This document discusses key concepts related to motion, including:
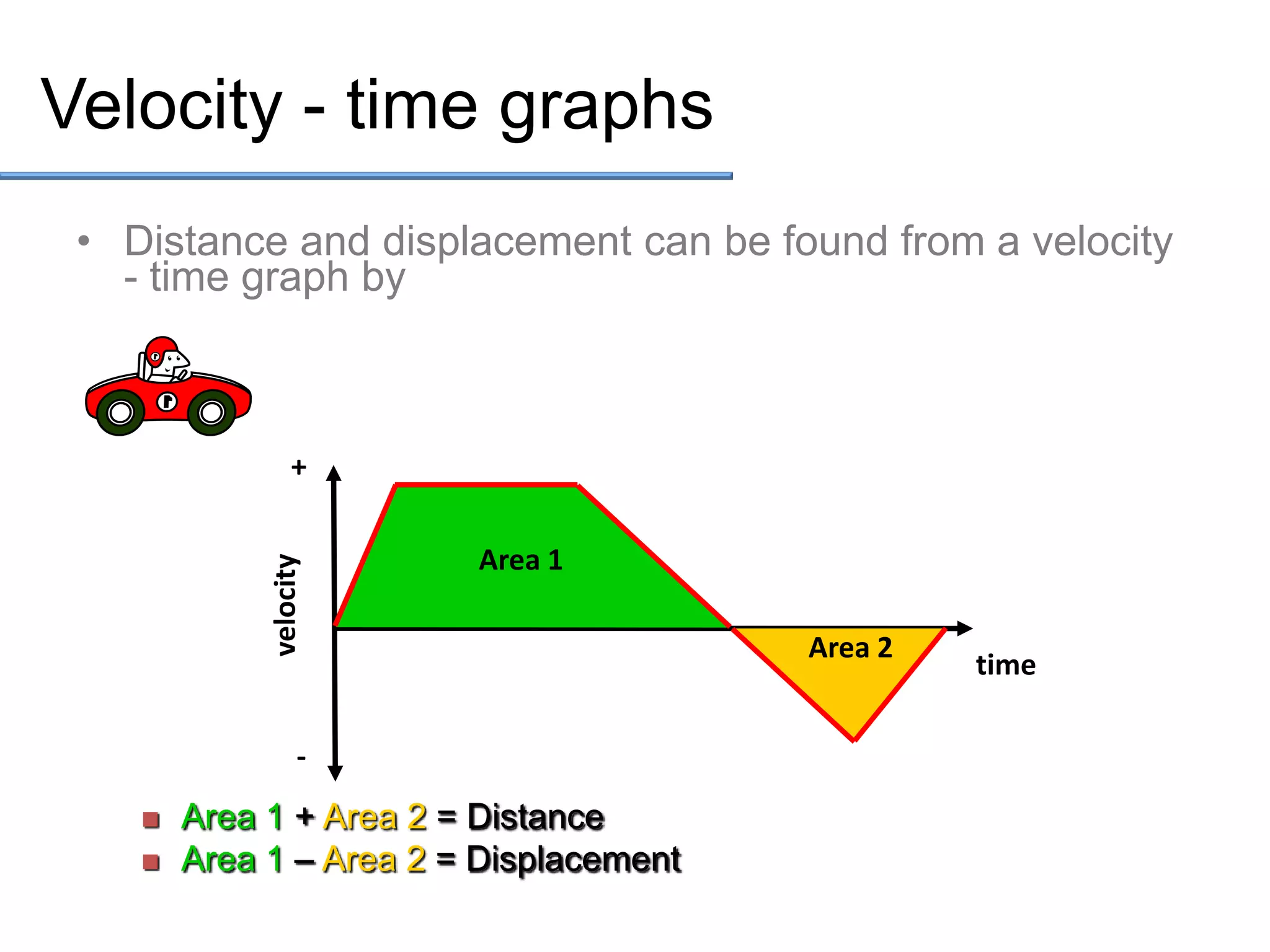
- Distance is a scalar quantity that measures the total length of an object's path, while displacement is a vector quantity that measures the change in an object's position.
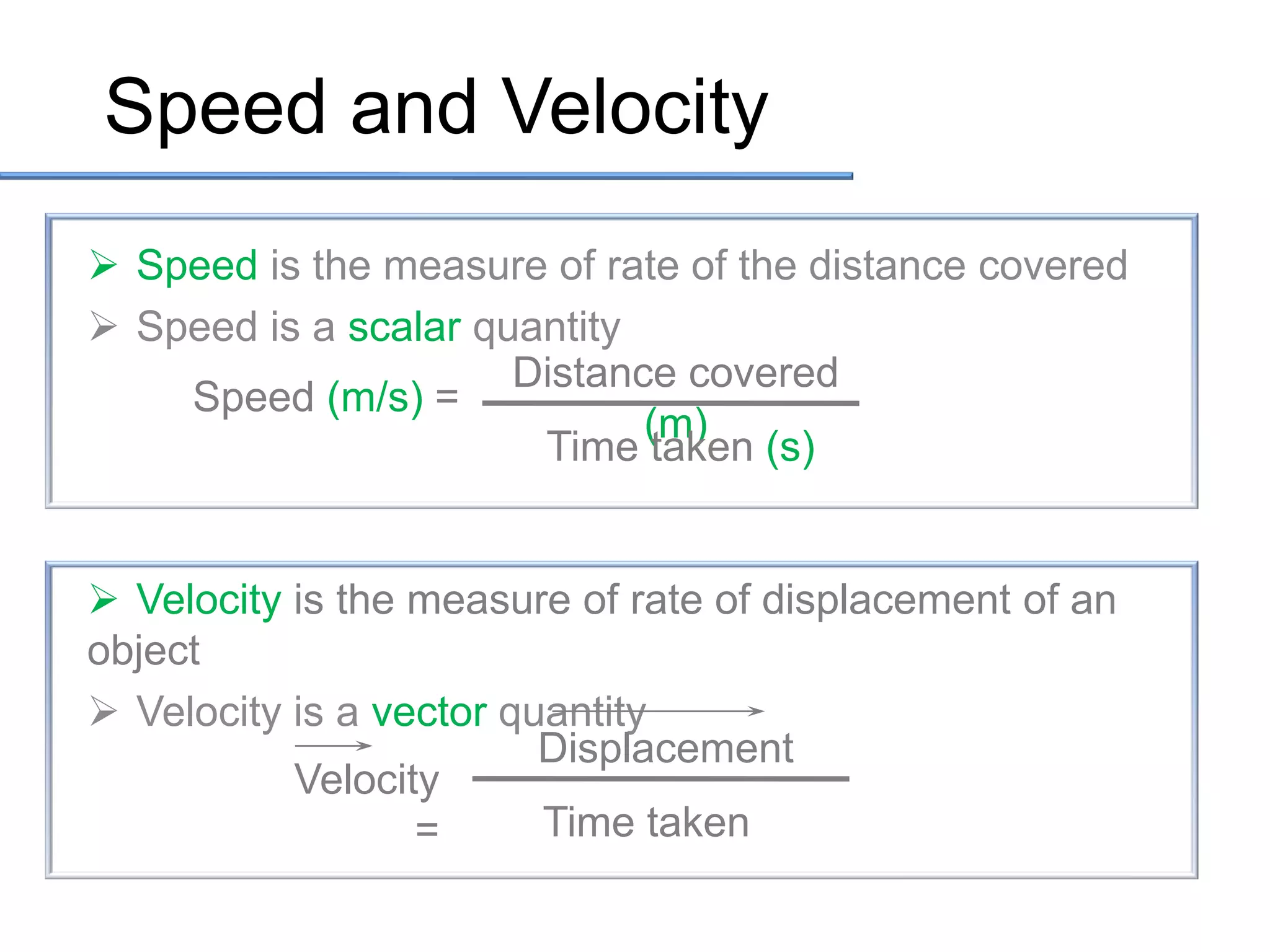
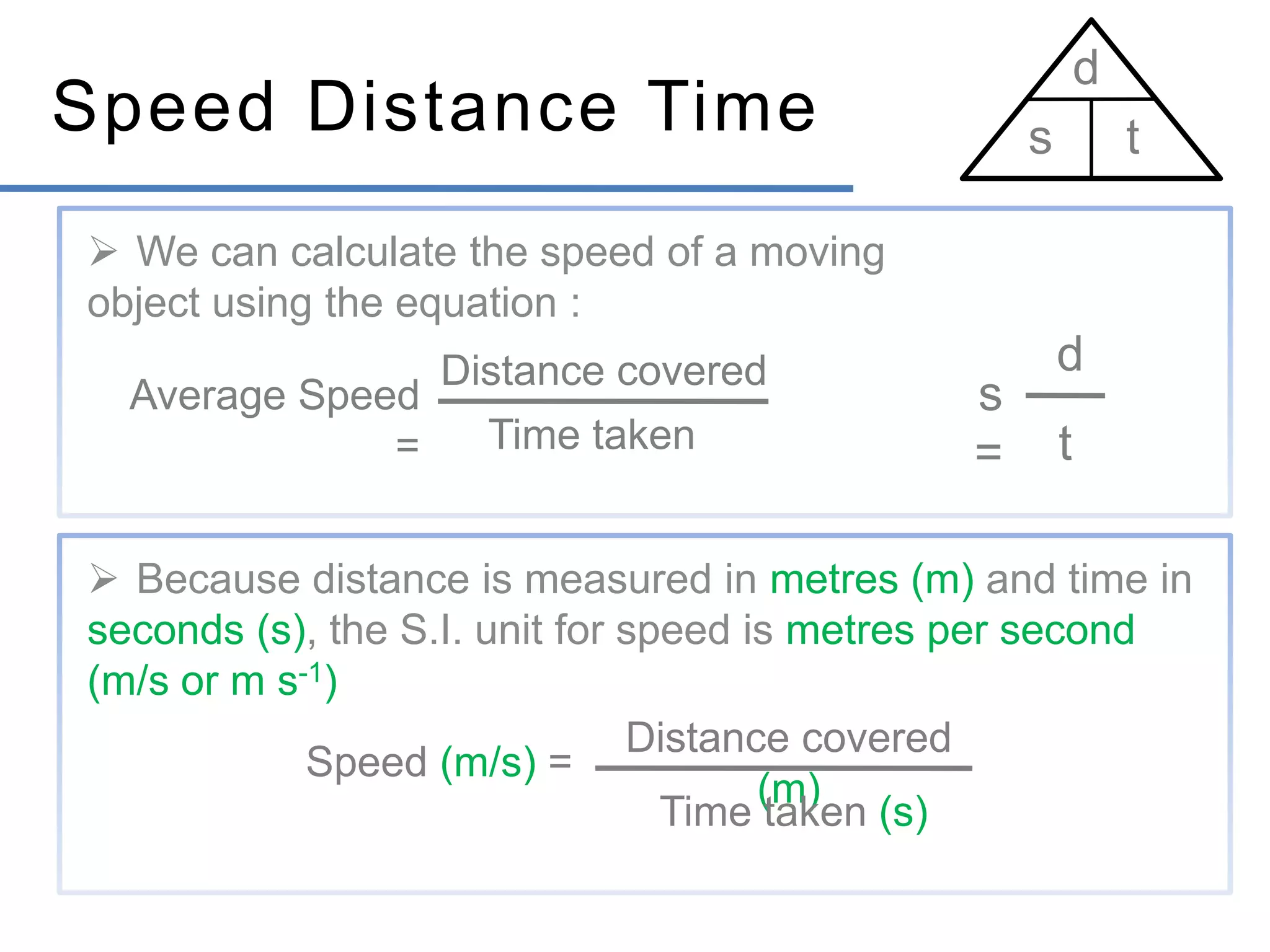
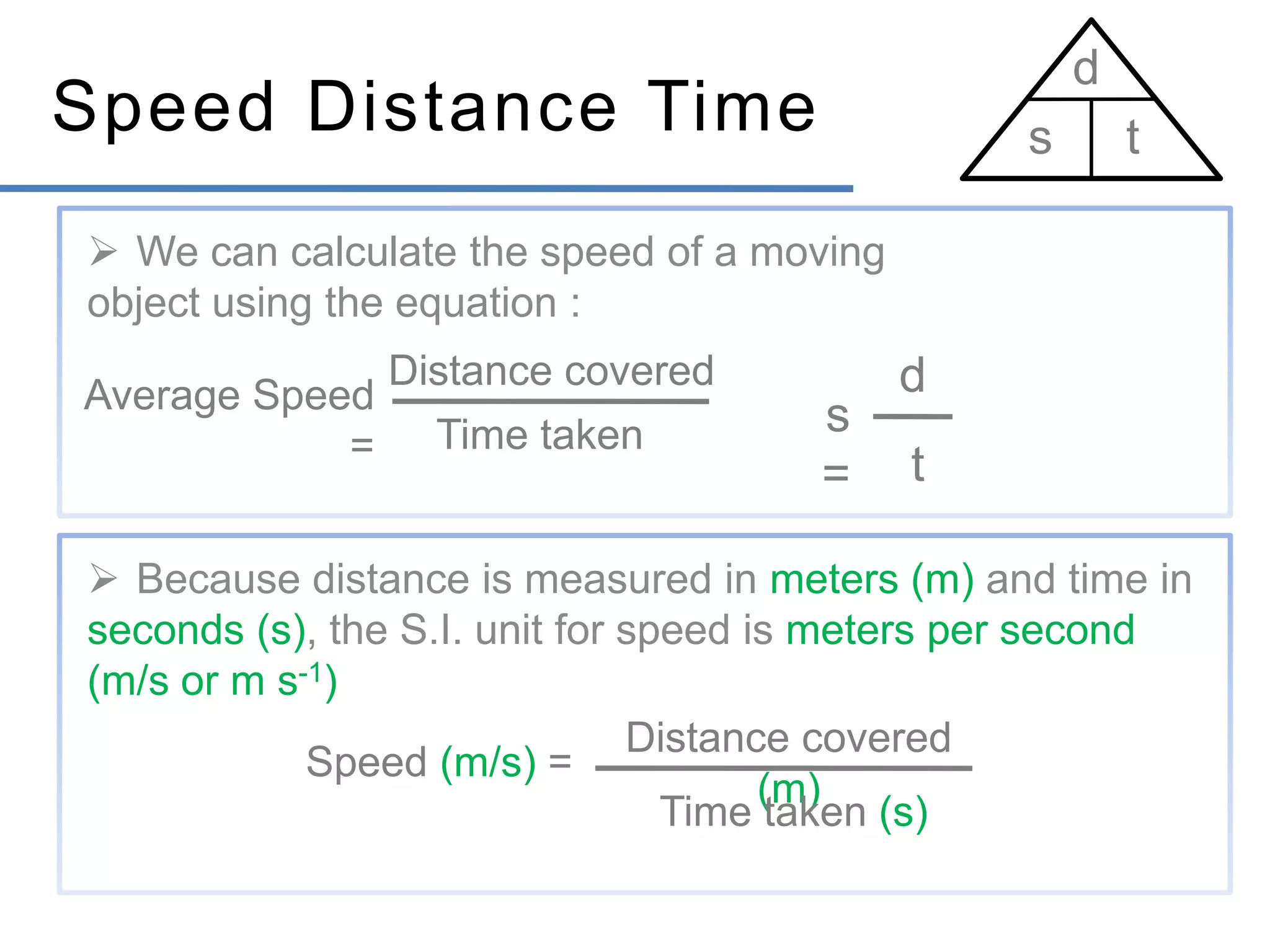
- Speed is the rate of change of distance and is a scalar, while velocity is the rate of change of displacement and is a vector.
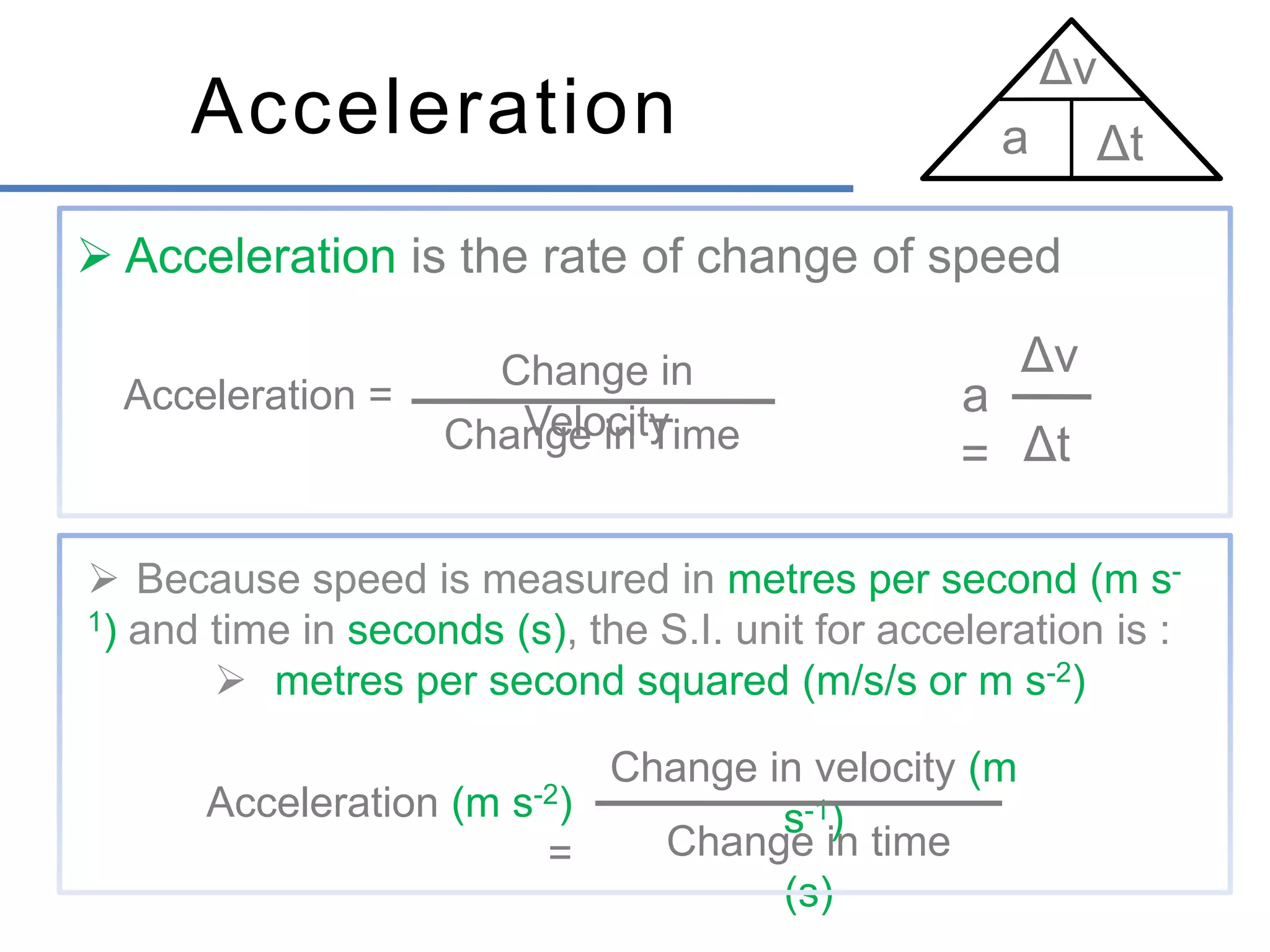
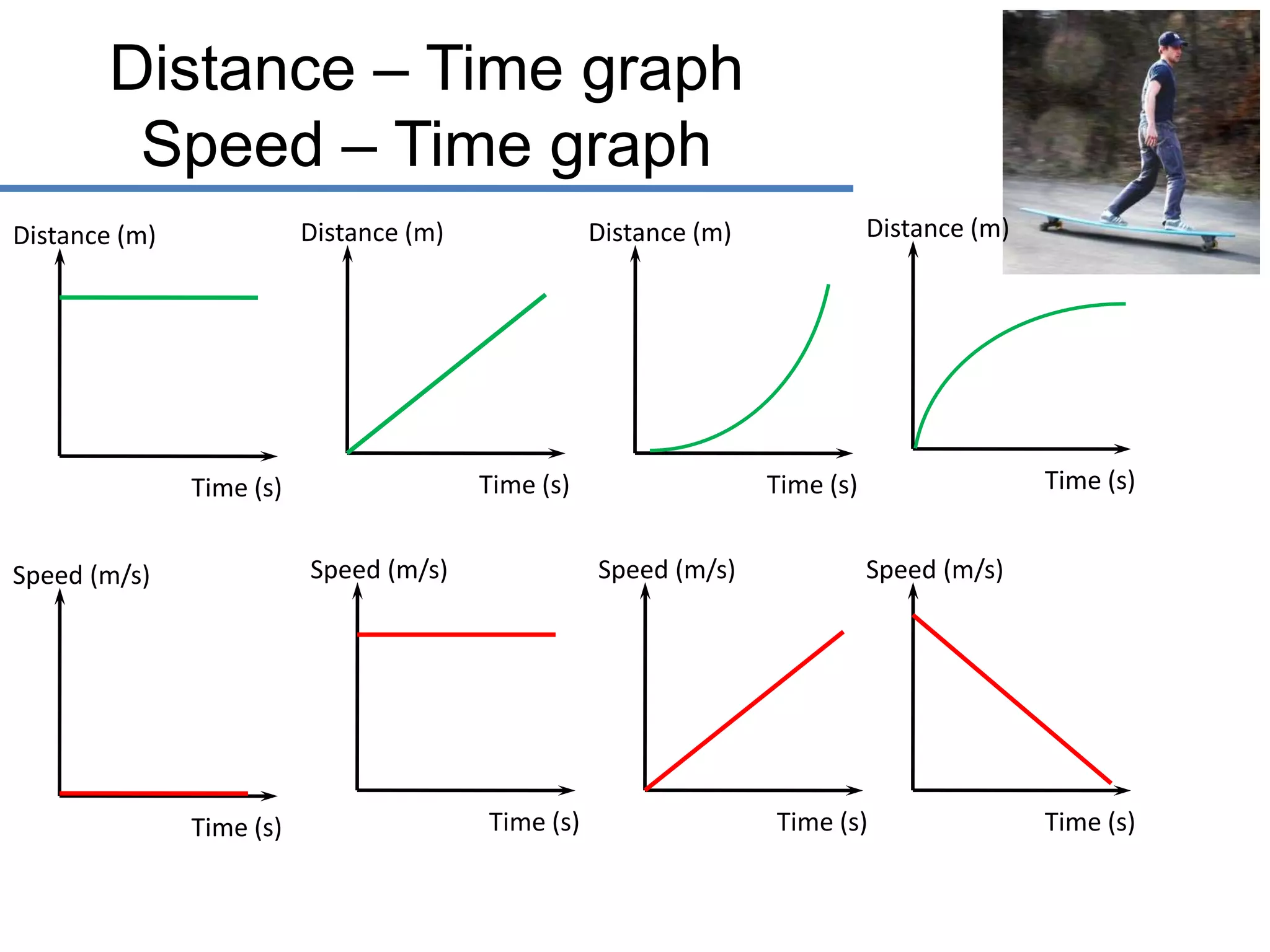
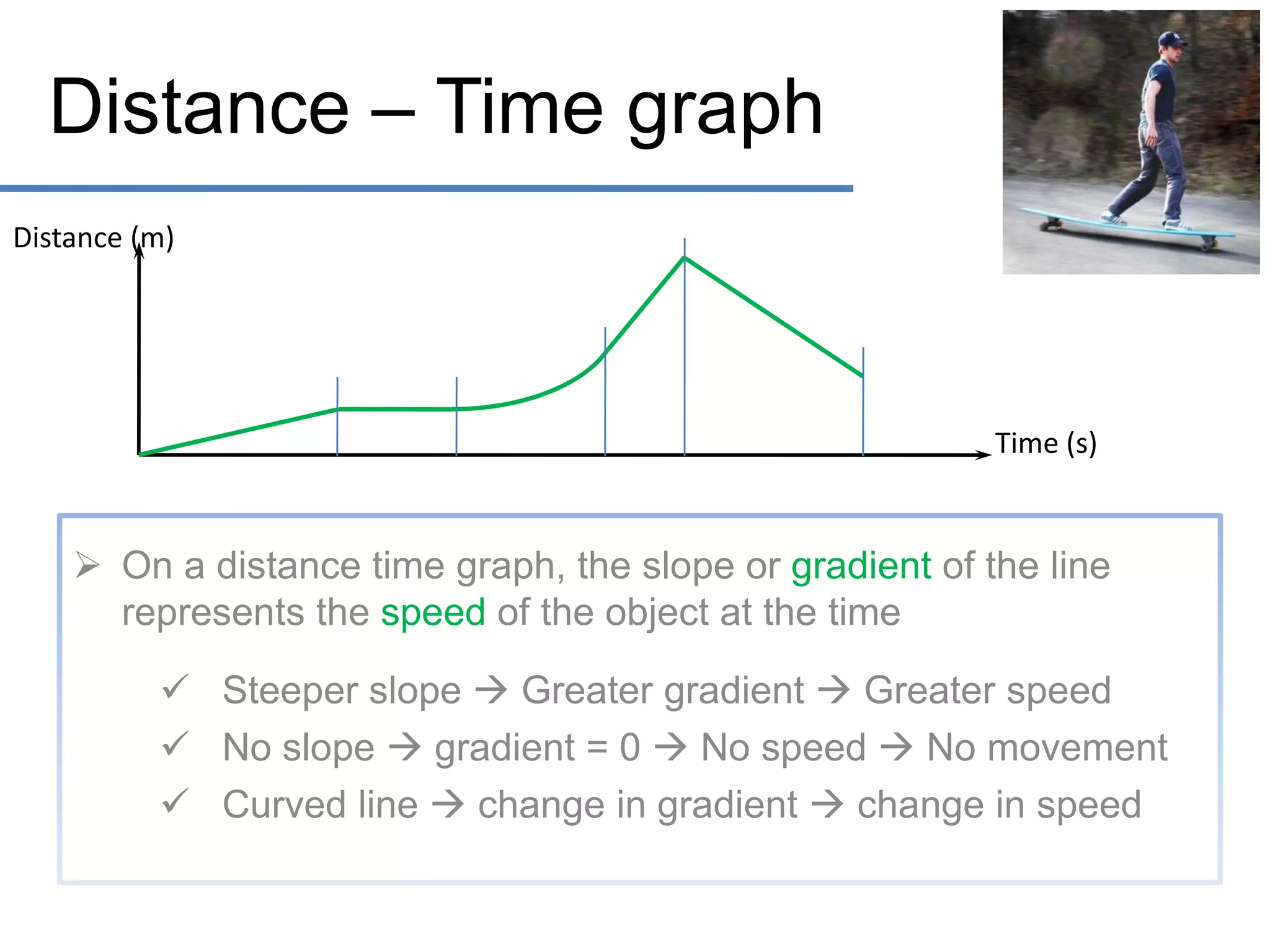
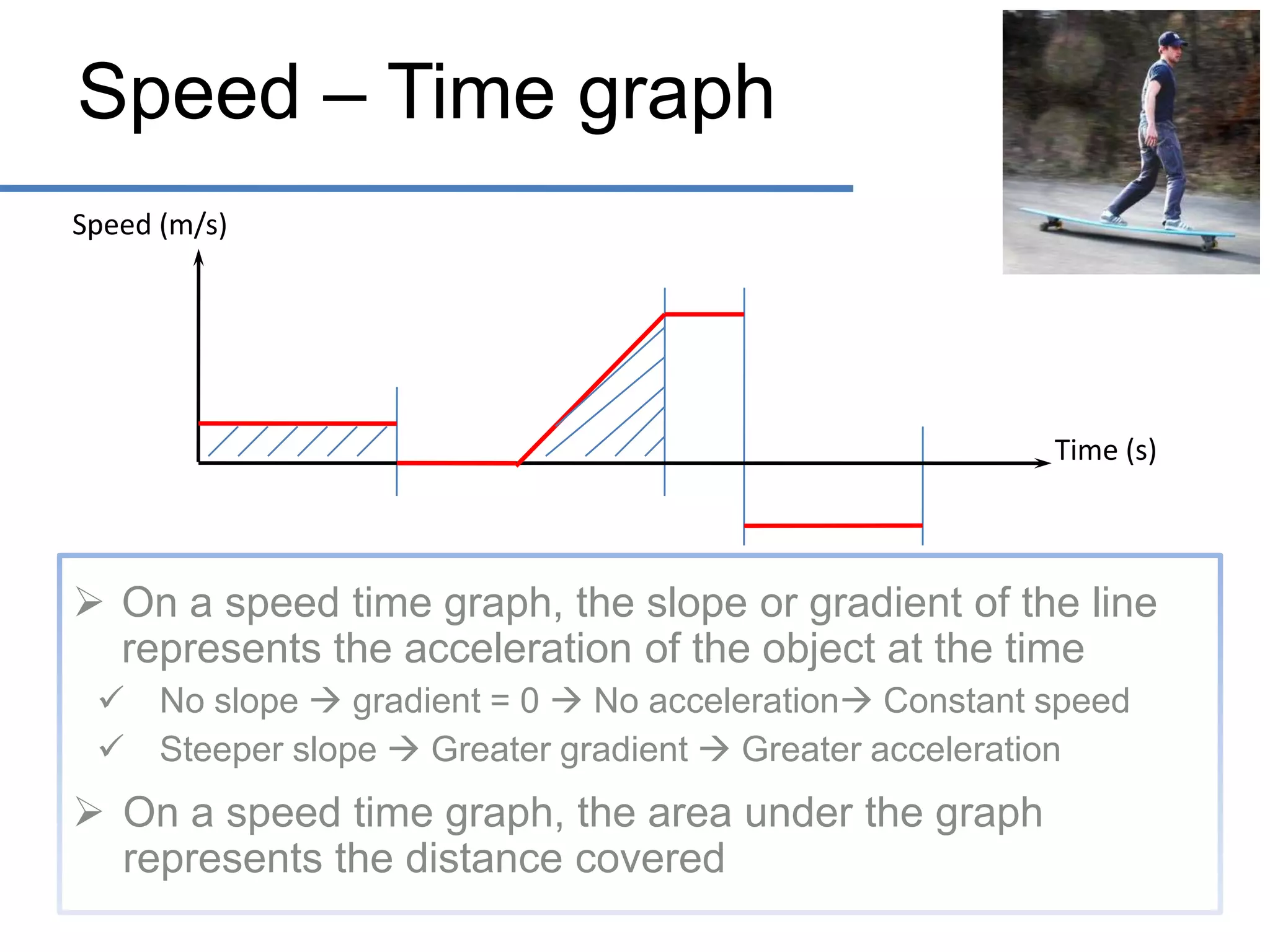
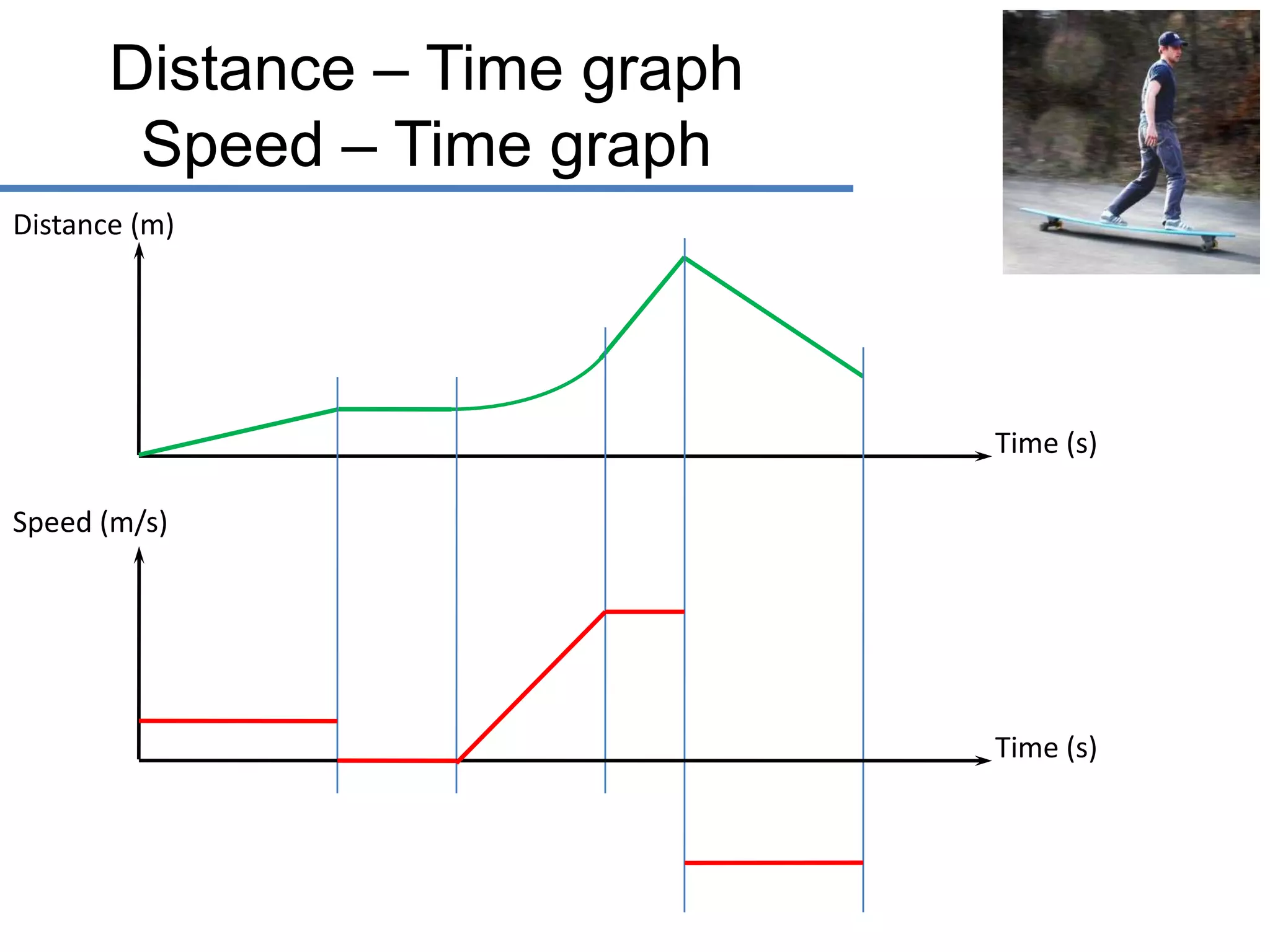
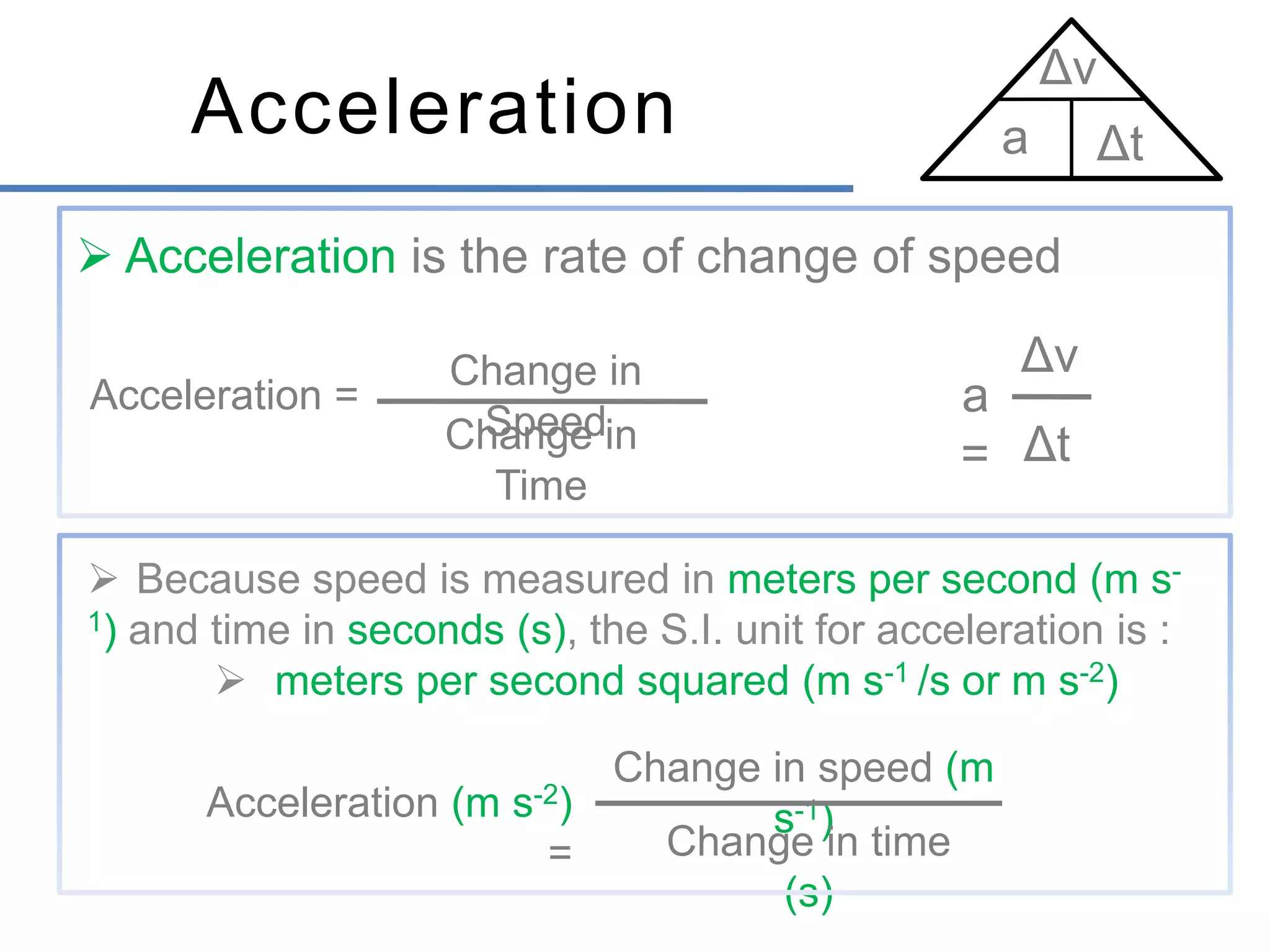
- Graphs can show the relationship between distance, speed, time, and other motion variables. The slope of a distance-time graph represents speed, while the slope of a speed-time graph represents acceleration.