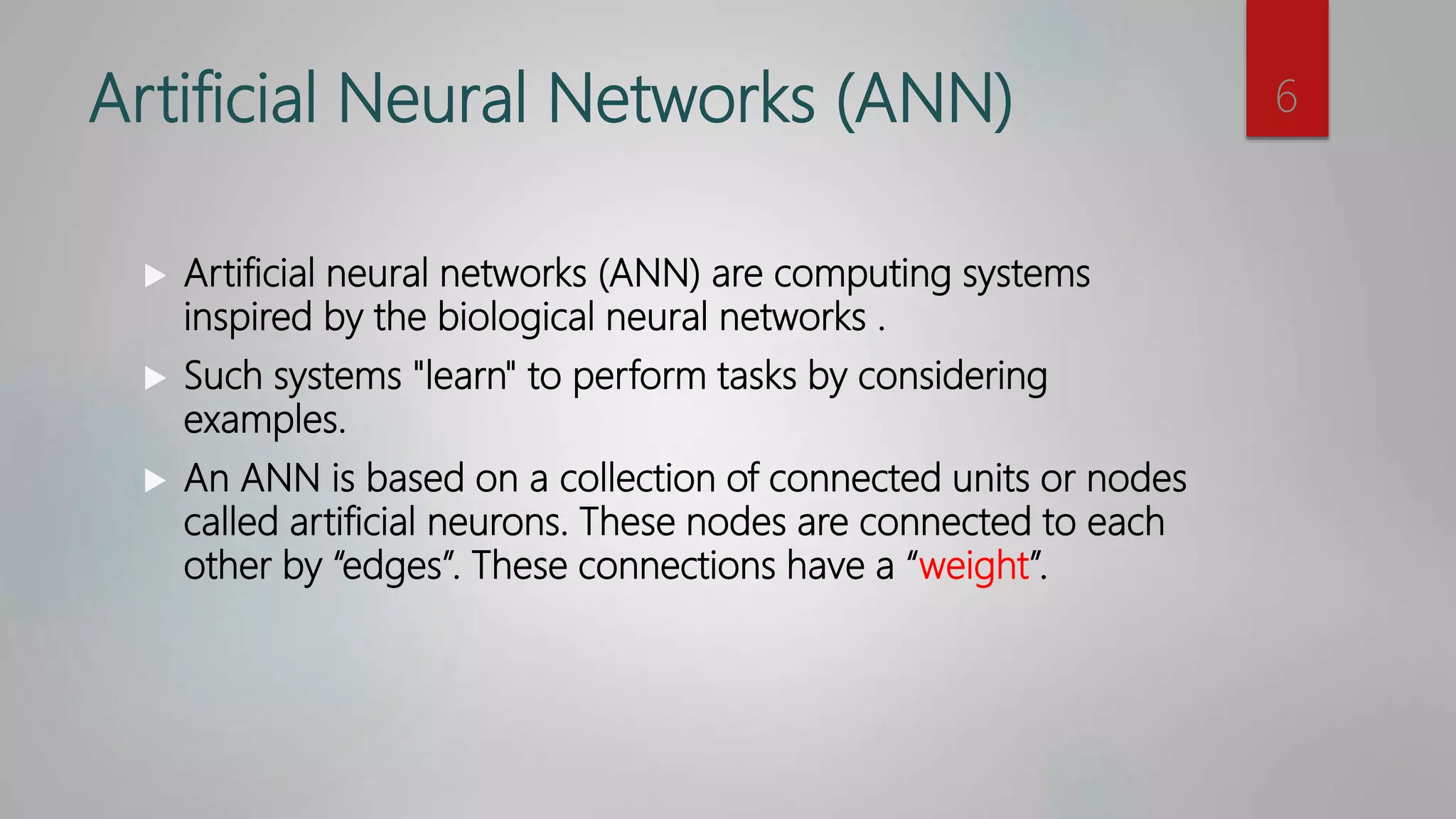
The document provides an overview of machine learning, focusing on artificial neural networks (ANN) and the perceptron algorithm for supervised learning. It explains various machine learning approaches, the structure of ANNs, the perceptron learning process, and principles such as bias and learning rate. Additionally, it includes a simple perceptron example and homework assignments related to designing an ANN and applying the perceptron algorithm.













![Algorithm of Perceptron
Get the training data (inputs and outputs).
Set the weights (W1 and W2) to random values.
While Global Error is not zero
For each input value in the training dataset
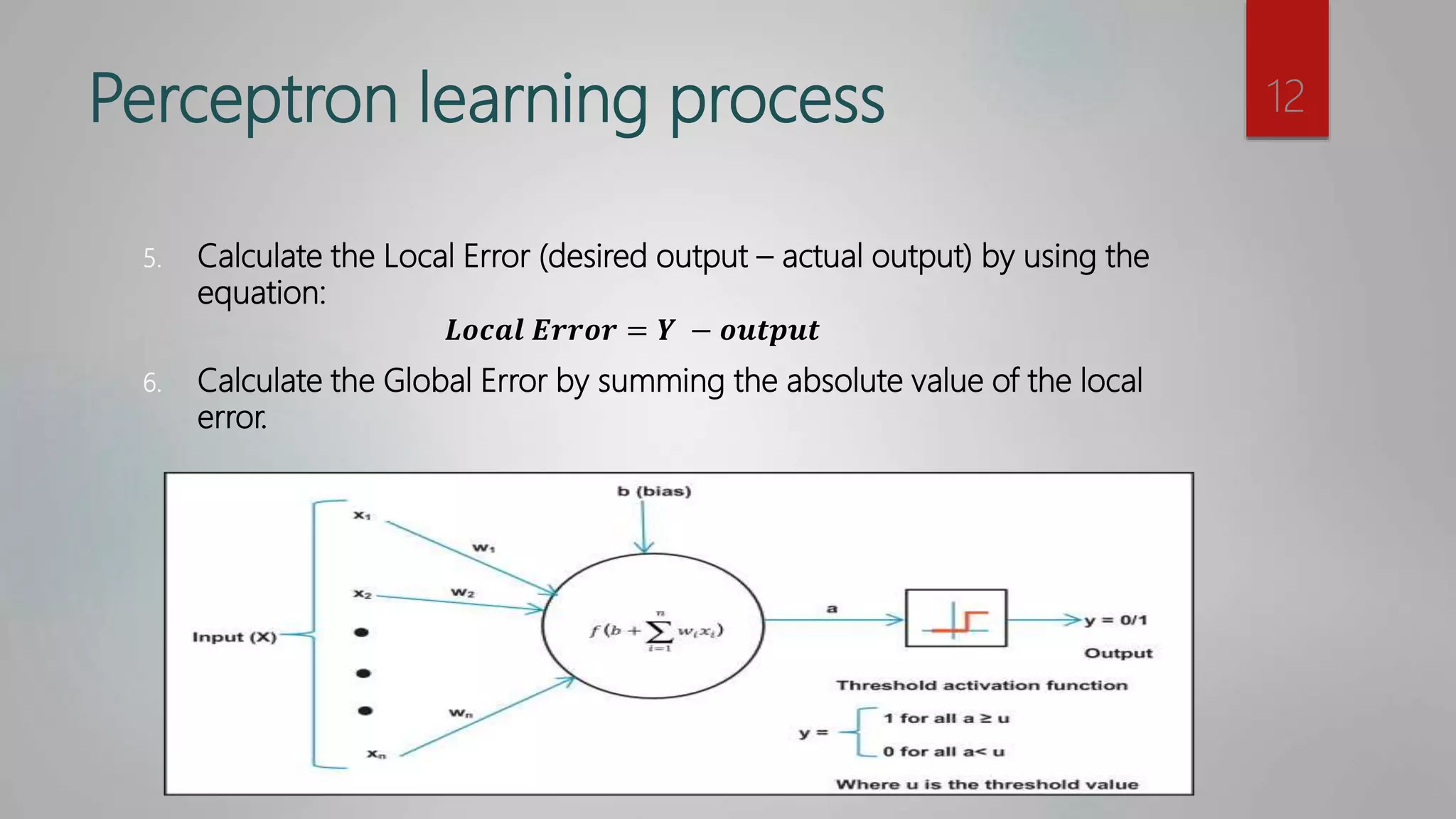
Calculate the output of the perceptron. By
1. Sum = Input1[i] * W1 + Input2[i] * W2
2. Apply activation function (e.g. Hard Limits)
Calculate the Local Error for this input. By
Local Error = Desired output – Actual output
If the Local Error is not zero, update both weights (W1 and W2) by
W[ j]=w[ j] + Learning rate * Local Error * Input[i][ j]
Global Error += Absolute of Local Error
End for
End while
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perceptroninann-190726162654/75/Perceptron-in-ANN-16-2048.jpg)


