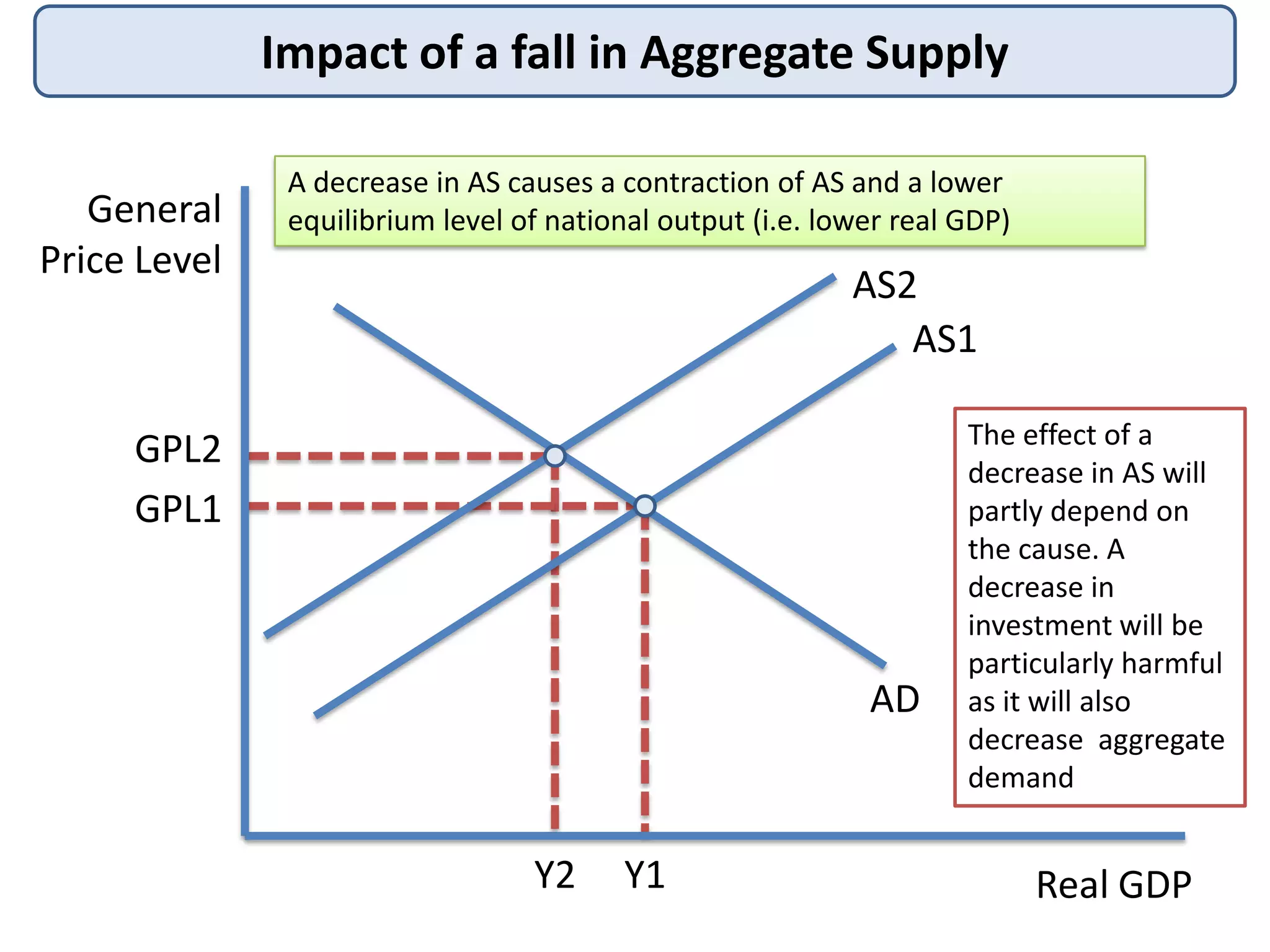
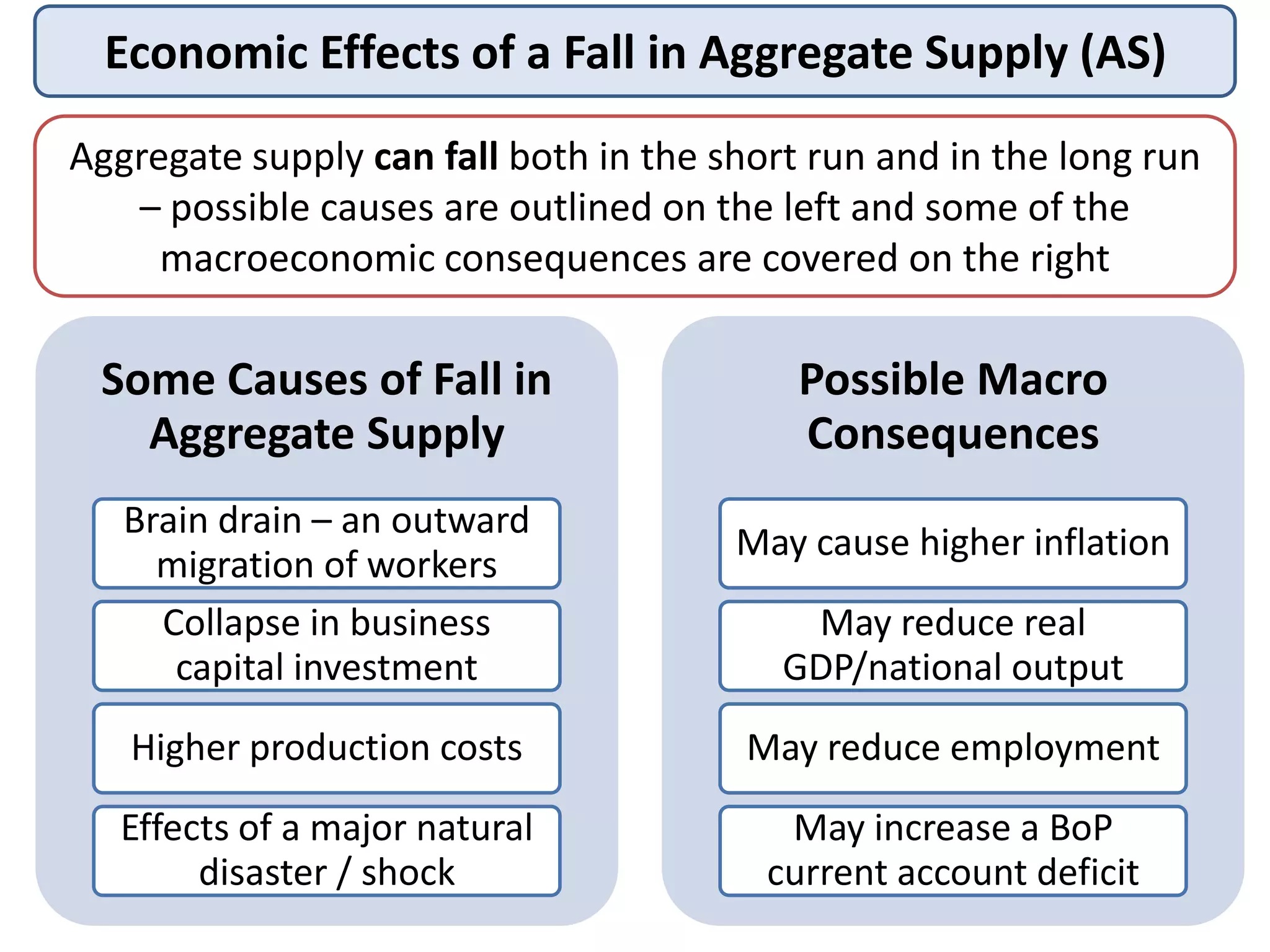
This document discusses macroeconomic equilibrium using aggregate demand (AD) and aggregate supply (AS) analysis. It provides diagrams showing:
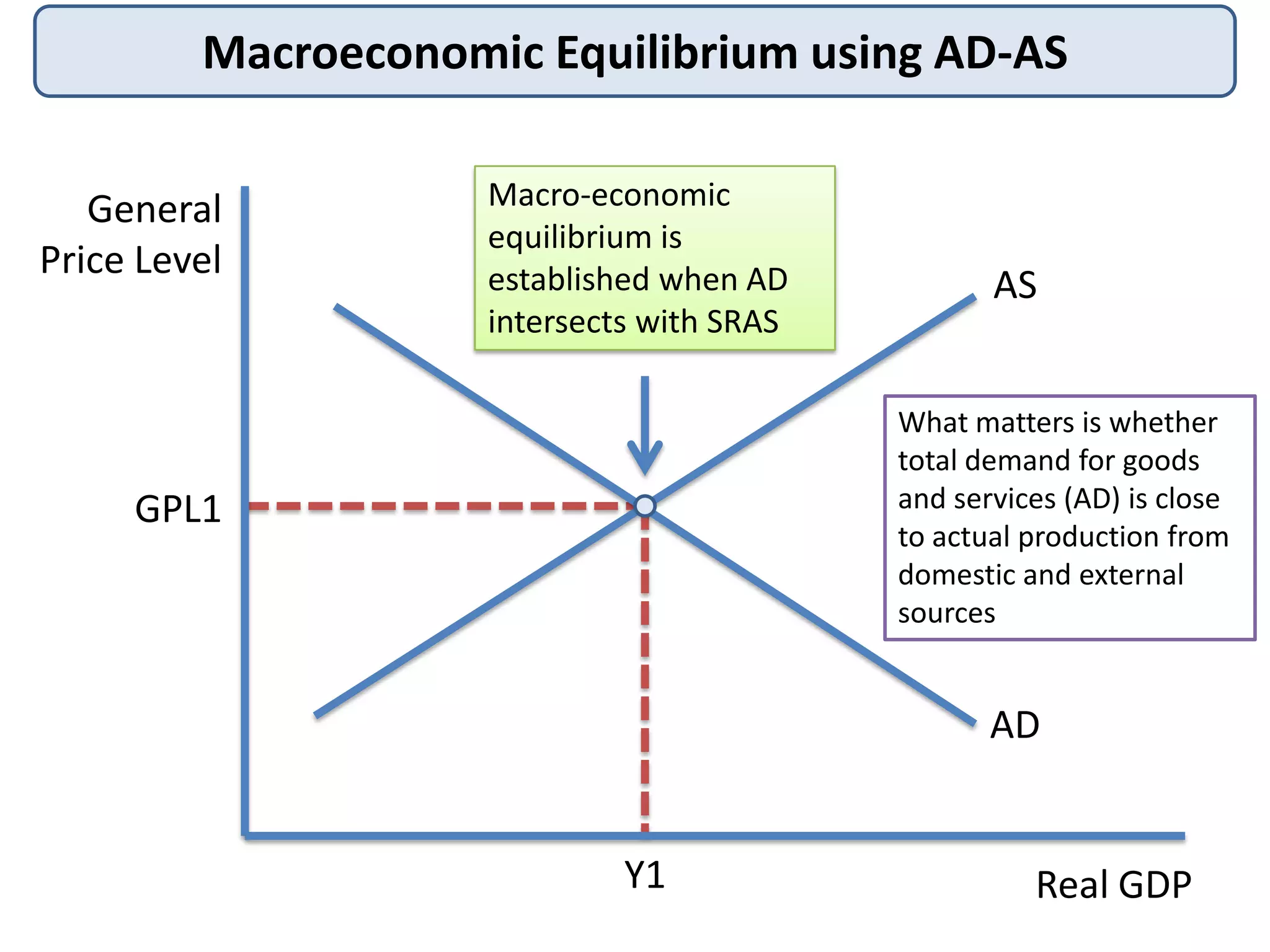
1) How macroeconomic equilibrium is established at the point where AD intersects short-run aggregate supply (SRAS).
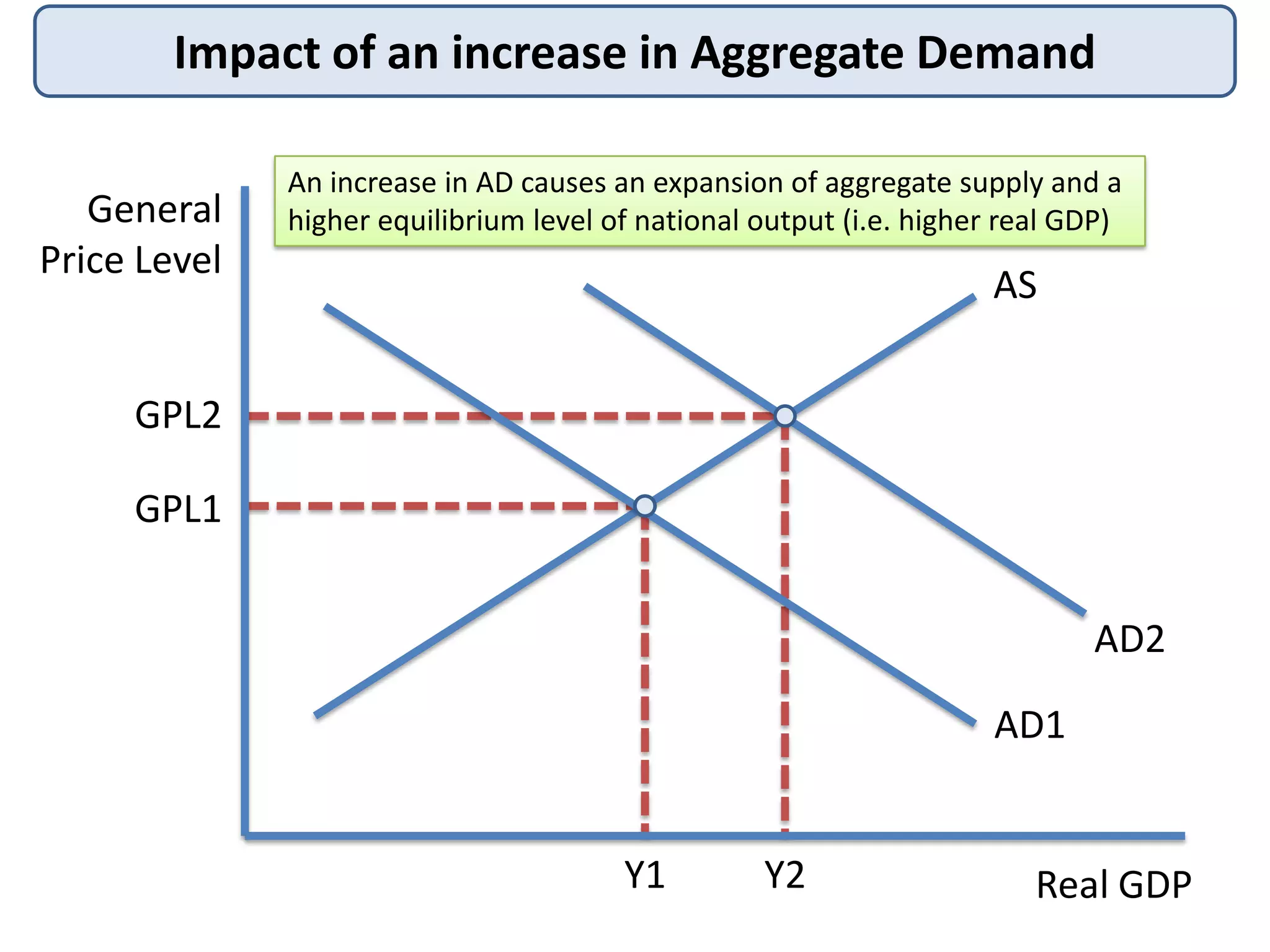
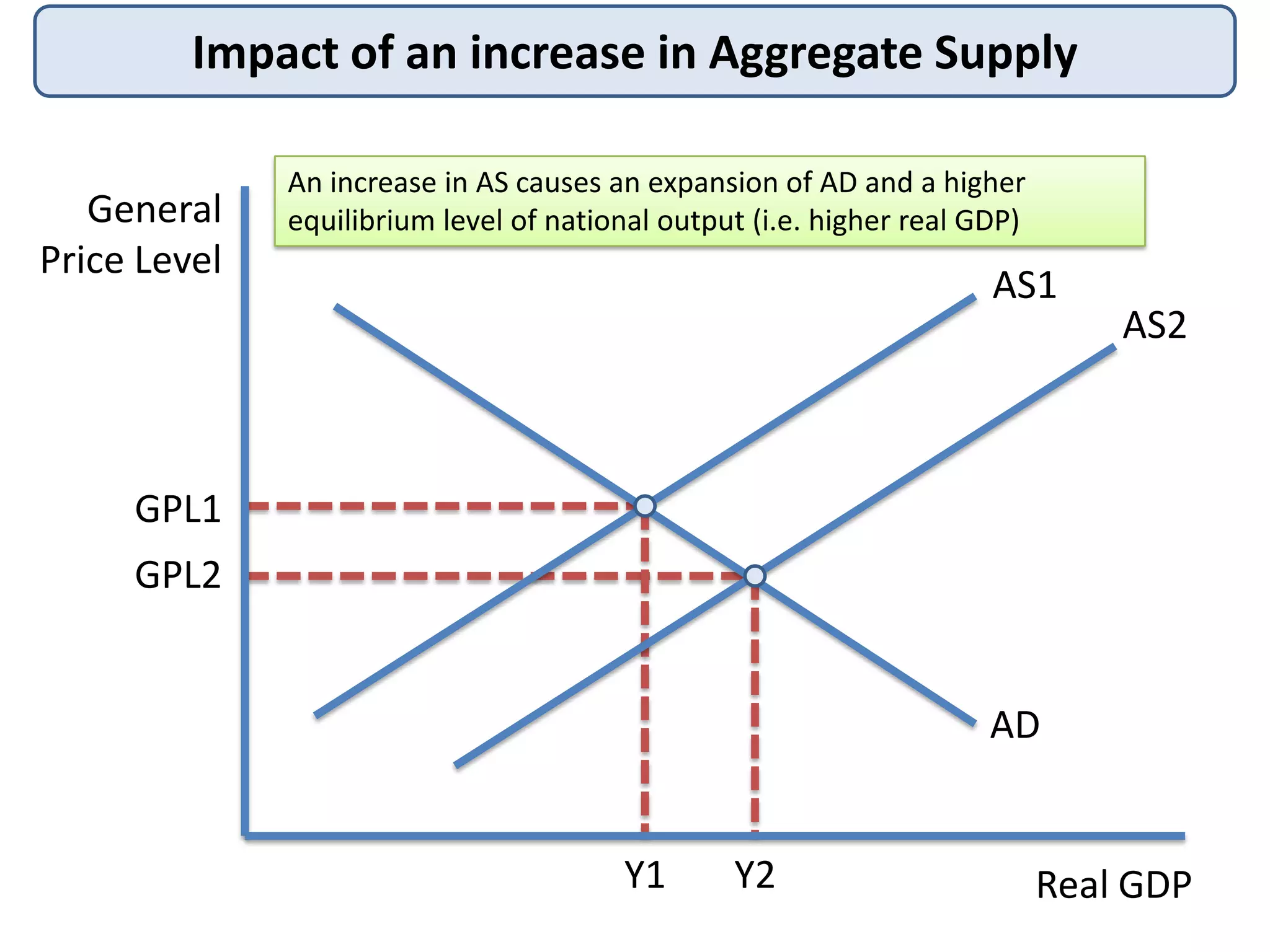
2) How an increase in AD leads to expansion of output and a higher equilibrium price level, while an increase in AS expands both AD and output.
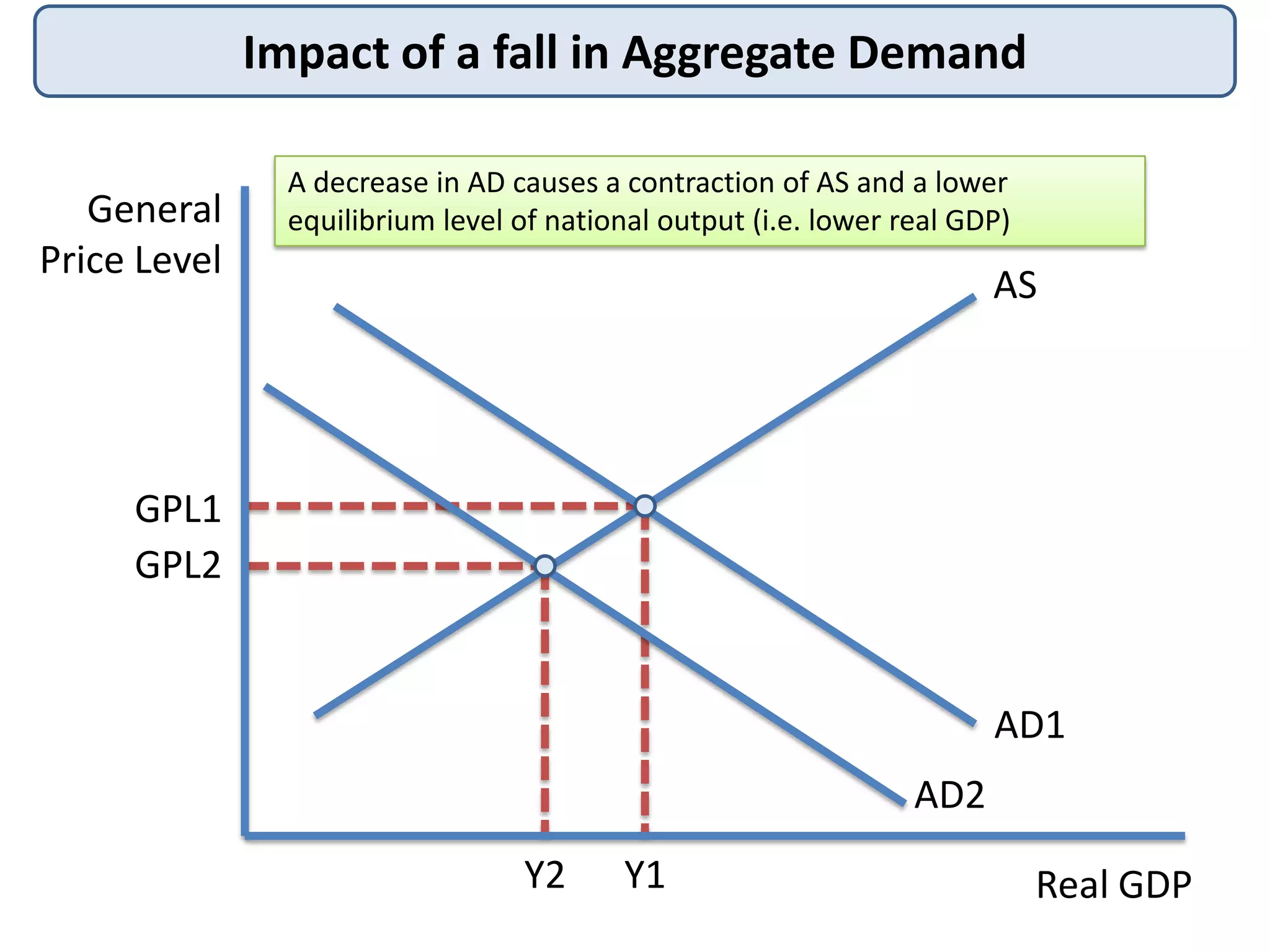
3) It also shows how a decrease in either AD or AS results in a contraction of output and a lower equilibrium price level.