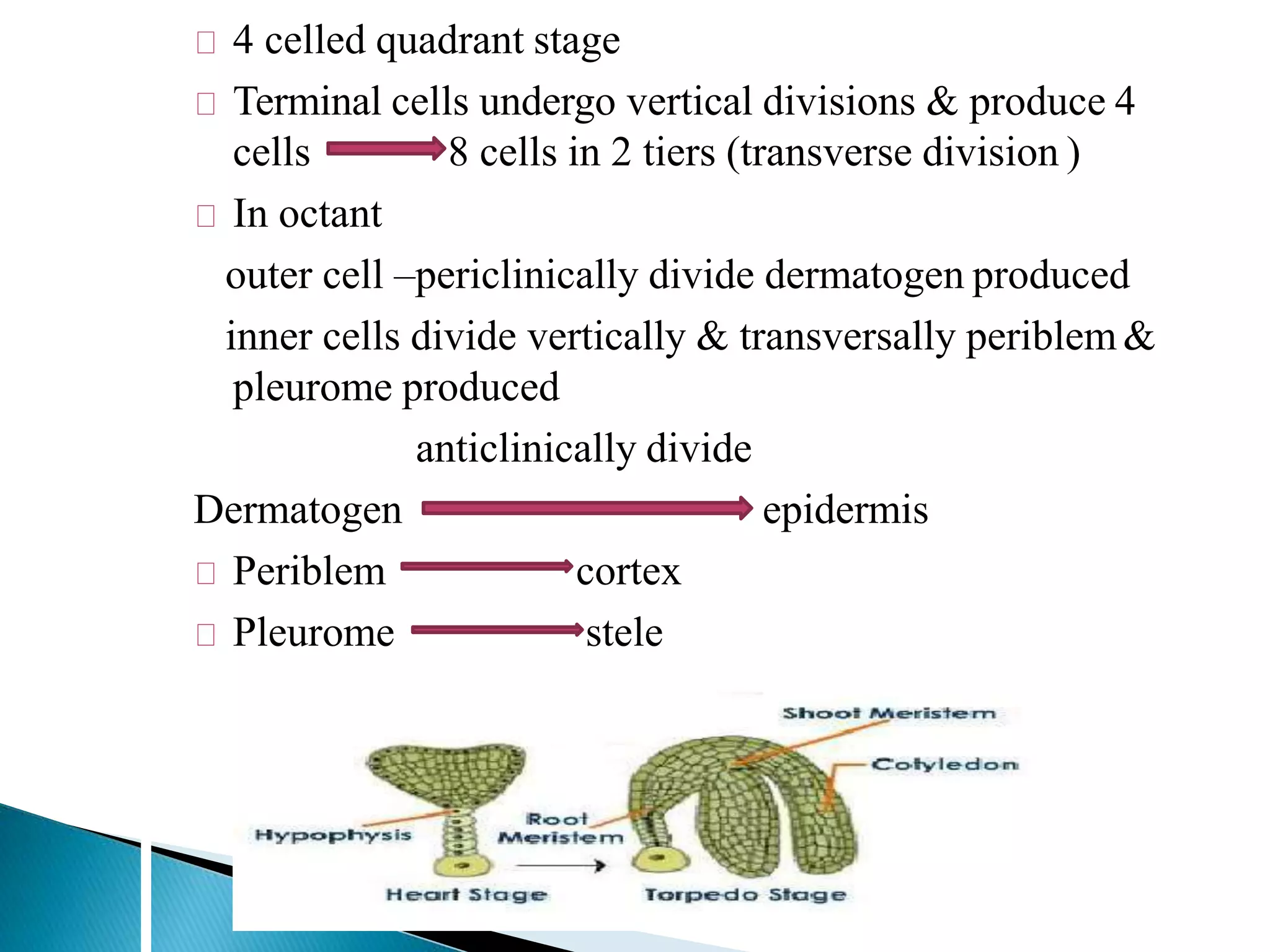
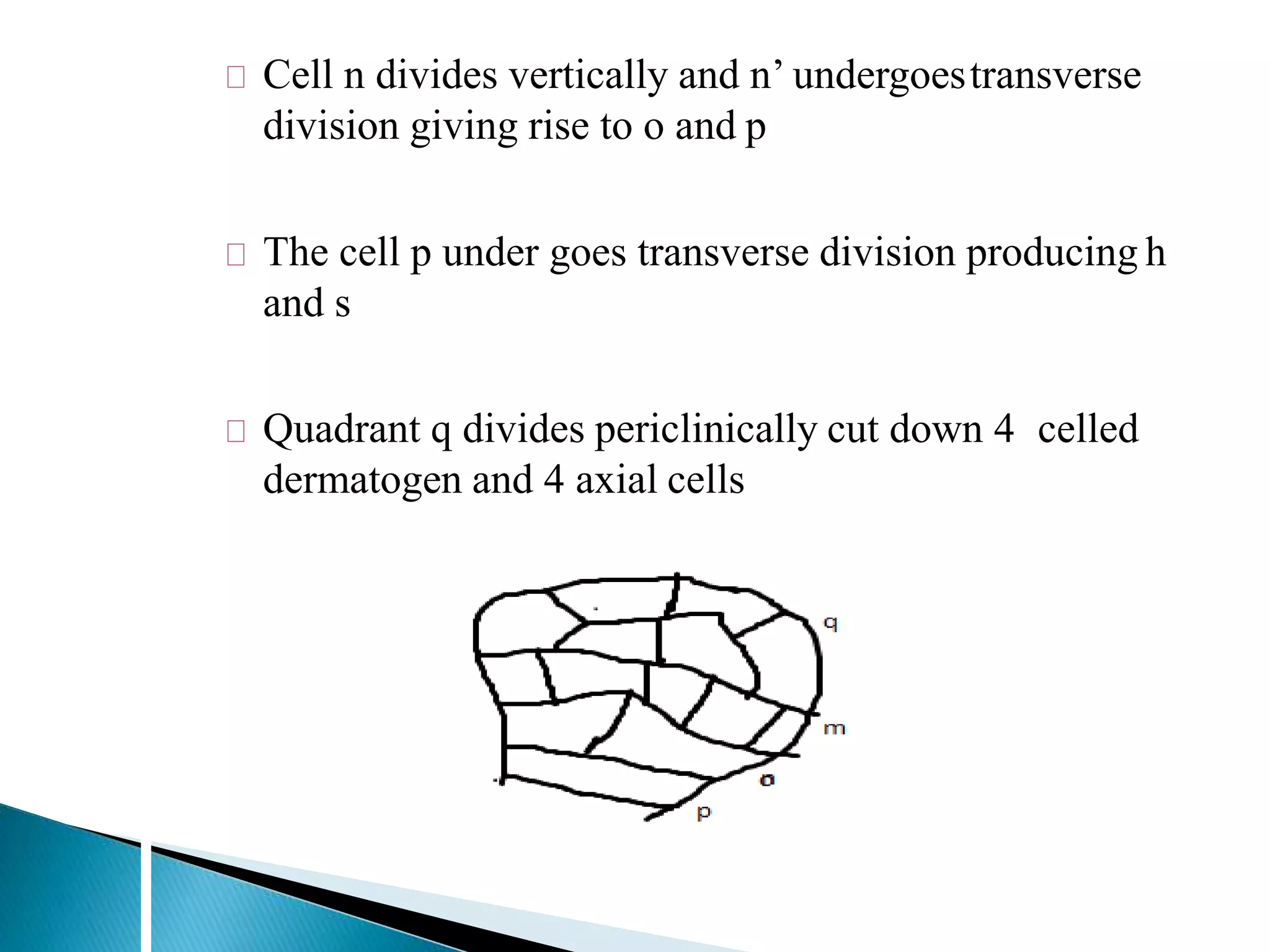
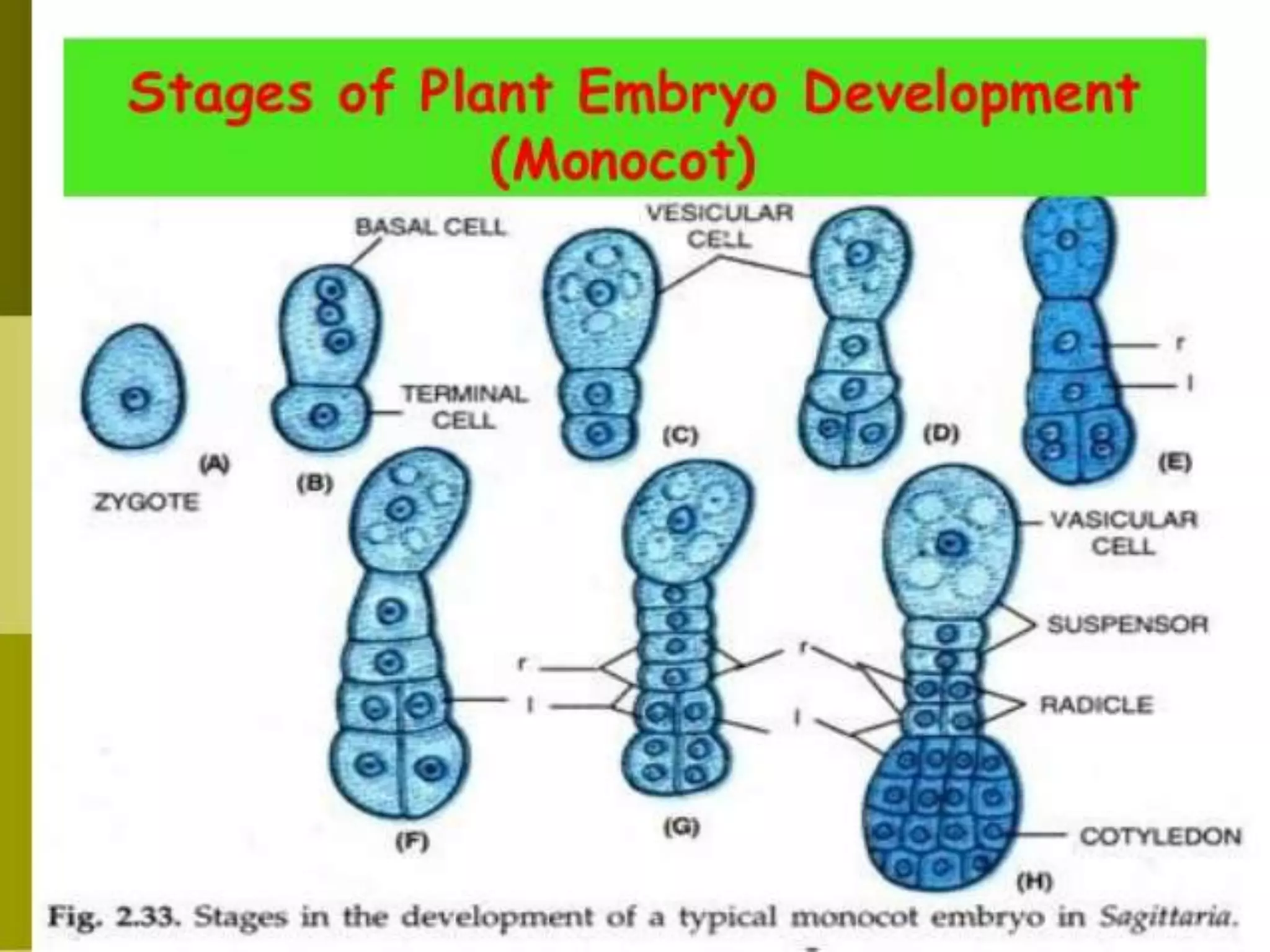
The document summarizes the development of different embryo types in plants, including dicot and monocot embryos. It describes the key stages of proembryo formation from the zygote through cell divisions that establish the suspensor and hypophysis and organize tissue layers. Specific embryo types discussed include Onagrad, Solanad, Caryophyllad, Chenopodiad, and Piperad. The development of the filament tube structure is also outlined.