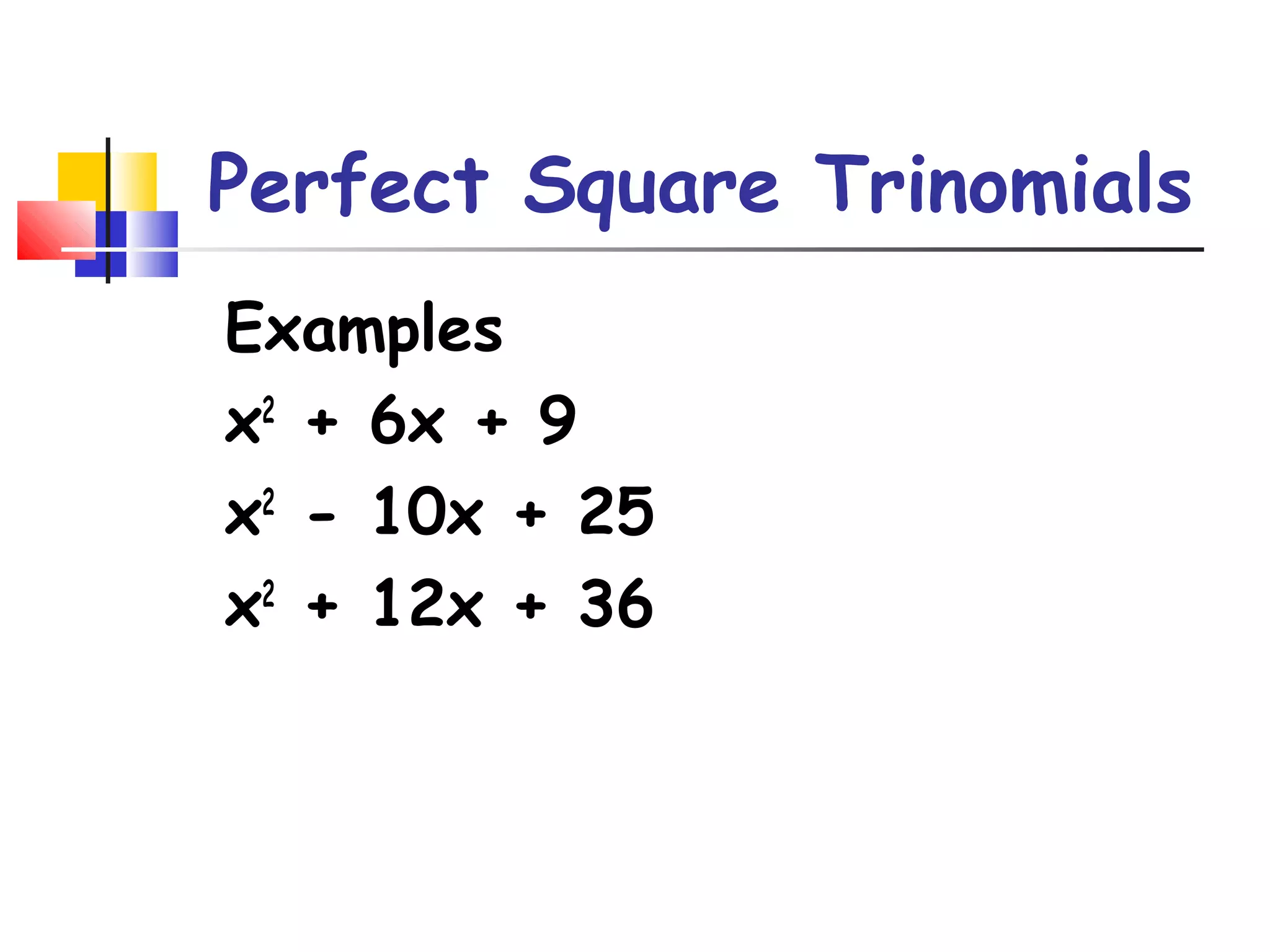
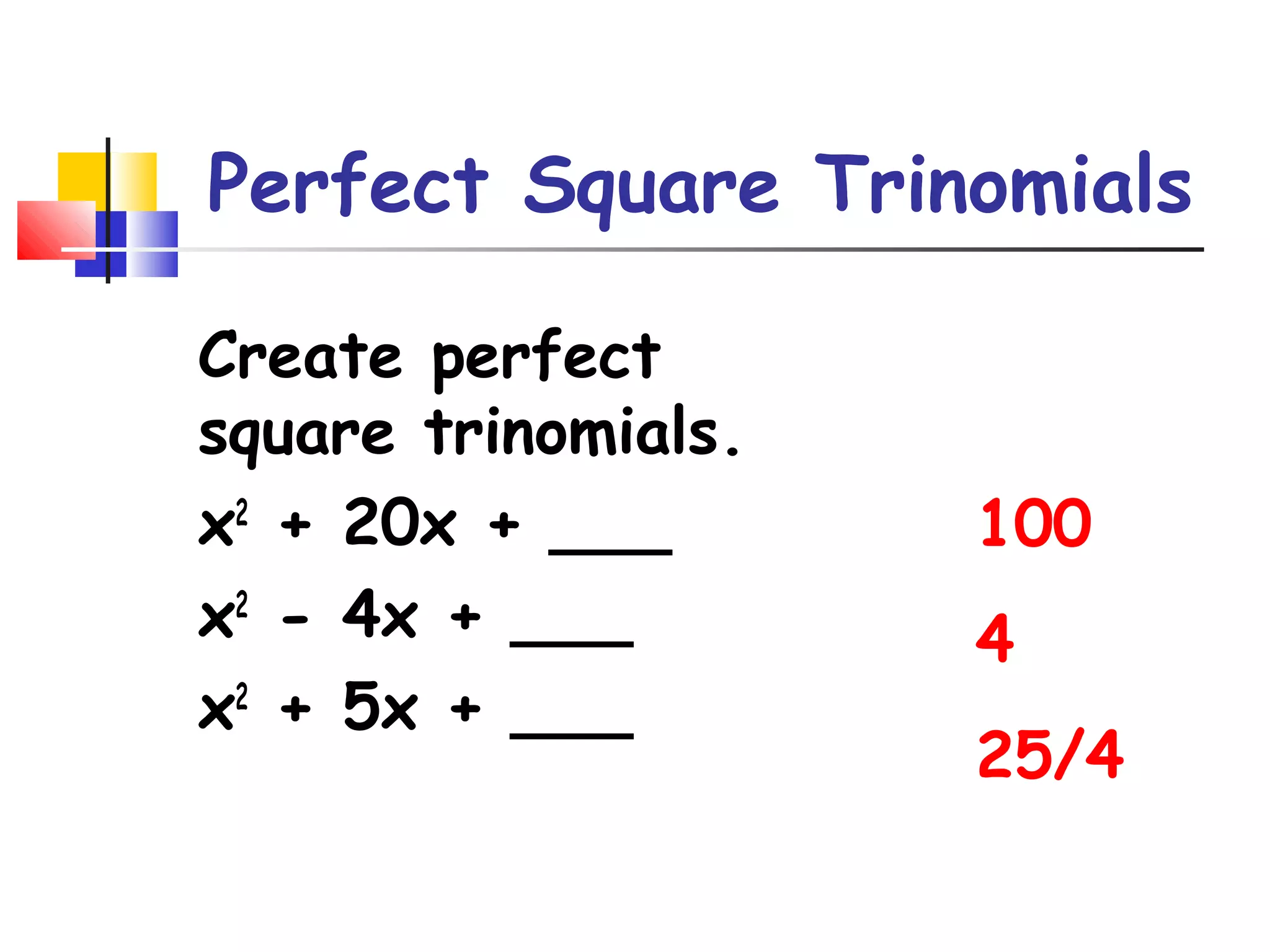
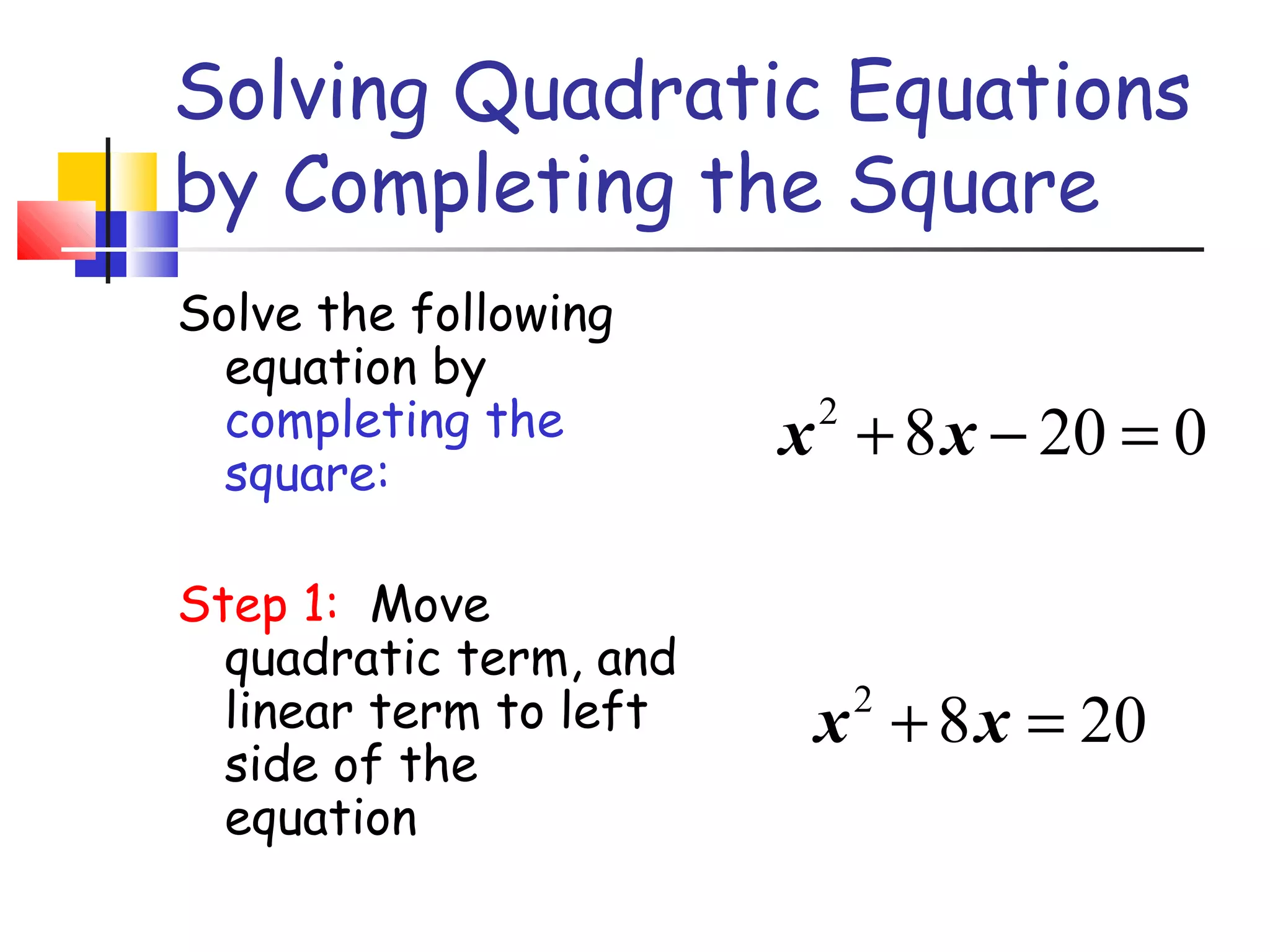
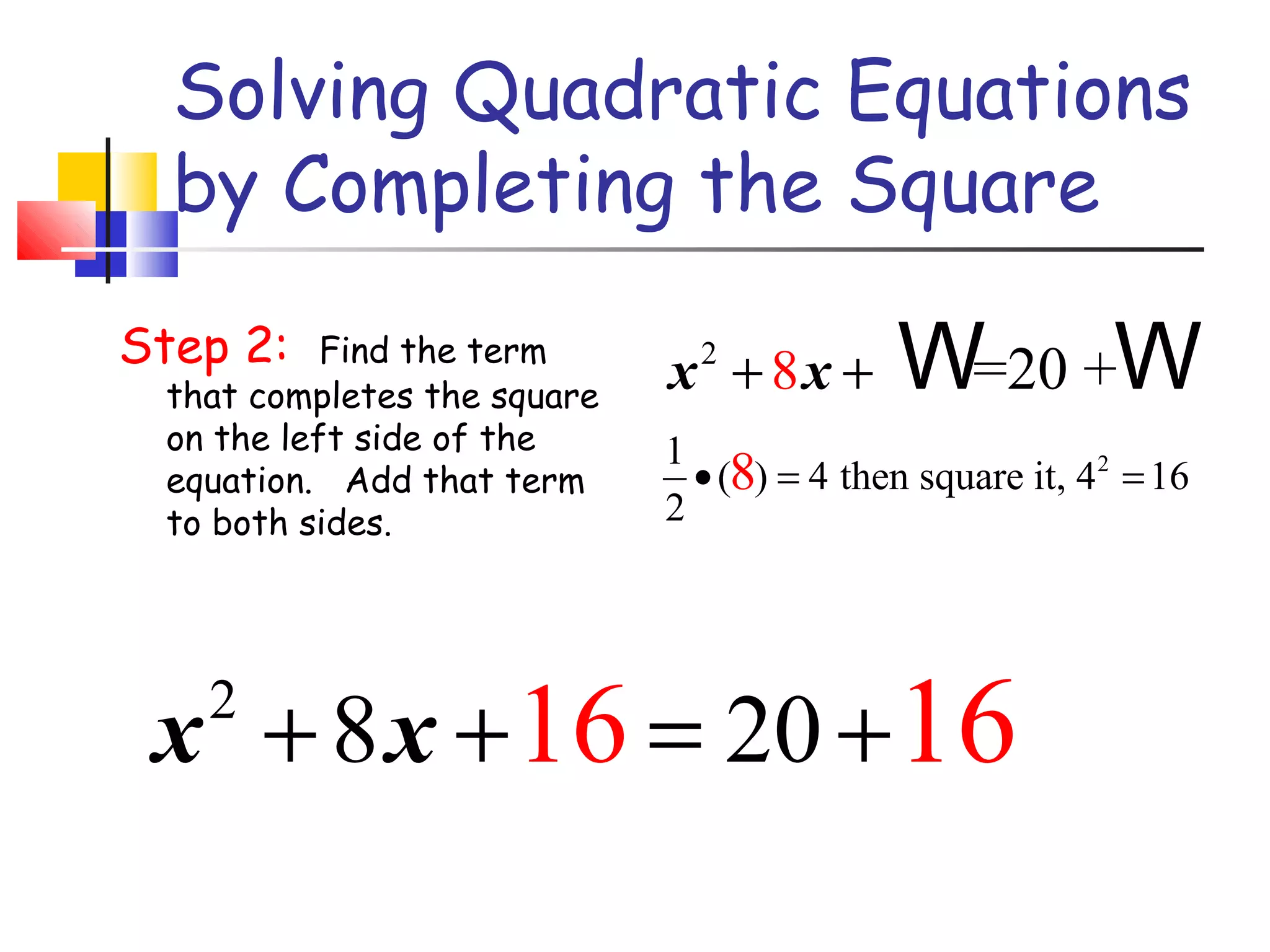
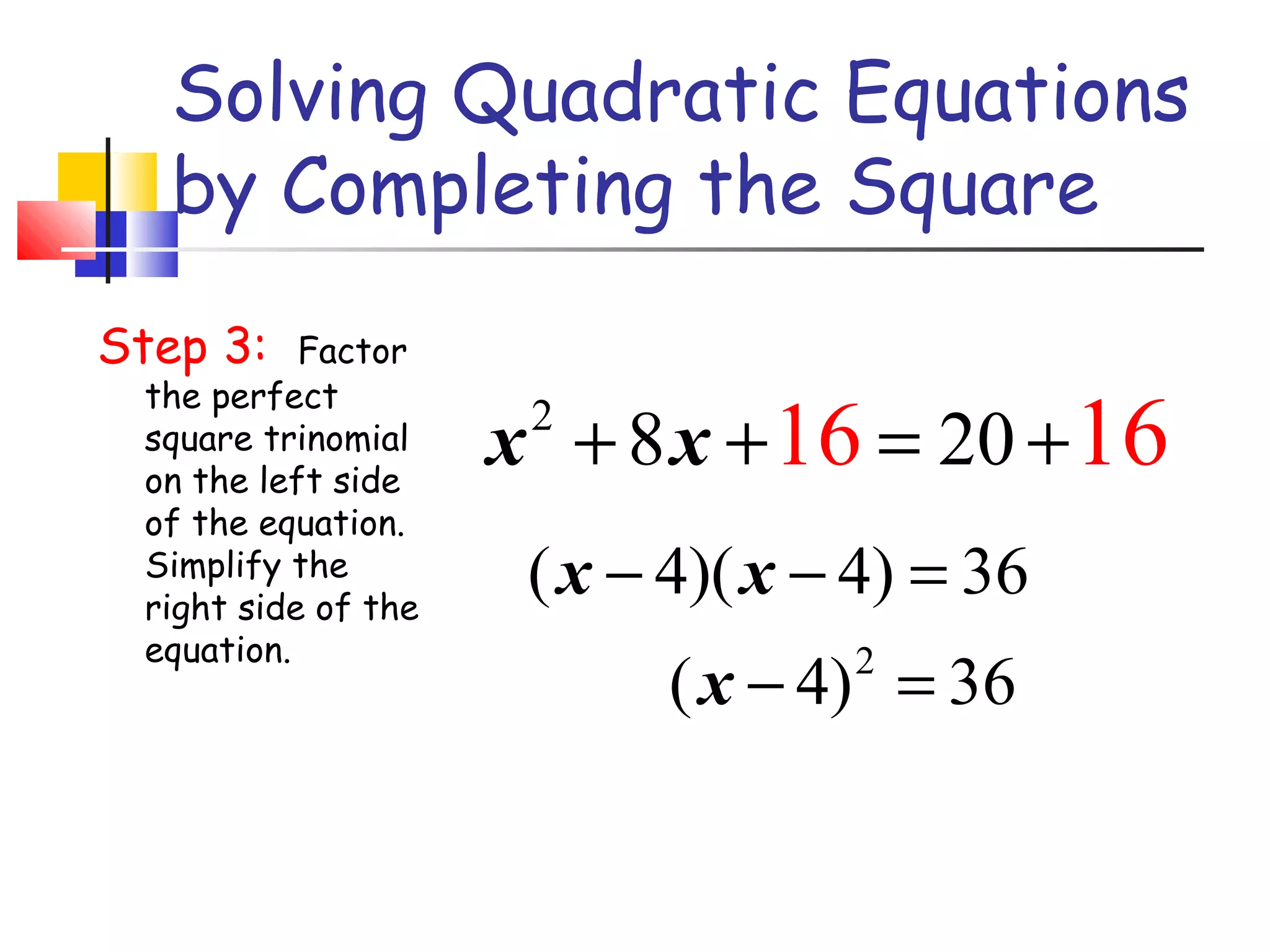
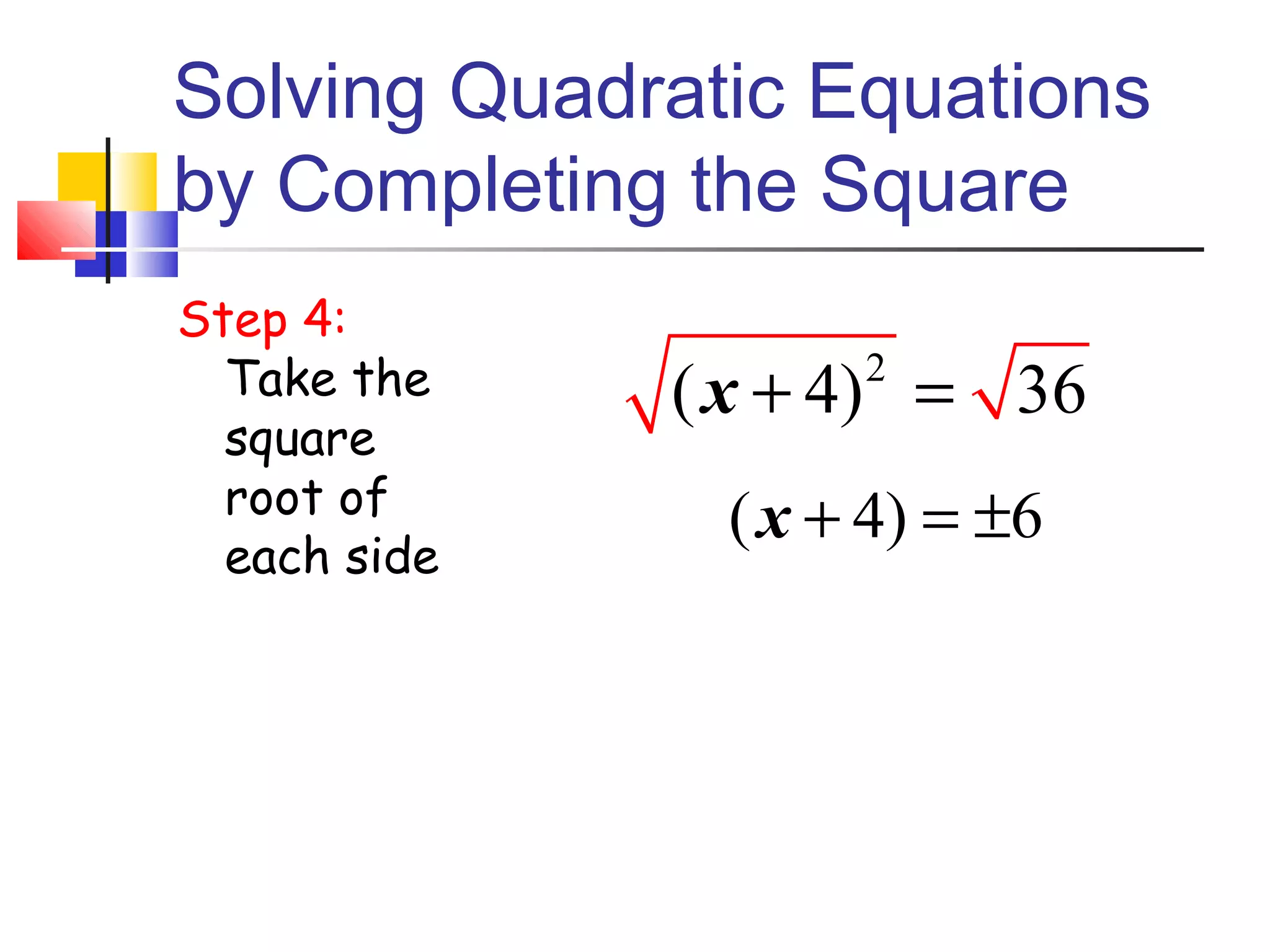
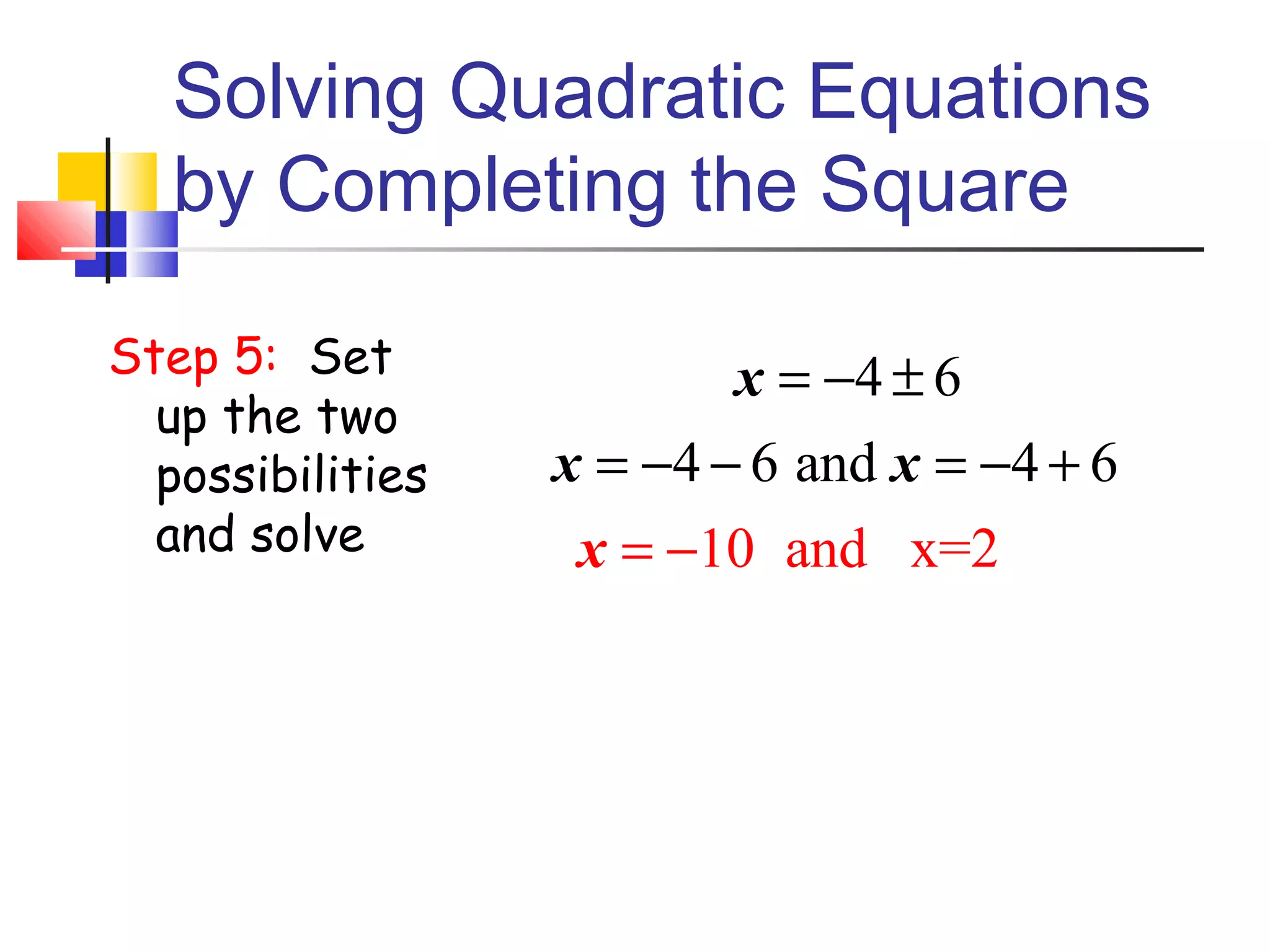
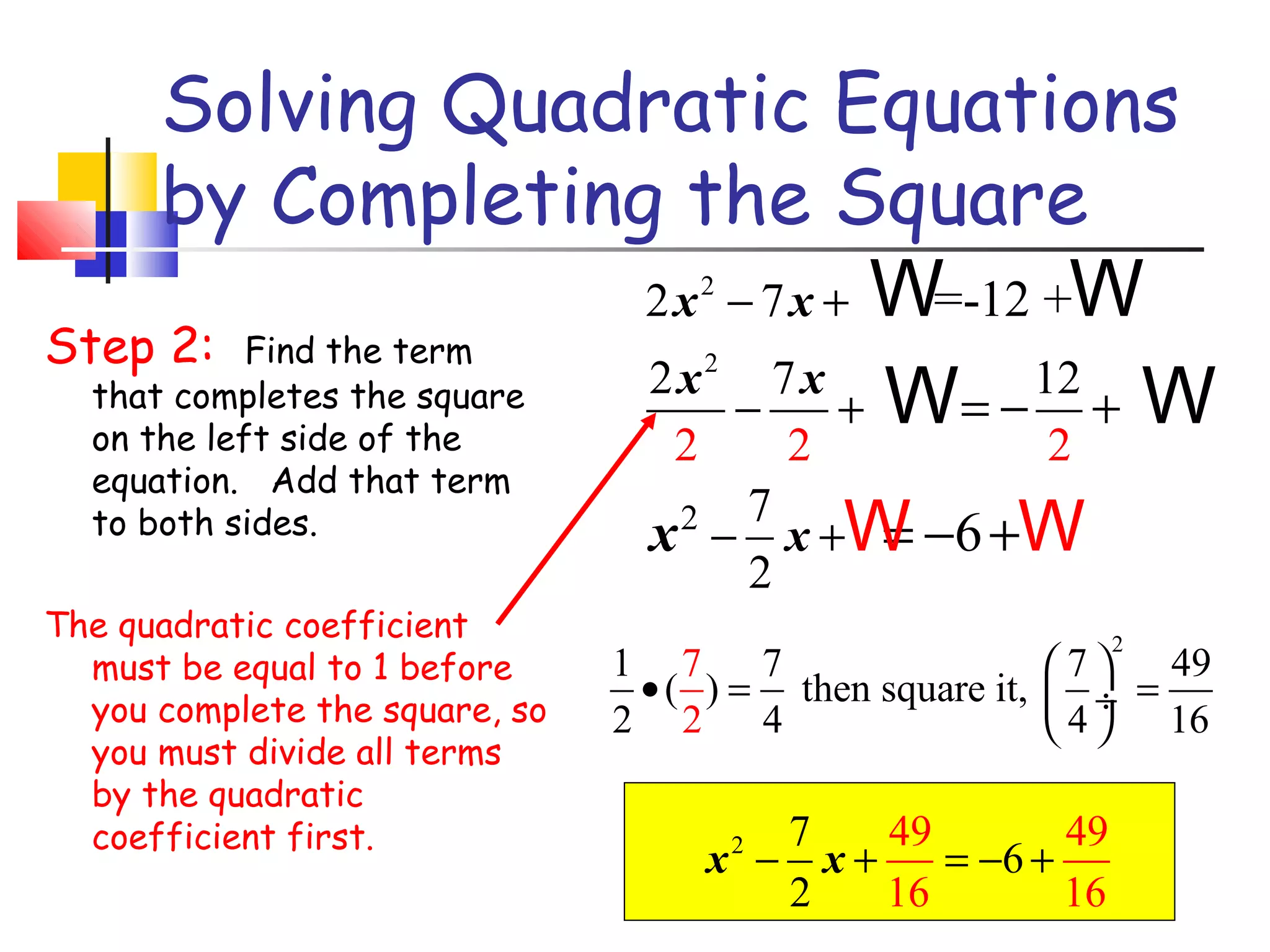
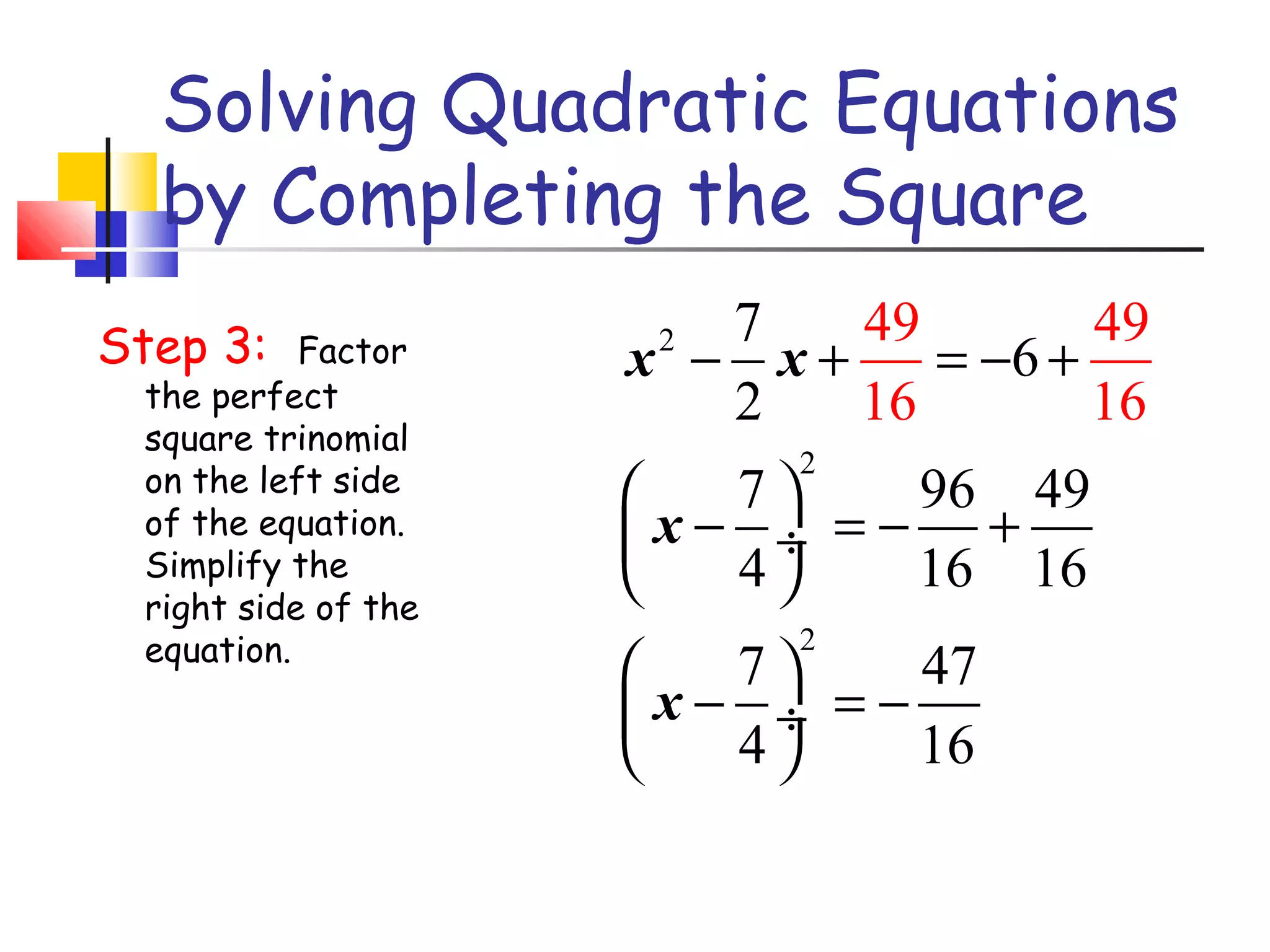
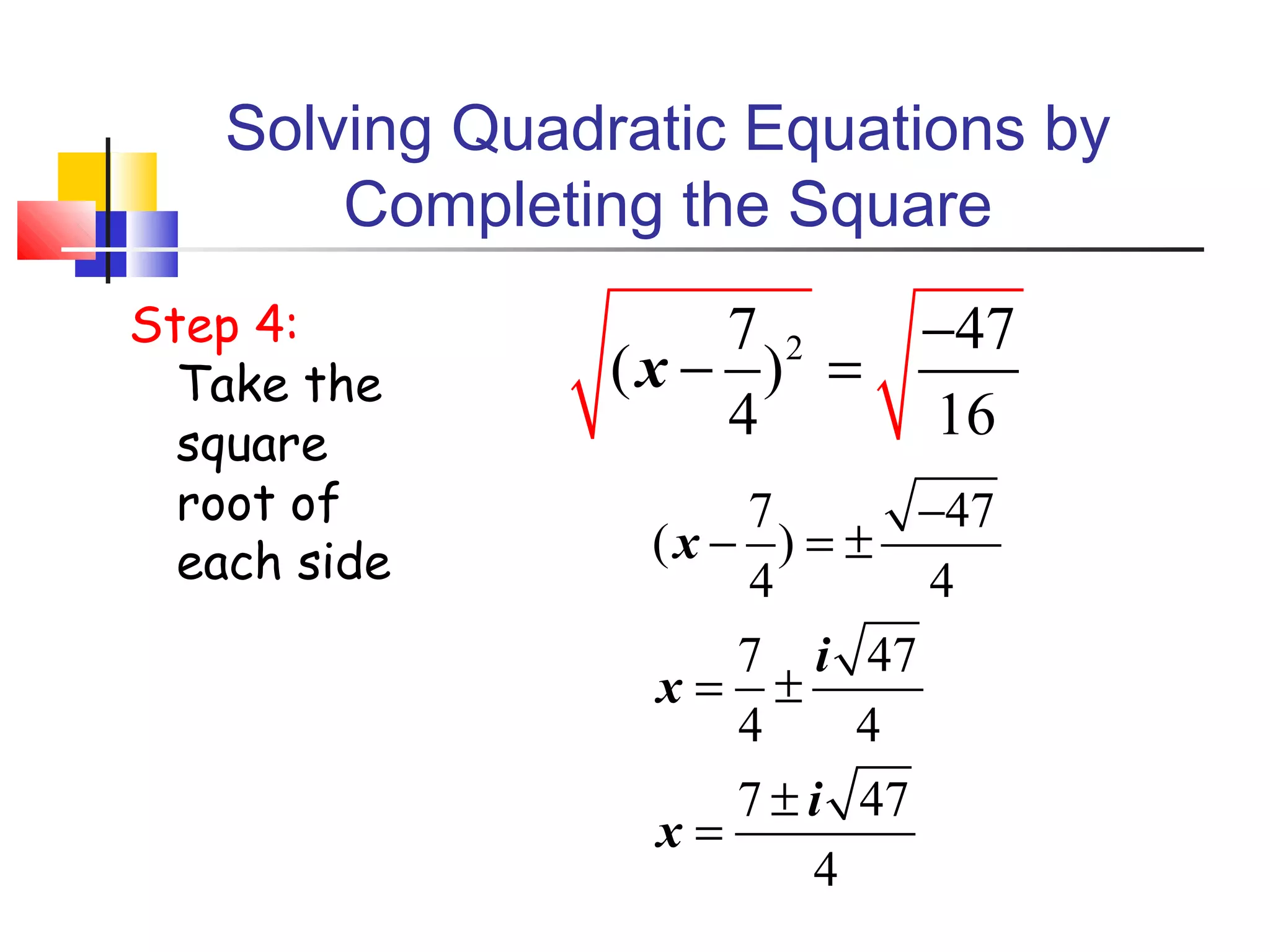
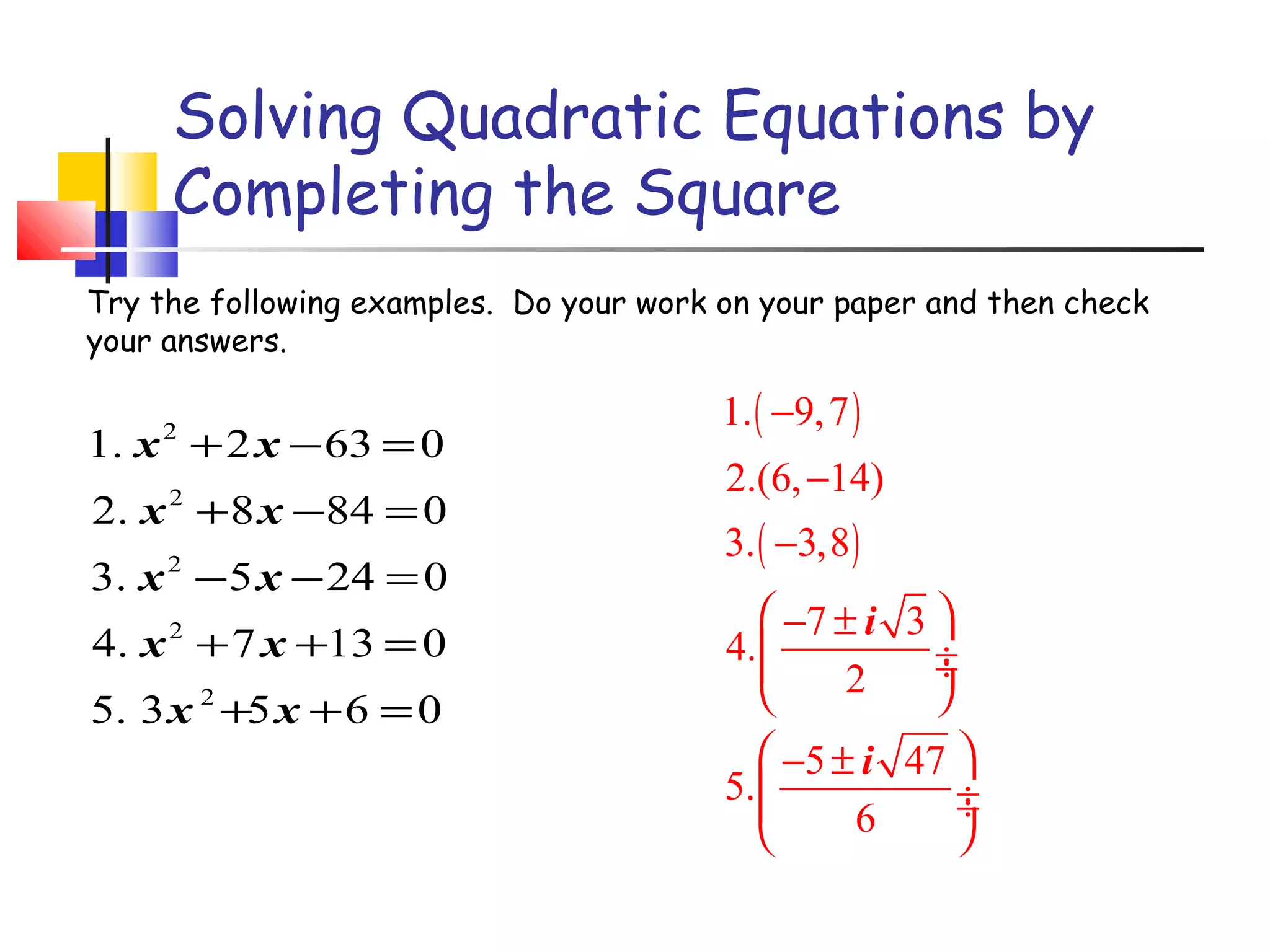
The document discusses solving quadratic equations by completing the square. It provides examples of perfect square trinomials and how to find the missing constant term to create them. The steps for solving a quadratic equation by completing the square are described: 1) move all terms to the left side, 2) find and add the "completing the square" term, 3) factor into a perfect square trinomial, 4) take the square root of each side, 5) solve the resulting equations. Additional examples demonstrate applying these steps to solve quadratic equations algebraically.