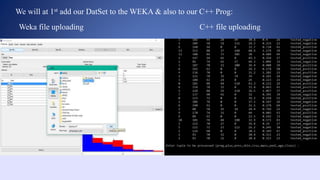
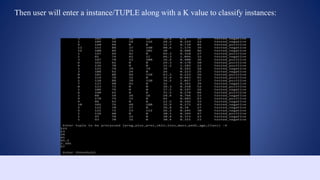
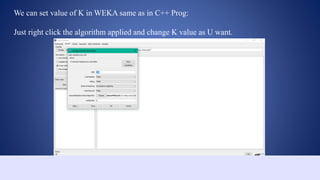
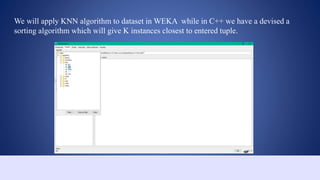
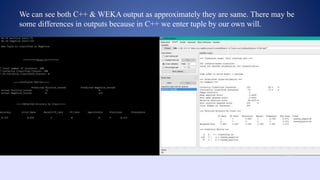
This document outlines a data structures project focused on the C++ implementation of the k-nearest neighbors (k-NN) algorithm, detailing its definition, background, and variations. It explains how k-NN classifies data based on proximity to neighbor points, discusses its advantages and disadvantages, and provides a working process for its implementation in C++. The project involves comparing the outputs of k-NN using C++ and Weka software for consistency.