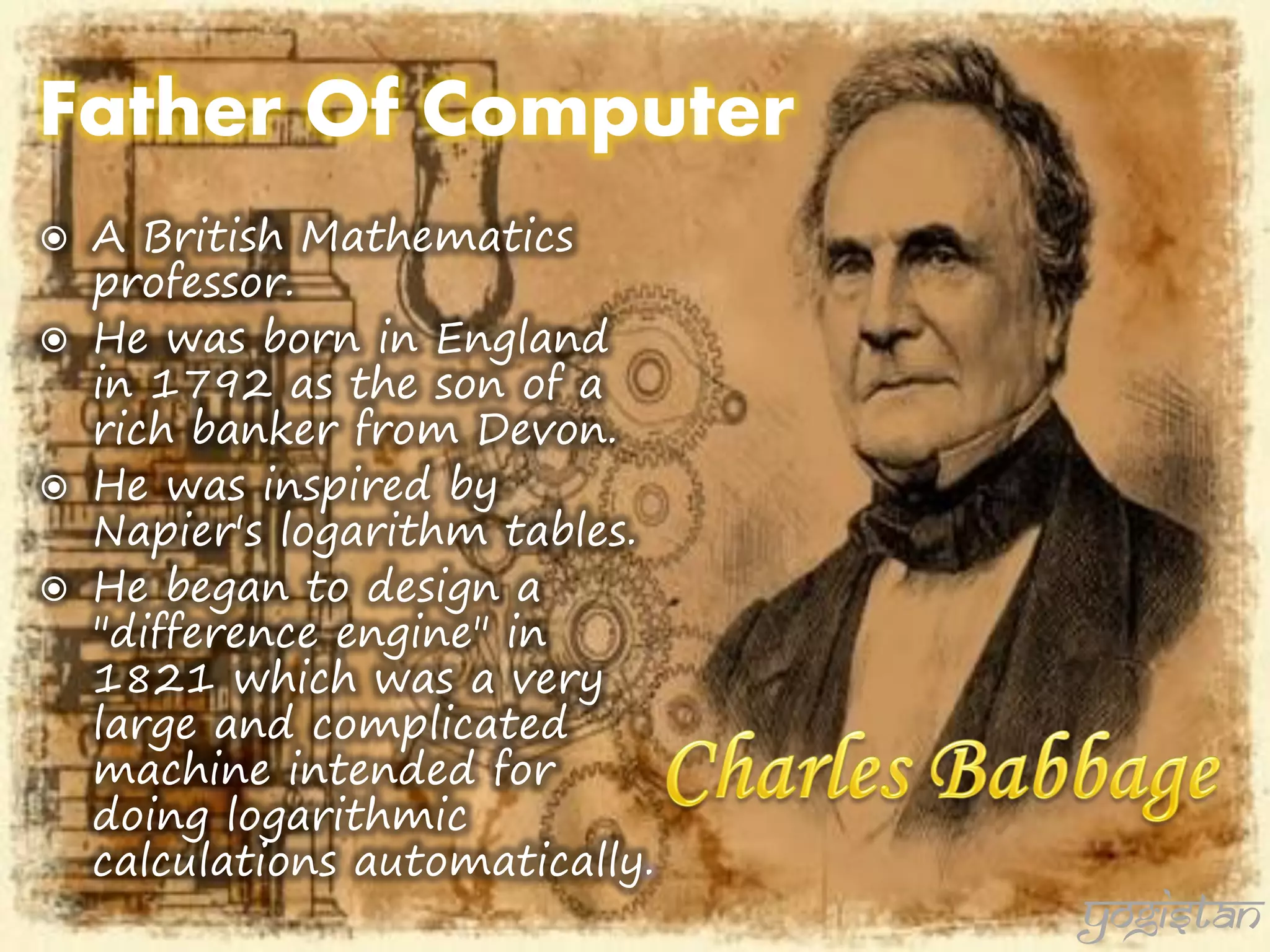
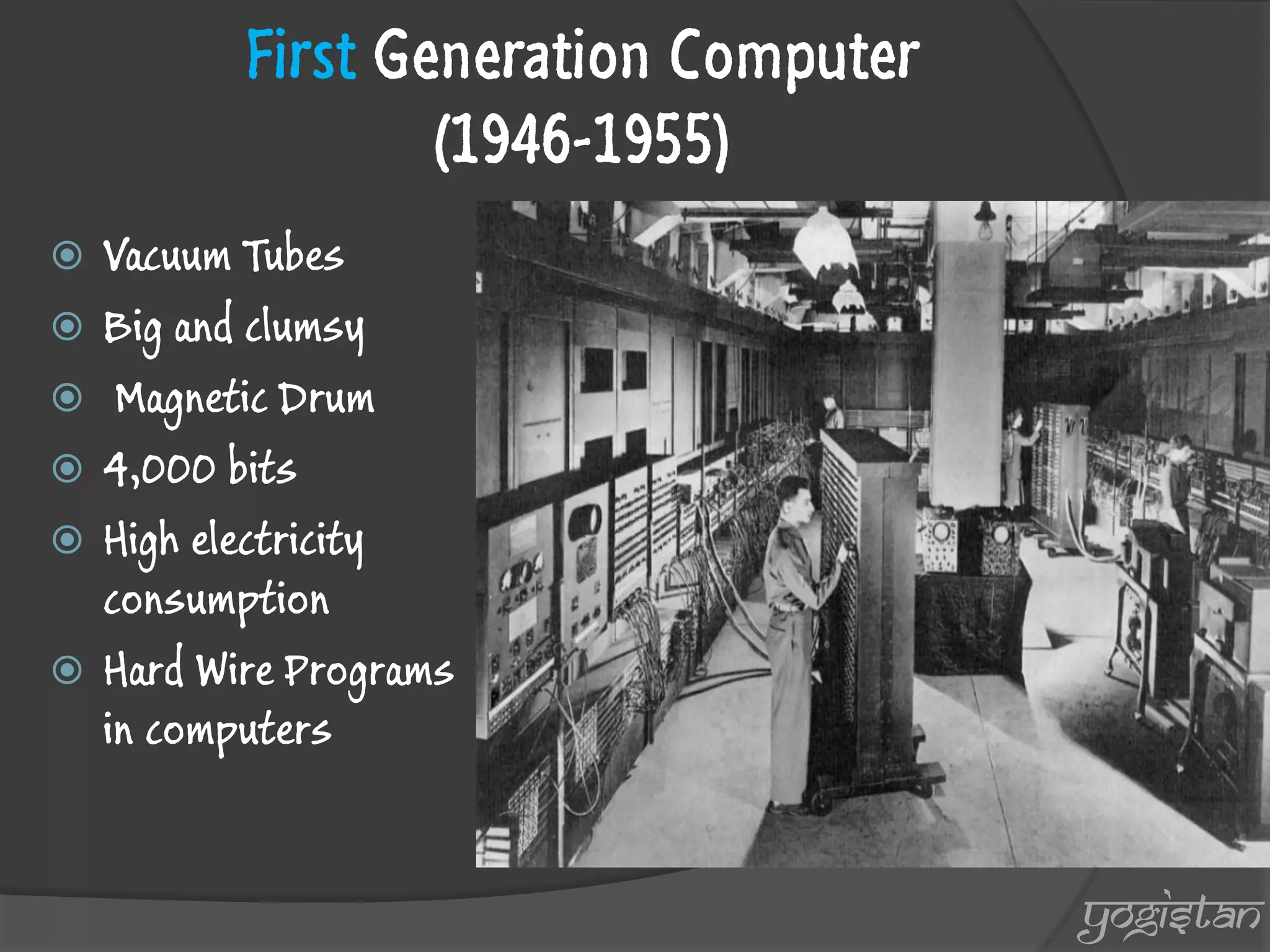
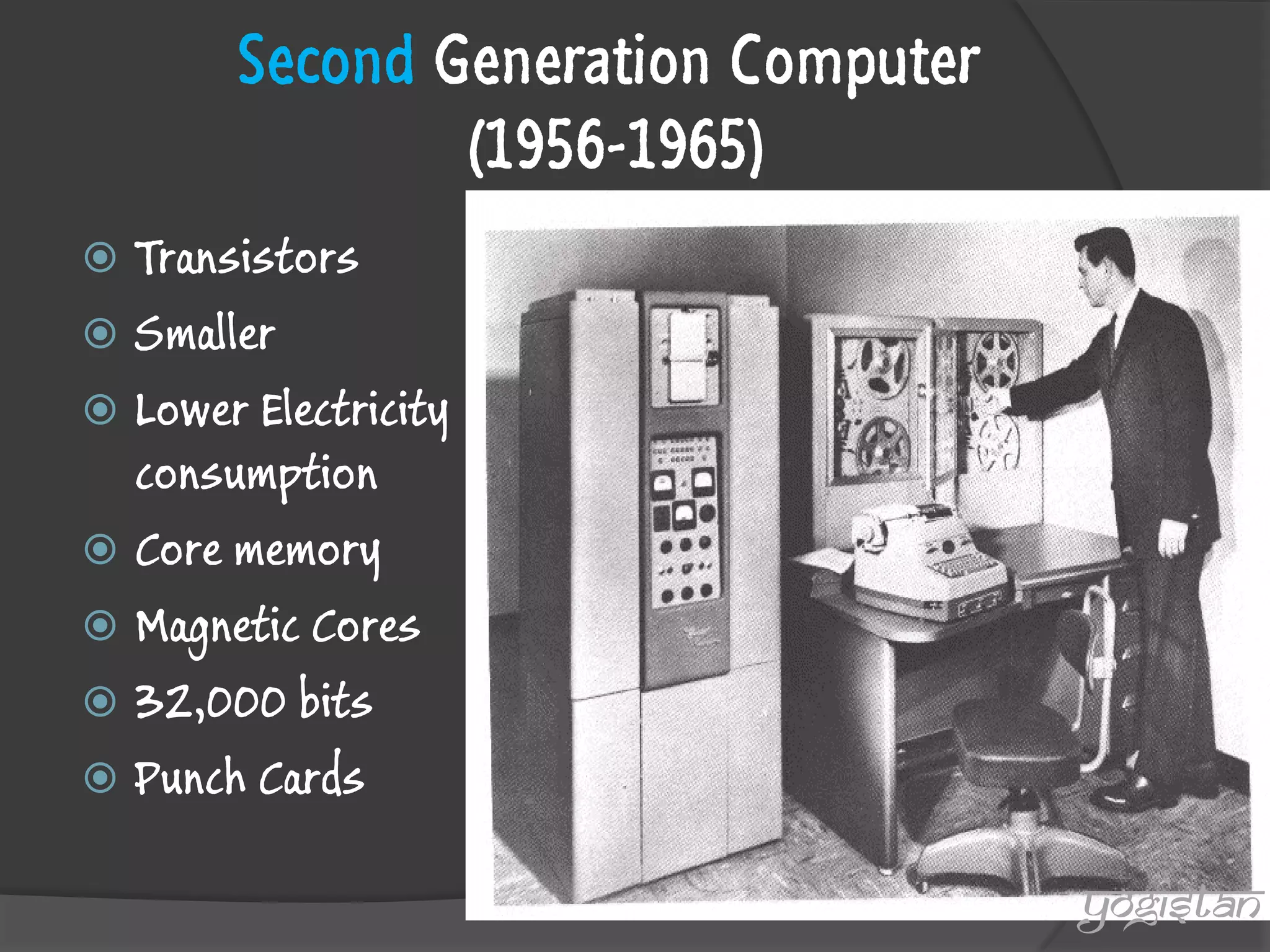
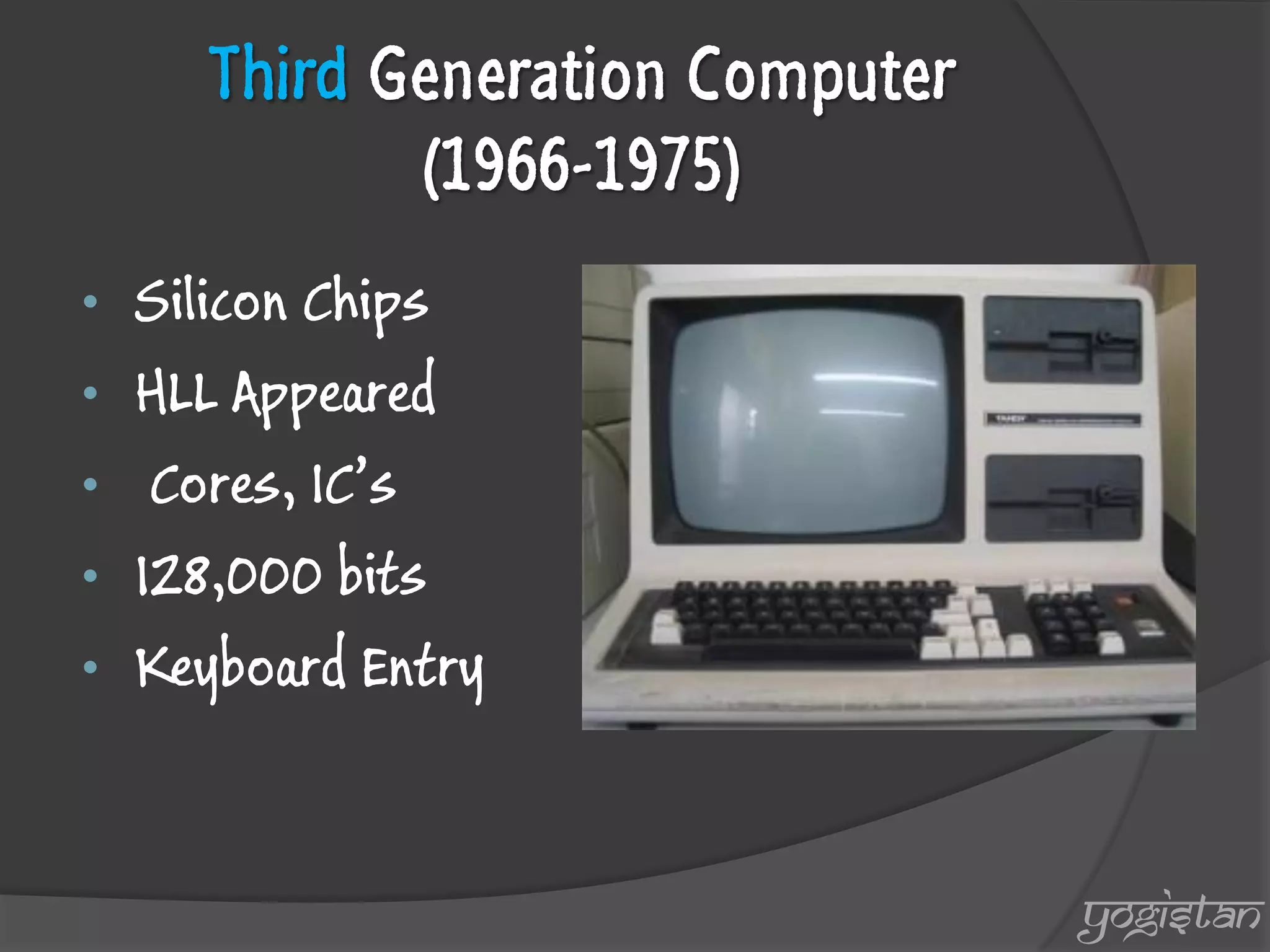
The document outlines the evolution and generations of computers, defining a computer as a device for processing and storing data. It details five generations of computers from 1946 to present, highlighting key features, technologies, and programming languages associated with each generation. The document also introduces the contributions of a British mathematician to the development of computing machinery.