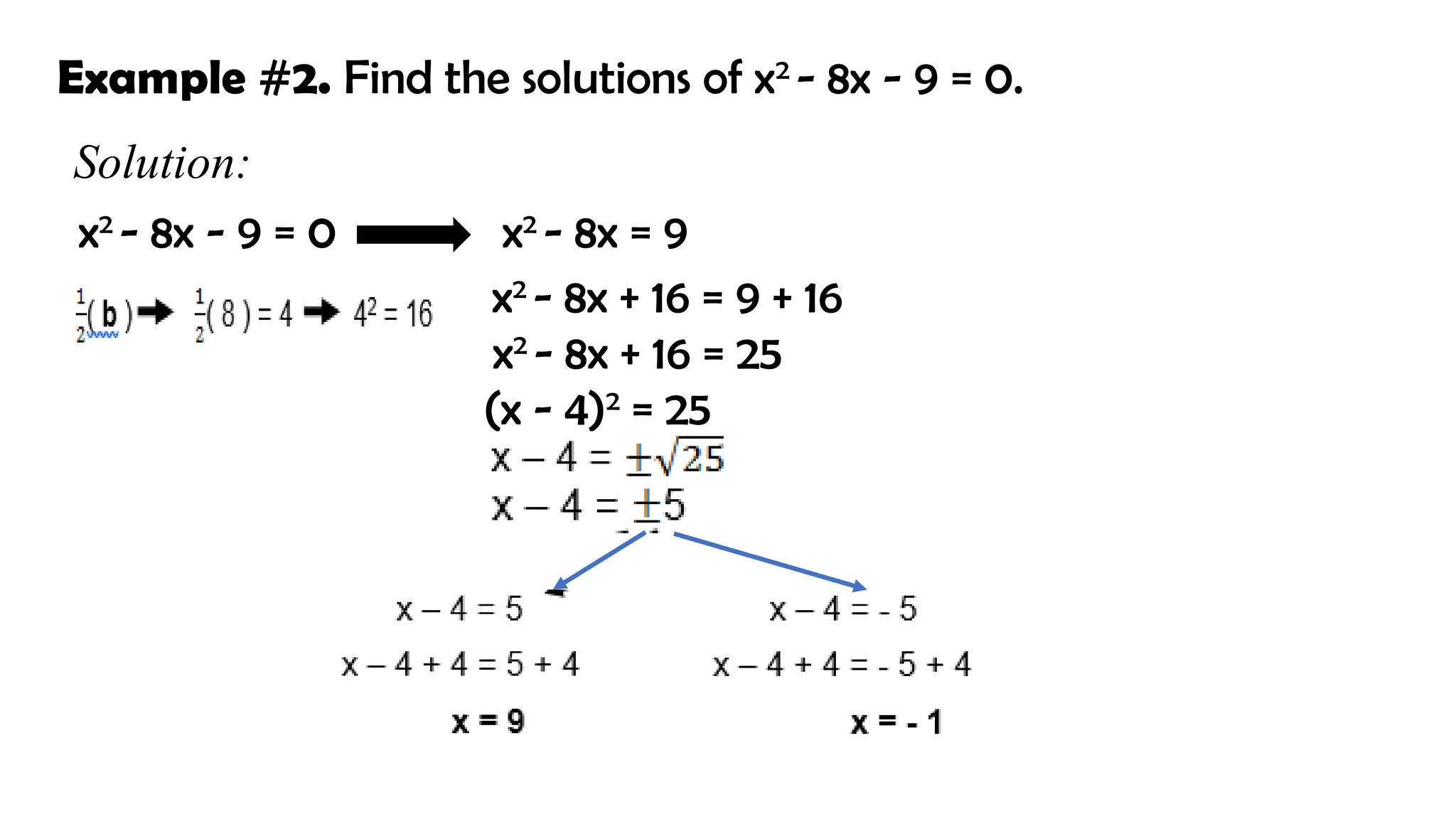
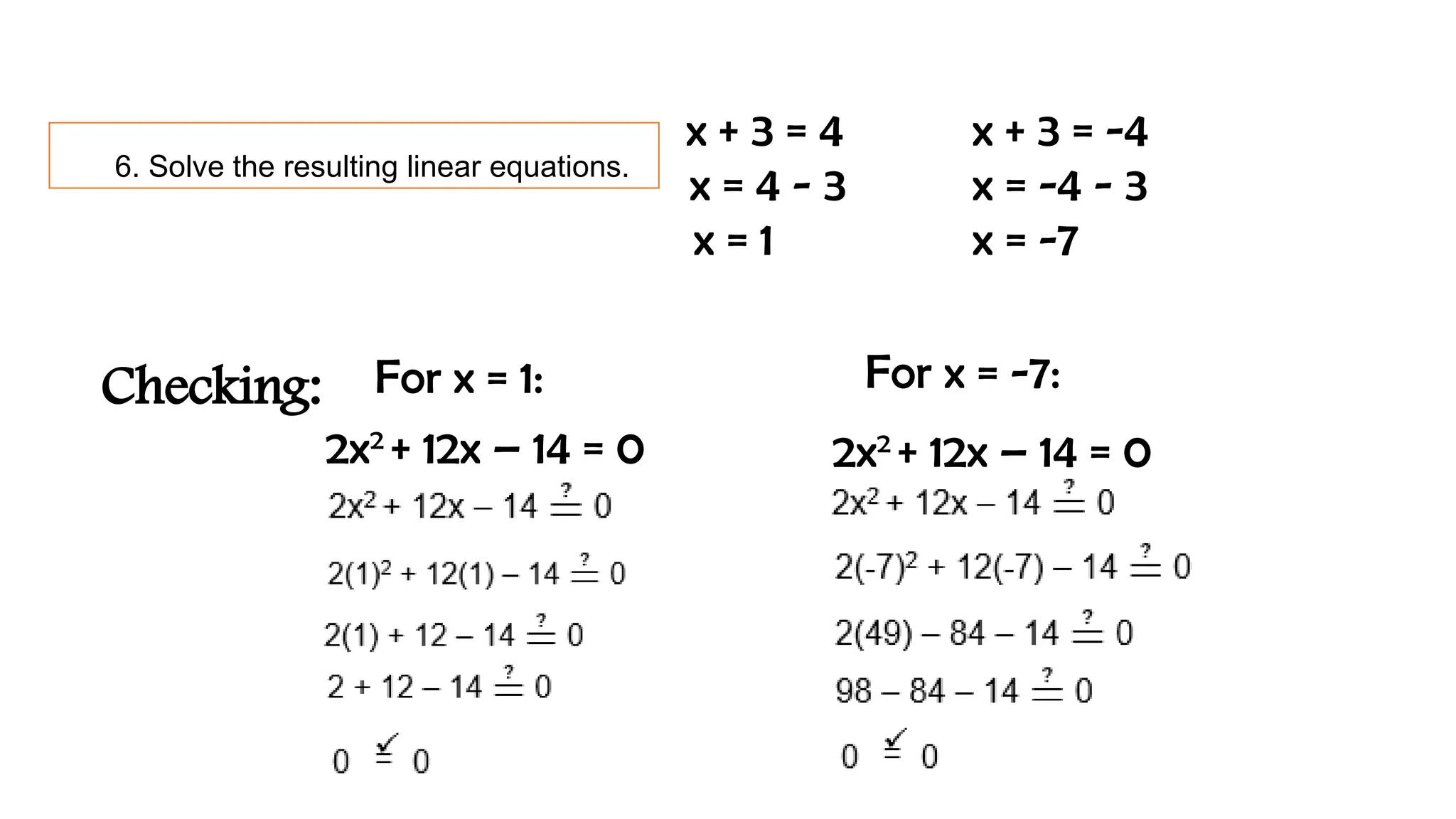The document outlines the method of solving quadratic equations by completing the square, detailing a series of steps to transform the equation into a solvable form. Specific examples illustrate how to apply the method and check solutions to ensure they satisfy the original equation. It emphasizes the importance of achieving a positive value for k to obtain real number solutions.