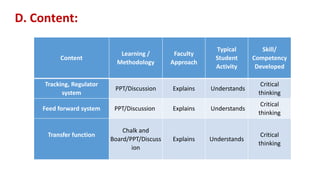
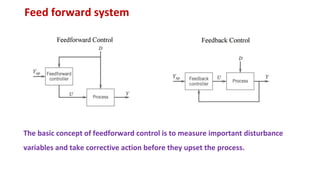
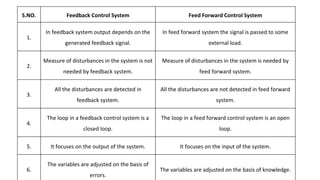
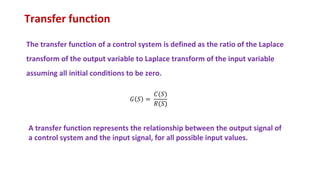
The document provides an overview of a control system engineering session presented by Mr. A. M. Suryawanshi, covering basic concepts such as tracking, regulator systems, feedforward systems, and transfer functions. It outlines the differences between feedback and feedforward systems and discusses their respective characteristics and applications. Additionally, it highlights student evaluation questions and the modeling of electrical and mechanical systems.